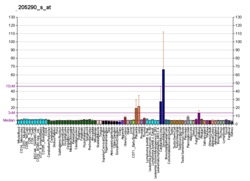
Bone morphogenetic protein 2
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 or BMP-2 belongs to the TGF-β superfamily of proteins.
Function
BMP-2 like other bone morphogenetic proteins, plays an important role in the development of bone and cartilage. It is involved in the hedgehog pathway, TGF beta signaling pathway, and in cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. It is also involved in cardiac cell differentiation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
Like many other proteins from the BMP family, BMP-2 has been demonstrated to potently induce osteoblast differentiation in a variety of cell types.
BMP-2 may be involved in white adipogenesis and may have metabolic effects.
Interactions
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 has been shown to interact with BMPR1A.
Clinical use and complications
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 is shown to stimulate the production of bone.Recombinant human protein (rhBMP-2) is currently available for orthopaedic usage in the United States. Implantation of BMP-2 is performed using a variety of biomaterial carriers ("metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites") and delivery systems ("hydrogel, microsphere, nanoparticles, and fibers"). While used primarily in orthopedic procedures such as spinal fusion, BMP-2 has also found its way into the field of dentistry.
The use of dual tapered threaded fusion cages and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on an absorbable collagen sponge obtained and maintained intervertebral spinal fusion, improved clinical outcomes, and reduced pain after anterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis in patients with degenerative lumbar disc disease. As an adjuvant to allograft bone or as a replacement for harvested autograft, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) appear to improve fusion rates after spinal arthrodesis in both animal models and humans, while reducing the donor-site morbidity previously associated with such procedures.
A study published in 2011 noted "reports of frequent and occasionally catastrophic complications associated with use of [BMP-2] in spinal fusion surgeries", with a level of risk far in excess of estimates reported in earlier studies. An additional review by Agrawal and Sinha of BMP-2 and its common delivery systems in early 2016 showed how "problems like ectopic growth, lesser protein delivery, [and] inactivation of the protein" reveal a further need "to modify the available carrier systems as well as explore other biomaterials with desired properties."
Further reading
- Nickel J, Dreyer MK, Kirsch T, Sebald W (2001). "The crystal structure of the BMP-2:BMPR-IA complex and the generation of BMP-2 antagonists". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A Suppl 1 (Pt 1): S7–14. PMID 11263668.
- Kawamura C, Kizaki M, Ikeda Y (2002). "Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 induces apoptosis in human myeloma cells". Leuk. Lymphoma. 43 (3): 635–9. doi:10.1080/10428190290012182. PMID 12002771. S2CID 42810021.
- Marie PJ, Debiais F, Haÿ E (2002). "Regulation of human cranial osteoblast phenotype by FGF-2, FGFR-2 and BMP-2 signaling". Histol. Histopathol. 17 (3): 877–85. doi:10.14670/HH-17.877. PMID 12168799.
External links
- bone morphogenetic protein 2 at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human BMP2 genome location and BMP2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
|
PDB gallery
| |
|---|---|
| TGF beta superfamily of ligands |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TGF beta receptors (Activin, BMP, family) |
|
||||||
| Transducers/SMAD | |||||||
| Ligand inhibitors | |||||||
| Coreceptors | |||||||
| Other | |||||||
| Type I |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type II |
|
||||||||||||||
| Type III |
|
||||||||||||||
| Unsorted |
|
||||||||||||||