
GTS-21
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
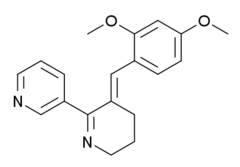
| Other names | 3-(2,4-dimethoxy-benzylidene)anabaseine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 308.374 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
GTS-21 (DMXBA) is a derivative of the natural product anabaseine that acts as a partial agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It binds to both the α4β2 and α7 subtypes, but activates only the α7 to any significant extent.
Both GTS-21 itself and its demethylated active metabolite 4-OH-GTS-21 display nootropic and neuroprotective effects, and GTS-21 is being investigated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, nicotine dependence, and, most significantly, for schizophrenia.
Phase one of a clinical trial using DXMBA as a potential treatment was completed in January of 2005. 12 non-smoking subjects each received 3 daily treatments. The treatments consisted of 150mg of DMXBA, with another dose of 75mg administered 2 hours later, 75mg of DXMBA, with another dose of 37.5mg administered 2 hours later, and a placebo treatment. The order of the doses was randomized over the 3-day course of the treatments. A P50 auditory-evoked test measured a significant effect on sensory gating, and a Repeatable Battery for Assessment of Neuropsychological Status test measured a significant effect on neurocognition. The subjects did not report any symptoms or side effects, however the leukocyte count of one subject decreased from slightly above normal on the placebo, to slightly below normal when administered the higher dose of DXMBA. After receiving no exposure to the drug, the subject's leukocyte count returned to normal 2 days later.
The laboratory name GTS-21 means that it is the 21st chemical compound created by Gainesville (University of Florida in Gainesville) and Tokushima (Taiho Pharmaceutical) Scientists.DMXBA – 3-2,4-dimethoxybenzylidene anabaseine.
GTS-21, also known as DMXB-A or DMBX-anabaseine, is a synthetic compound that has been studied for its potential therapeutic uses, particularly in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders.
GTS-21 is a partial agonist of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), which is a ligand-gated ion channel found in the brain and other tissues. Activation of the alpha7 nAChR has been shown to have neuroprotective effects and to improve cognitive function, making it an attractive target for drug development.
Several studies have investigated the effects of GTS-21 in various animal models of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis. In these studies, GTS-21 has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, and to improve cognitive function.
GTS-21 has also been studied in humans, primarily as a treatment for schizophrenia. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of GTS-21 in patients with schizophrenia found that the drug improved several measures of cognitive function, including attention and working memory, without causing significant side effects (Olincy et al., 2006).
Another study of GTS-21 in healthy volunteers found that the drug improved attention and memory performance, and enhanced the effects of caffeine on cognitive function (Levin et al., 2007).
Overall, the available evidence suggests that GTS-21 has potential as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders. However, more research is needed to fully understand its safety and efficacy, and to determine the optimal dosing and administration regimens.
References:
Levin, E. D., McClernon, F. J., Rezvani, A. H., & Nicotine Research, G. (2007). Effects of oral nicotine and GTS-21 (DMXB-A) on working memory in smokers. Psychopharmacology, 194(2), 173-181.
Olincy, A., Harris, J. G., Johnson, L. L., Pender, V., Kongs, S., Allensworth, D., ... & Soti, F. (2006). Proof-of-concept trial of an alpha7 nicotinic agonist in schizophrenia. Archives of general psychiatry, 63(6), 630-638.
| AChE inhibitor medications | |
|---|---|
| Other medications | |
| Experimental BACE inhibitors | |