
Adrenergic receptor

The adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are targets of many catecholamines like norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and epinephrine (adrenaline) produced by the body, but also many medications like beta blockers, beta-2 (β2) agonists and alpha-2 (α2) agonists, which are used to treat high blood pressure and asthma, for example.
Many cells have these receptors, and the binding of a catecholamine to the receptor will generally stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The SNS is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, which is triggered by experiences such as exercise or fear-causing situations. This response dilates pupils, increases heart rate, mobilizes energy, and diverts blood flow from non-essential organs to skeletal muscle. These effects together tend to increase physical performance momentarily.
History
By the turn of the 19th century, it was agreed that the stimulation of sympathetic nerves could cause different effects on body tissues, depending on the conditions of stimulation (such as the presence or absence of some toxin). Over the first half of the 20th century, two main proposals were made to explain this phenomenon:
- There were (at least) two different types of neurotransmitters released from sympathetic nerve terminals, or
- There were (at least) two different types of detector mechanisms for a single neurotransmitter.
The first hypothesis was championed by Walter Bradford Cannon and Arturo Rosenblueth, who interpreted many experiments to then propose that there were two neurotransmitter substances, which they called sympathin E (for 'excitation') and sympathin I (for 'inhibition').
The second hypothesis found support from 1906 to 1913, when Henry Hallett Dale explored the effects of adrenaline (which he called adrenine at the time), injected into animals, on blood pressure. Usually, adrenaline would increase the blood pressure of these animals. Although, if the animal had been exposed to ergotoxine, the blood pressure decreased. He proposed that the ergotoxine caused "selective paralysis of motor myoneural junctions" (i.e. those tending to increase the blood pressure) hence revealing that under normal conditions that there was a "mixed response", including a mechanism that would relax smooth muscle and cause a fall in blood pressure. This "mixed response", with the same compound causing either contraction or relaxation, was conceived of as the response of different types of junctions to the same compound.
This line of experiments were developed by several groups, including DT Marsh and colleagues, who in February 1948 showed that a series of compounds structurally related to adrenaline could also show either contracting or relaxing effects, depending on whether or not other toxins were present. This again supported the argument that the muscles had two different mechanisms by which they could respond to the same compound. In June of that year, Raymond Ahlquist, Professor of Pharmacology at Medical College of Georgia, published a paper concerning adrenergic nervous transmission. In it, he explicitly named the different responses as due to what he called α receptors and β receptors, and that the only sympathetic transmitter was adrenaline. While the latter conclusion was subsequently shown to be incorrect (it is now known to be noradrenaline), his receptor nomenclature and concept of two different types of detector mechanisms for a single neurotransmitter, remains. In 1954, he was able to incorporate his findings in a textbook, Drill's Pharmacology in Medicine, and thereby promulgate the role played by α and β receptor sites in the adrenaline/noradrenaline cellular mechanism. These concepts would revolutionise advances in pharmacotherapeutic research, allowing the selective design of specific molecules to target medical ailments rather than rely upon traditional research into the efficacy of pre-existing herbal medicines.
