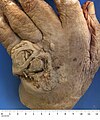
Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma
| Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin, squamous-cell skin cancer, epidermoid carcinoma, squamous-cell epithelioma of the skin |
 | |
| Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma tends to arise from actinic keratoses (premalignant lesions); surface is usually scaly and often ulcerates (as shown here). | |
| Specialty | Dermatology, plastic surgery, otorhinolaryngology |
| Symptoms | Hard lump with a scaly top or ulceration. |
| Risk factors | Ultraviolet radiation, actinic keratosis, tobacco smoking, lighter skin, arsenic exposure, radiotherapy, poor immune system function, HPV infection |
| Diagnostic method | Tissue biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Keratoacanthoma, actinic keratosis, melanoma, warts, basal cell cancer |
| Prevention | Decreased UV radiation exposure, sunscreen |
| Treatment | Surgical removal, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy |
| Prognosis | Usually good |
| Frequency | 2.2 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 51,900 (2015) |
Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), or squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin, also known as squamous-cell skin cancer, is, with basal-cell carcinoma and melanoma, one of the three principal types of skin cancer. cSCC typically presents as a hard lump with a scaly top layer, but it may instead form an ulcer. Onset often occurs over a period of months. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma is more likely to spread to distant areas than basal cell cancer. When confined to the outermost layer of the skin, a pre-invasive, or in situ, form of cSCC is known as Bowen's disease.
The most significant risk factor for cSCC is high lifetime exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Other risks include prior scars, chronic wounds, actinic keratosis, paler skin that sunburns easily, Bowen's disease, arsenic exposure, radiation therapy, tobacco smoking, poor immune system function, prior basal cell carcinoma, and HPV infection. Risk from UV radiation is related to total exposure, rather than exposure early in life.Tanning beds have become another frequent source of ultraviolet radiation. Risk is also elevated in certain genetic skin disorders, such as xeroderma pigmentosum and certain forms of epidermolysis bullosa. cSCC begins from squamous cells found in the upper layers of the skin. Diagnosis is often based on skin examination, and confirmed by tissue biopsy.
In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that the upregulation of FGFR2, a subset of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) immunoglobin family, has a critical role to play in the progression of cSCC cells. Mutations in the TPL2 gene cause over-expression of FGFR2, which activates the mTORC1 and AKT pathways in both primary and metastatic cSCC cell lines. By using a chemical substance, called a "pan FGFR inhibitor", cell migration and cell proliferation in cSCC have been attenuated in vitro.
Avoiding exposure to ultraviolet radiation and the use of sunscreen appear to be effective methods of preventing cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. Treatment is typically by surgical removal. This can be by simple excision if the cancer is small; otherwise, Mohs surgery is generally recommended. Other options may include application of cold and radiation therapy. In cases in which distant spread has occurred, chemotherapy or biologic therapy may be used.
As of 2015, about 2.2 million people worldwide have cSCC at any given time. About 20% of all skin cancer cases consist of cSCC. About 12% of males and 7% of females in the United States develop cSCC at some point in time. While prognosis is usually good, when distant spread occurs five-year survival is ~34%. In 2015, cSCC resulted in approximately 52,000 deaths globally. The mean age at diagnosis is around 66 years. Following the successful treatment of one case of cSCC, a person is at significant risk of developing further cSCC lesions.
Signs and symptoms

SCC of the skin begins as a small nodule and as it enlarges the center becomes necrotic and sloughs and the nodule turns into an ulcer, and generally are developed from an actinic keratosis. Once keratinocytes begin to grow uncontrollably, they have the potential to become cancerous and produce cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma.
- The lesion caused by cSCC is often asymptomatic
- Ulcer or reddish skin plaque that is slow growing
- Intermittent bleeding from the tumor, especially on the lip
- The clinical appearance is highly variable
- Usually the tumor presents as an ulcerated lesion with hard, raised edges
- The tumor may be in the form of a hard plaque or a papule, often with an opalescent quality, with tiny blood vessels
- The tumor can lie below the level of the surrounding skin, and eventually ulcerates and invades the underlying tissue
- The tumor commonly presents on sun-exposed areas (e.g. back of the hand, scalp, lip, and superior surface of pinna)
- On the lip, the tumor forms a small ulcer, which fails to heal and bleeds intermittently
- Evidence of chronic skin photodamage, as in multiple actinic keratoses (solar keratoses)
- The tumor grows relatively slowly
Spread
- Unlike basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC) has a higher risk of metastasis.
- Risk of metastasis is higher clinically in SCC arising in scars, on the lower lips or mucosa, and occurring in immunosuppressed and solid organ transplant patients. Risk of metastasis is also higher in SCC that are > 2 cm in diameter, growth into the fat layer and along nerves, thickness > 6 mm.
