
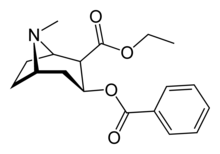
Cocaethylene
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | benzoylecgonine ethyl ester, ethylbenzoylecgonine, |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Produced from ingestion of cocaine and ethanol |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.816 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H23NO4 |
| Molar mass | 317.385 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Cocaethylene (ethylbenzoylecgonine) is the ethyl ester of benzoylecgonine. It is structurally similar to cocaine, which is the methyl ester of benzoylecgonine. Cocaethylene is formed by the liver when cocaine and ethanol coexist in the blood. In 1885, cocaethylene was first synthesized (according to edition 13 of the Merck Index), and in 1979, cocaethylene's side effects were discovered.
Metabolic production from cocaine
Cocaethylene is the byproduct of concurrent consumption of alcohol and cocaine as metabolized by the liver. Normally, metabolism of cocaine produces two primarily biologically inactive metabolites—benzoylecgonine and ecgonine methyl ester. The hepatic enzyme carboxylesterase is an important part of cocaine's metabolism because it acts as a catalyst for the hydrolysis of cocaine in the liver, which produces these inactive metabolites. If ethanol is present during the metabolism of cocaine, a portion of the cocaine undergoes transesterification with ethanol, rather than undergoing hydrolysis with water, which results in the production of cocaethylene.
- cocaine + H2O → benzoylecgonine + methanol (with liver carboxylesterase 1)
- benzoylecgonine + ethanol → cocaethylene + H2O
- cocaine + ethanol → cocaethylene + methanol (with liver carboxylesterase 1)
Physiological effects
Cocaethylene is largely considered a recreational drug in and of itself, with stimulant, euphoriant, anorectic, sympathomimetic, and local anesthetic properties. The monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine play important roles in cocaethylene's action in the brain. Cocaethylene increases the levels of serotonergic, noradrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the brain by inhibiting the action of the serotonin transporter, norepinephrine transporter, and dopamine transporter. These pharmacological properties make cocaethylene a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI; also known as a "triple reuptake inhibitor").
In most users, cocaethylene produces euphoria and has a longer duration of action than cocaine. Some studies suggest that consuming alcohol in combination with cocaine may be more cardiotoxic than cocaine and "it also carries an 18 to 25 fold increase over cocaine alone in risk of immediate death". Cocaethylene has a higher affinity for the dopamine transporter than does cocaine, but has a lower affinity for the serotonin and norepinephrine transporters.
In McCance-Katz et alia's 1993 study cocaethylene "produced greater subjective ratings of 'High' in comparison with administration of cocaine or alcohol alone."
See also
- Ethylphenidate
- Euphoriants
- Methylvanillylecgonine
- Local anesthetics
- Stimulants
- Tropanes
- Vin Mariani
- Pemberton's French Wine Coca
Further reading
- Cocaethylene: responding to combined alcohol and cocaine use
- Landry MJ (1992). "An overview of cocaethylene, an alcohol-derived, psychoactive, cocaine metabolite". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 24 (3): 273–6. doi:10.1080/02791072.1992.10471648. PMID 1432406.
- Warning of extra heart dangers from mixing cocaine and alcohol
- Hearn WL, Rose S, Wagner J, Ciarleglio A, Mash DC (June 1991). "Cocaethylene is more potent than cocaine in mediating lethality". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 39 (2): 531–3. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(91)90222-N. PMID 1946594. S2CID 36163843.
- Hearn WL, Flynn DD, Hime GW, Rose S, Cofino JC, Mantero-Atienza E, Wetli CV, Mash DC (February 1991). "Cocaethylene: a unique cocaine metabolite displays high affinity for the dopamine transporter". Journal of Neurochemistry. 56 (2): 698–701. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08205.x. PMID 1988563. S2CID 35719923.