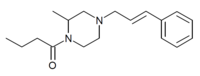
Bucinnazine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | AP-237 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H24N2O |
| Molar mass | 272.392 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Bucinnazine (AP-237, 1-butyryl-4-cinnamylpiperazine) is an opioid analgesic drug that was widely used in China to treat pain in cancer patients as of 1986. It is one of the most potent compounds among a series of piperazine-amides first synthesized and reported in Japan in the 1970s. Bucinnazine has analgesic potency comparable to that of morphine but with a relatively higher therapeutic index.
The drug was initially claimed to be a non-narcotic analgesic. However, subsequent studies have shown bucinnazine and similar acyl piperazines to be potent and selective agonists of μ-opioid receptor (MOR) with relatively low affinity for the δ-opioid receptor and the κ-opioid receptor. In accordance with these studies, results from the intravenous self-administration experiments in rats showed that bucinnazine has a marked reinforcing effect with tolerance and dependence quickly developing. In addition, the morphine antagonist naloxone reverses the effect of bucinnazine and precipitates withdrawal symptoms in bucinnazine treated rats further indicating a mechanism of analgesia mediated via selective agonist activity at μ-opioid receptors.
Derivatives
2-methyl-AP-237 has been sold on the grey market as a designer opioid, first identified by a police forensic laboratory in Slovenia in March 2019.