Causes
Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma is the second-most common cancer of the skin (after basal-cell carcinoma, but more common than melanoma). It usually occurs in areas exposed to the sun. Sunlight exposure and immunosuppression are risk factors for SCC of the skin, with chronic sun exposure being the strongest environmental risk factor. There is a risk of metastasis starting more than 10 years after diagnosable appearance of squamous-cell carcinoma, but the risk is low, though much higher than with basal-cell carcinoma. Squamous-cell cancers of the lip and ears have high rates of local recurrence and distant metastasis. In a recent study, it has also been shown that the deletion or severe down-regulation of a gene titled Tpl2 (tumor progression locus 2) may be involved in the progression of normal keratinocytes into becoming squamous-cell carcinoma.
cSCC represents about 20% of the non-melanoma skin cancers; 80-90% of cSCCs with metastatic potential are located on the head and neck.
Tobacco smoking also increases the risk for cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma.
The vast majority of cSCC cases are located on exposed skin, and are often the result of ultraviolet exposure. cSCC usually occurs on portions of the body commonly exposed to the sun; the face, ears, neck, hands, or arms. The primary sign is a growing bump that may have a rough, scaly surface, and flat, reddish patches. Unlike basal-cell carcinoma, cSCC carries a higher risk of metastasis than does basal-cell carcinoma, and may spread to the regional lymph nodes,
Erythroplasia of Queyrat (SCC in situ of the glans or prepuce in males, M or the vulva in females.) may be induced by human papilloma virus. It is reported to occur in the corneoscleral limbus. Erythroplasia of Queyrat may also occur on the anal mucosa or the oral mucosa.
Genetically, cSCC tumors harbor high frequencies of NOTCH and p53 mutations as well as less frequent alterations in histone acetyltransferase EP300, subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex PBRM1, DNA-repair deubiquitinase USP28, and NF-κB signaling regulator CHUK.
Immunosuppression
People who have received solid organ transplants are at a significantly increased risk of developing squamous-cell carcinoma due to the use of chronic immunosuppressive medication. While the risk of developing all skin cancers increases with these medications, this effect is particularly severe for cSCC, with hazard ratios as high as 250 being reported, versus 40 for basal cell carcinoma. The incidence of cSCC development increases with time posttransplant. Heart and lung transplant recipients are at the highest risk of developing cSCC due to more intensive immunosuppressive medications used.
Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma in individuals on immunotherapy or who have lymphoproliferative disorders (e.g. leukemia) tend to be much more aggressive, regardless of their location. The risk of cSCC, and non-melanoma skin cancers generally, varies with the immunosuppressive drug regimen chosen. The risk is greatest with calcineurin inhibitors like cyclosporine and tacrolimus, and least with mTOR inhibitors, such as sirolimus and everolimus. The antimetabolites azathioprine and mycophenolic acid have an intermediate risk profile.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is confirmed via skin biopsy of the tissue or tissues suspected to be affected by SCC. The pathological appearance of a squamous-cell cancer varies with the depth of the biopsy. For that reason, a biopsy including the subcutaneous tissue and basilar epithelium, to the surface is necessary for correct diagnosis. The performance of a shave biopsy (see skin biopsy) might not acquire enough information for a diagnosis. An inadequate biopsy might be read as actinic keratosis with follicular involvement. A deeper biopsy down to the dermis or subcutaneous tissue might reveal the true cancer. An excision biopsy is ideal, but not practical in most cases. An incisional or punch biopsy is preferred. A shave biopsy is least ideal, especially if only the superficial portion is acquired.
Histological characteristics
Histopathologically, the epidermis in cSCC in situ (Bowen's disease) will show hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis. There will also be marked acanthosis with elongation and thickening of the rete ridges. These changes will overly keratinocytic cells which are often highly atypical and may in fact have a more unusual appearance than invasive cSCC. The atypia spans the full thickness of the epidermis, with the keratinocytes demonstrating intense mitotic activity, pleomorphism, and greatly enlarged nuclei. They will also show a loss of maturity and polarity, giving the epidermis a disordered or "windblown" appearance.
Two types of multinucleated cells may be seen: the first will present as a multinucleated giant cell, and the second will appear as a dyskeratotic cell engulfed in the cytoplasm of a keratinocyte. Occasionally, cells of the upper epidermis will undergo vacuolization, demonstrating an abundant and strongly eosinophilic cytoplasm. There may be a mild to moderate lymphohistiocytic infiltrate detected in the upper dermis.
