
Huperzine A
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | HupA |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 10-14h |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.430 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
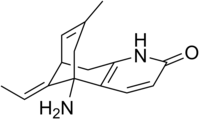
| Formula | C15H18N2O |
| Molar mass | 242.322 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 217 to 219 °C (423 to 426 °F) |
| |
| |
|
| |
Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata and in varying quantities in other food Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian. Huperzine A has been investigated as a treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, but a meta-analysis of those studies concluded that they were of poor methodological quality and the findings should be interpreted with caution. Huperzine A inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. It is commonly available over the counter as a nutrient supplement, and is marketed as a cognitive enhancer for improving memory and concentration.
Pharmacological effects
Huperzine A is extracted from Huperzia serrata. It is a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and NMDA receptor antagonist that crosses the blood–brain barrier.Acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and of some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters. The structure of the complex of huperzine A with acetylcholinesterase has been determined by X-ray crystallography (PDB code: 1VOT; see the 3D structure).
For some years, huperzine A has been investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration, particularly Alzheimer's disease. A 2013 meta-analysis found that huperzine A may be efficacious in improving cognitive function, global clinical status, and activities of daily living for individuals with Alzheimer's disease. However, due to the poor size and quality of the clinical trials reviewed, huperzine A should not be recommended as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease unless further high quality studies confirm such findings.
Huperzine A is also marketed as a dietary supplement with claims made for its ability to improve memory and mental function, based on positive results from animal studies and clinical research.
Huperzine A has also been noted to help induce lucid dreaming.
Most notably in the sports industry, Huperzine is used as a sublingual dietary supplement to increase muscular contraction and force output during weighted strength training by increasing the amount of acetylcholine in the neuromuscular junction, allowing more stimulation of ACh receptors
Adverse effects
Huperzine A may present with mild cholinergic side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Slight muscle twitching and slurred speech might also occur, as well as excessive saliva excretion and sweating. The use of huperzine A during pregnancy and lactation is not recommended due to the lack of sufficient safety data.
Drug interactions
Huperzine A may have additive effects if taken with drugs causing bradycardia, such as beta-blockers, which may decrease heart rate. Theoretically, there may be possible additive cholinergic effects if huperzine A is taken with other acetylcholinesterase inhibitors or cholinergic agents.
Safety
Huperzine A, in spite of the possible cholinergic side effects, seems to have a wide margin of safety. Toxicology studies show Huperzine A to be non-toxic even when administered at 50-100 times the human therapeutic dose. The extract is active for 6 hours at a dose of 2 μg/kg with no remarkable side effects.
Other possible uses
Huperzine A might be useful in the treatment of organophosphate nerve agent poisoning, preventing damage to the central nervous system caused by such agents.
Synthesis
Two scalable and efficient total syntheses of huperzine A have been reported.
External links
| AChE inhibitor medications | |
|---|---|
| Other medications | |
| Experimental BACE inhibitors | |
| AMPAR |
|
|---|---|
| KAR |
|
| NMDAR |
|