Categories
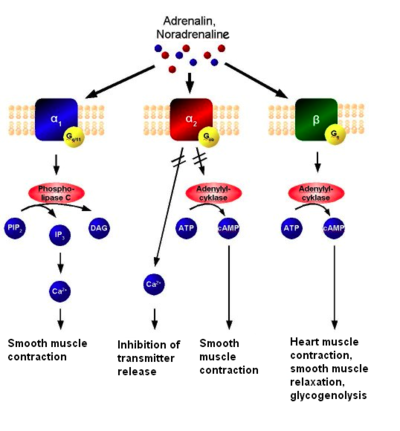
The mechanism of adrenoreceptors. Adrenaline or noradrenaline are receptor ligands to either α1, α2 or β-adrenoreceptors. The α1 couples to Gq, which results in increased intracellular Ca2+ and subsequent smooth muscle contraction. The α2, on the other hand, couples to Gi, which causes a decrease in neurotransmitter release, as well as a decrease of cAMP activity resulting in smooth muscle contraction. The β receptor couples to Gs and increases intracellular cAMP activity, resulting in e.g. heart muscle contraction, smooth muscle relaxation and glycogenolysis. There are two main groups of adrenoreceptors, α and β, with 9 subtypes in total:
- α are divided to α1 (a Gq coupled receptor) and α2 (a Gi coupled receptor)
- α1 has 3 subtypes: α1A, α1B and α1D
- α2 has 3 subtypes: α2A, α2B and α2C
- β are divided to β1, β2 and β3. All 3 are coupled to Gs proteins, but β2 and β3 also couple to Gi
Gi and Gs are linked to adenylyl cyclase. Agonist binding thus causes a rise in the intracellular concentration of the second messenger (Gi inhibits the production of cAMP) cAMP. Downstream effectors of cAMP include cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), which mediates some of the intracellular events following hormone binding.
Roles in circulation
Epinephrine (adrenaline) reacts with both α- and β-adrenoreceptors, causing vasoconstriction and vasodilation, respectively. Although α receptors are less sensitive to epinephrine, when activated at pharmacologic doses, they override the vasodilation mediated by β-adrenoreceptors because there are more peripheral α1 receptors than β-adrenoreceptors. The result is that high levels of circulating epinephrine cause vasoconstriction. However, the opposite is true in the coronary arteries, where β2 response is greater than that of α1, resulting in overall dilation with increased sympathetic stimulation. At lower levels of circulating epinephrine (physiologic epinephrine secretion), β-adrenoreceptor stimulation dominates since epinephrine has a higher affinity for the β2 adrenoreceptor than the α1 adrenoreceptor, producing vasodilation followed by decrease of peripheral vascular resistance.
Subtypes
Smooth muscle behavior is variable depending on anatomical location. Smooth muscle contraction/relaxation is generalized below. One important note is the differential effects of increased cAMP in smooth muscle compared to cardiac muscle. Increased cAMP will promote relaxation in smooth muscle, while promoting increased contractility and pulse rate in cardiac muscle.
α receptors
α receptors have actions in common, but also individual effects. Common (or still receptor unspecified) actions include:
- vasoconstriction
- decreased flow of smooth muscle in gastrointestinal tract
Subtype unspecific α agonists (see actions above) can be used to treat rhinitis (they decrease mucus secretion). Subtype unspecific α antagonists can be used to treat pheochromocytoma (they decrease vasoconstriction caused by norepinephrine).
α1 receptor
α1-adrenoreceptors are members of the Gq protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Upon activation, a heterotrimeric G protein, Gq, activates phospholipase C (PLC). The PLC cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), which in turn causes an increase in inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). The former interacts with calcium channels of endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum, thus changing the calcium content in a cell. This triggers all other effects, including a prominent slow after depolarizing current (sADP) in neurons.
Actions of the α1 receptor mainly involve smooth muscle contraction. It causes vasoconstriction in many blood vessels, including those of the skin, gastrointestinal system, kidney (renal artery) and brain. Other areas of smooth muscle contraction are:
- ureter
- vas deferens
- hair (arrector pili muscles)
- uterus (when pregnant)
- urethral sphincter
- urothelium and lamina propria
- bronchioles (although minor relative to the relaxing effect of β2 receptor on bronchioles)
- blood vessels of ciliary body and (stimulation of dilator pupillae muscles of iris causes mydriasis)
Actions also include glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis from adipose tissue and liver; secretion from sweat glands and Na+ reabsorption from kidney.