In situ disease
Bowen's disease is essentially equivalent to and used interchangeably with cSCC in situ, when not having invaded through the basement membrane. Depending on source, it is classified as precancerous or cSCC in situ (technically cancerous but non-invasive). In cSCC in situ (Bowen's disease), atypical squamous cells proliferate through the whole thickness of the epidermis. The entire tumor is confined to the epidermis and does not invade into the dermis. The cells are often highly atypical under the microscope, and may in fact look more unusual than the cells of some invasive squamous-cell carcinomas.
Erythroplasia of Queyrat is a particular type of Bowen's disease that can arise on the glans or prepuce in males, and the vulva in females. It mainly occurs in uncircumcised males, over the age of 40.
Invasive disease
In invasive cSCC, tumor cells infiltrate through the basement membrane. The infiltrate can be somewhat difficult to detect in the early stages of invasion: however, additional indicators such as full thickness epidermal atypia and the involvement of hair follicles can be used to facilitate the diagnosis. Later stages of invasion are characterized by the formation of nests of atypical tumor cells in the dermis, often with a corresponding inflammatory infiltrate.
Gross slice of squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin
Degree of differentiation
Well-differentiated (yet invasive) cSCC, showing prominent keratinization. It may form pearl-like structures where dermal nests of keratinocytes attempt to mature in a layered fashion. Well-differentiated cSCC has slightly enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei with abundant amounts of cytoplasm. Intercellular bridges will frequently be visible.
Poorly differentiated, where attempts at keratinization are often no longer evident. This is a clear-cell squamous-cell carcinoma. The dysplastic cells infiltrated cords through the dermis. Poorly differentiated cSCC has greatly enlarged pleomorphic nuclei showing a high degree of atypia and frequent mitoses.
Poorly differentiated clear-cell squamous-cell carcinoma. For this type of cSCC, immunostains will likely be required to classify it unless other areas of the tumor show obvious squamous-cell features such as seen here (arrow).
Prevention
Appropriate sun-protective clothing, use of broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with at least SPF 50, and avoidance of intense sun exposure may prevent skin cancer. A 2016 review of sunscreen for preventing cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma found insufficient evidence to demonstrate whether it was effective.
Management
Most cutaneous squamous-cell carcinomas are removed with surgery. A few selected cases are treated with topical medication. Surgical excision with a free margin of healthy tissue is a frequent treatment modality. Radiotherapy, given as external beam radiotherapy or as brachytherapy (internal radiotherapy), can also be used to treat cSCC. There is little evidence comparing the effectiveness of different treatments for non-metastatic cSCC.
Mohs surgery is frequently utilized; considered the treatment of choice for squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin, physicians have also utilized the method for the treatment of squamous-cell carcinoma of the mouth, throat, and neck. An equivalent method of the CCPDMA standards can be utilized by a pathologist in the absence of a Mohs-trained physician. Radiation therapy is often used afterward in high risk cancer or patient types. Radiation or radiotherapy can also be a standalone option in treating cSCC. As a non-invasive option brachytherapy serves a painless possibility to treat in particular but not only difficult to operate areas like the earlobes or genitals. An example of this kind of therapy is the high-dose brachytherapy Rhenium-SCT which makes use of the beta rays emitting property of rhenium-188. The radiation source is enclosed in a compound which is applied to a thin protection foile directly over the lesion. This way the radiation source can be applied to complex locations and minimize radiation to healthy tissue.
After removal of the cancer, closure of the skin for patients with a decreased amount of skin laxity involves a split-thickness skin graft. A donor site is chosen and enough skin is removed so that the donor site can heal on its own. Only the epidermis and a partial amount of dermis is taken from the donor site which allows the donor site to heal. Skin can be harvested using either a mechanical dermatome or Humby knife.
Electrodessication and curettage (EDC) can be done on selected squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin. In areas where cSCC is known to be non-aggressive, and where the patient is not immunosuppressed, EDC can be performed with good to adequate cure rate.
Treatment options for cSCC in situ (Bowen's disease) include photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid, cryotherapy, topical 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod, and excision. A meta-analysis showed evidence that PDT is more effective than cryotherapy and has better cosmetic outcomes. There is generally a lack of evidence comparing the effectiveness of all treatment options.
High-risk squamous-cell carcinoma, as defined by that occurring around the eye, ear, or nose, is of large size, is poorly differentiated, and grows rapidly, requires more aggressive, multidisciplinary management.
Nodal spread:
- Surgical block dissection if palpable nodes or in cases of Marjolin's ulcers but the benefit of prophylactic block lymph node dissection with Marjolin's ulcers is not proven.
- Radiotherapy
- Adjuvant therapy may be considered in those with high-risk cSCC even in the absence of evidence for local metastasis. Imiquimod (Aldara) has been used with success for squamous-cell carcinoma in situ of the skin and the penis, but the morbidity and discomfort of the treatment is severe. An advantage is the cosmetic result: after treatment, the skin resembles normal skin without the usual scarring and morbidity associated with standard excision. Imiquimod is not FDA-approved for any squamous-cell carcinoma.
In general, squamous-cell carcinomas have a high risk of local recurrence, and up to 50% do recur. Frequent skin exams with a dermatologist is recommended after treatment.
Prognosis
The long-term outcome of squamous-cell carcinoma is dependent upon several factors: the sub-type of the carcinoma, available treatments, location and severity, and various patient health-related variables (accompanying diseases, age, etc.). Generally, the long-term outcome is positive, as less than 4% of squamous-cell carcinoma cases are at risk of metastasis. When it does metastasize, the most commonly involved organs are the lungs, brain, bone and other skin locations.
One study found squamous-cell carcinoma of the penis had a much greater rate of mortality than some other forms of squamous-cell carcinoma, that is, about 23%, although this relatively high mortality rate may be associated with possibly latent diagnosis of the disease due to patients avoiding genital exams until the symptoms are debilitating, or refusal to submit to a possibly scarring operation upon the genitalia. Squamous-cell carcinoma occurring in the organ transplant population is also associated with a higher risk of mortality.
Epidemiology

The incidence of cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma continues to rise around the world. A recent study estimated that there are between 180,000 and 400,000 cases of cSCC in the United States in 2013. Risk factors for cSCC varies with age, gender, race, geography, and genetics. The incidence of cSCC increases with age and the peak incidence is usually around 60 years old. Males are affected with cSCC at a ratio of 2:1 in comparison to females. Caucasians are more likely to be affected, especially those with fair skin or those chronically exposed to UV radiation.
Squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin can be found on all areas of the body but is most common on frequently sun-exposed areas, such as the face, legs and arms. Solid organ transplant recipients (heart, lung, liver, pancreas, among others) are also at a heightened risk of developing aggressive, high-risk cSCC. There are also a few rare congenital diseases predisposed to cutaneous malignancy. In certain geographic locations, exposure to arsenic in well water or from industrial sources may significantly increase the risk of cSCC.
Additional images
See also
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growths |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rashes |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous disorders |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melanoma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nevus/ melanocytic nevus |
|
||||||||||
|
Glandular and epithelial cancer
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelium |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glands |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Skin cancer of the epidermis
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Cancer involving the respiratory tract
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper RT | |||||||||||||
| Lower RT |
|
||||||||||||
| Pleura | |||||||||||||

![Squamous-cell carcinoma in situ, showing prominent dyskeratosis and aberrant mitoses at all levels of the epidermis, along with marked parakeratosis.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/ba/Micrograph_of_squamous_cell_carcinoma_in_situ_-_100x.jpg/367px-Micrograph_of_squamous_cell_carcinoma_in_situ_-_100x.jpg)
![cSCC in situ, high magnification, demonstrating an intact basement membrane.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/01/Micrograph_of_squamous_cell_carcinoma_in_situ_-_400x.jpg/299px-Micrograph_of_squamous_cell_carcinoma_in_situ_-_400x.jpg)





![Superficially invasive cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. These lesions often do not show the marked pleomorphism and atypical nuclei of cSCC in situ, but manifest early keratinocyte invasion of the dermis.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f8/Micrograph_of_invasive_squamous_cell_carcinoma_-_150x.jpg/305px-Micrograph_of_invasive_squamous_cell_carcinoma_-_150x.jpg)
![High magnification demonstrates the pleomorphism of the invading keratinocytes[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/26/Micrograph_of_invasive_squamous_cell_carcinoma_-_200x.jpg/340px-Micrograph_of_invasive_squamous_cell_carcinoma_-_200x.jpg)

![Well-differentiated (yet invasive) cSCC, showing prominent keratinization. It may form pearl-like structures where dermal nests of keratinocytes attempt to mature in a layered fashion. Well-differentiated cSCC has slightly enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei with abundant amounts of cytoplasm. Intercellular bridges will frequently be visible.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3c/Micrograph_of_well-differentiated_and_invasive_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg/306px-Micrograph_of_well-differentiated_and_invasive_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg)
![Moderately differentiated lesions of invasive cSCC show much less organization and maturation with significantly less keratin formation.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f2/Micrograph_of_moderately_differentiated_and_invasive_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg/310px-Micrograph_of_moderately_differentiated_and_invasive_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg)
![Poorly differentiated, where attempts at keratinization are often no longer evident. This is a clear-cell squamous-cell carcinoma. The dysplastic cells infiltrated cords through the dermis. Poorly differentiated cSCC has greatly enlarged pleomorphic nuclei showing a high degree of atypia and frequent mitoses.[12]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/61/Micrograph_of_clear-cell_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg/296px-Micrograph_of_clear-cell_squamous-cell_carcinoma.jpg)