α1 antagonists can be used to treat:
- hypertension – decrease blood pressure by decreasing peripheral vasoconstriction
- benign prostate hyperplasia – relax smooth muscles within the prostate thus easing urination
α2 receptor
The α2 receptor couples to the Gi/o protein. It is a presynaptic receptor, causing negative feedback on, for example, norepinephrine (NE). When NE is released into the synapse, it feeds back on the α2 receptor, causing less NE release from the presynaptic neuron. This decreases the effect of NE. There are also α2 receptors on the nerve terminal membrane of the post-synaptic adrenergic neuron.
Actions of the α2 receptor include:
- decreased insulin release from the pancreas
- increased glucagon release from the pancreas
- contraction of sphincters of the GI-tract
- negative feedback in the neuronal synapses - presynaptic inhibition of norepinephrine release in CNS
- decreased platelet aggregation
- decreases peripheral vascular resistance
α2 agonists (see actions above) can be used to treat:
- hypertension – decrease blood pressure-raising actions of the sympathetic nervous system
α2 antagonists can be used to treat:
- impotence – relax penile smooth muscles and ease blood flow
- depression – enhance mood by increasing norepinephrine secretion
β receptors
Subtype unspecific β agonists can be used to treat:
- heart failure – increase cardiac output acutely in an emergency
- circulatory shock – increase cardiac output thus redistributing blood volume
- anaphylaxis – bronchodilation
Subtype unspecific β antagonists (beta blockers) can be used to treat:
- heart arrhythmia – decrease the output of sinus node thus stabilizing heart function
- coronary artery disease – reduce heart rate and hence increasing oxygen supply
- heart failure – prevent sudden death related to this condition, which is often caused by ischemias or arrhythmias
- hyperthyroidism – reduce peripheral sympathetic hyper-responsiveness
- migraine – reduce number of attacks
- stage fright – reduce tachycardia and tremor
- glaucoma – reduce intraocular pressure
β1 receptor
Actions of the β1 receptor include:
- increase cardiac output by increasing heart rate (positive chronotropic effect), conduction velocity (positive dromotropic effect), stroke volume (by enhancing contractility – positive inotropic effect), and rate of relaxation of the myocardium, by increasing calcium ion sequestration rate (positive lusitropic effect), which aids in increasing heart rate
- increase renin secretion from juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney
- increase renin secretion from kidney
- increase ghrelin secretion from the stomach
β2 receptor
Actions of the β2 receptor include:
- smooth muscle relaxation throughout many areas of the body, e.g. in bronchi (bronchodilation, see salbutamol),GI tract (decreased motility), veins (vasodilation of blood vessels), especially those to skeletal muscle (although this vasodilator effect of norepinephrine is relatively minor and overwhelmed by α adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction)
- lipolysis in adipose tissue
- anabolism in skeletal muscle
- uptake of potassium into cells
- relax non-pregnant uterus
- relax detrusor urinae muscle of bladder wall
- dilate arteries to skeletal muscle
- glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
- stimulates insulin secretion
- contract sphincters of GI tract
- thickened secretions from salivary glands
- inhibit histamine-release from mast cells
- involved in brain - immune communication
β2 agonists (see actions above) can be used to treat:
- asthma and COPD – reduce bronchial smooth muscle contraction thus dilating the bronchus
- hyperkalemia – increase cellular potassium intake
- preterm birth – reduce uterine smooth muscle contractions
β3 receptor
Actions of the β3 receptor include:
- increase of lipolysis in adipose tissue
- relax the bladder
β3 agonists could theoretically be used as weight-loss drugs, but are limited by the side effect of tremors.
See also
Further reading
- Rang HP, Dale MM, Ritter JM, Flower RJ (2007). "Chapter 11: Noradrenergic transmission". Rang and Dale's Pharmacology (6th ed.). Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. pp. 169–170. ISBN 978-0-443-06911-6.
External links
- Alpha receptors illustrated
- The Adrenergic Receptors
- Adrenoceptors - IUPHAR/BPS guide to pharmacology
- Basic Neurochemistry: α- and β-Adrenergic Receptors
- Theory of receptor activation
- Desensitization of β1 receptors
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

