
Ibrutinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Imbruvica, others |
| Other names | PCI-32765, CRA-032765 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a614007 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 97.3% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A & CYP2D6) |
| Elimination half-life | 4–6 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (80%), urine (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.232.543 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
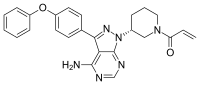
| Formula | C25H24N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 440.507 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ibrutinib, sold under the brand name Imbruvica among others, is a small molecule drug that inhibits B-cell proliferation and survival by irreversibly binding the protein Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Blocking BTK inhibits the B-cell receptor pathway, which is often aberrantly active in B cell cancers. Ibrutinib is therefore used to treat such cancers, including mantle cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. Ibrutinib also binds to C-terminal Src Kinases. These are off-target receptors for the BTK inhibitor. Ibrutinib binds to these receptors and inhibits the kinase from promoting cell differentiation and growth. This leads to many different side effects like left atrial enlargement and atrial fibrillation during the treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Medical uses
Ibrutinib is indicated for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM), marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), and chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD).
Adverse effects
Very common (>10% frequency) adverse effects include pneumonia, upper respiratory tract infection, sinusitis, skin infection, low neutrophil count, low platelet counts, headache, bleeding, bruising, diarrhea, vomiting, inflammation of mouth and lips, nausea, constipation, rash, joint pain, muscle spasms, musculoskeletal pain, fever, and edema.
Common (1–10% frequency) adverse effects include sepsis, urinary tract infection, non-melanoma skin cancer (basal-cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma), low leukocyte count, low lymphocyte count, interstitial lung disease, tumor lysis syndrome,high uric acid levels, dizziness, blurred vision, atrial fibrillation, subdural hematoma, nosebleeds, small bruises from broken blood vessels, high blood pressure, hives, and skin redness or blushing.
Pharmacology
Ibrutinib oral bioavailability is 3.9% in a fasting state, 8.4% in a fed state, and 15.9% after consumption of grapefruit juice.
Mechanism
Ibrutinib is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). It forms a covalent bond with the cysteine residue C481 in the BTK active site, leading to sustained inhibition of BTK enzymatic activity. BTK is an important signalling molecule of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) pathway, which is plays a role in the pathogenesis of several B-cell malignancies including mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Preclinical studies have shown that ibrutinib effectively inhibits malignant B-cell proliferation and survival in vivo as well as cell migration and substrate adhesion in vitro.
In early clinical studies, the activity of ibrutinib has been described to include a rapid reduction in lymphadenopathy accompanied by a transient lymphocytosis, suggesting that the drug might have direct effects on cell homing or migration to factors in tissue microenvironments.
In preclinical studies on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells, ibrutinib has been reported to promote apoptosis, inhibit proliferation, and also prevent CLL cells from responding to survival stimuli provided by the microenvironment. This also leads to a reduction of MCL1 levels (anti-apoptotic protein) in malignant B cells. Treatment of activated CLL cells with ibrutinib resulted in inhibition of BTK tyrosine phosphorylation and also effectively abrogated downstream survival pathways activated by this kinase including ERK1/2, PI3K, and NF-κB. Additionally, ibrutinib inhibited proliferation of CLL cells in vitro, effectively blocking survival signals provided externally to CLL cells from the microenvironment including soluble factors (BAFF, IL-6, IL-4, and TNF-α), fibronectin engagement and stromal cell contact.
Ibrutinib has also been reported to reduce chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell chemotaxis towards the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13, and inhibit cellular adhesion following stimulation at the B-cell receptor (BCR). Additionally, ibrutinib down-modulates the expression of CD20 (target of rituximab/ofatumumab) by targeting the CXCR4/SDF1 axis. Together, these data are consistent with a mechanistic model whereby ibrutinib blocks BCR signaling, which drives cells into apoptosis and/or disrupts cell migration and adherence to protective tumour microenvironments.
History
Ibrutinib was created by scientists at Celera Genomics as a tool compound for studying BTK function; it covalently binds its target which is ideal for a reagent but generally not considered ideal for drugs.
In 2006, in the course of acquiring an HDAC-focused program from Celera after its own initial discovery program had failed, Pharmacyclics also picked up Celera's small molecule BTK inhibitor discovery program for $2M in cash and $1M in stock and named the tool compound PCI-32765. In 2011 after the drug had completed Phase II trials, Johnson & Johnson and Pharmacyclics agreed to co-develop the drug, and J&J paid Pharmacyclics $150 million upfront and $825 million in milestones. Pharmacyclics was acquired by AbbVie in May 2015, and Abbvie projected global sales of US$1 billion in 2016 and $5 billion in 2020.
It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in November 2013, for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma. In February 2014, the FDA expanded the approved use of ibrutinib to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It was approved for Waldenström's macroglobulinemia in 2015.
In March 2015, Pharmacyclics and AbbVie agreed that Abbvie would acquire Pharmacyclics for $21 billion; the deal was completed that May.
In March 2016, a new indication for ibrutinib was approved in the United States for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
In May 2016, a new indication for ibrutinib was approved in the United States for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).
In January 2017, a new indication for ibrutinib was approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with relapsed/refractory (R/R) marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) who require systemic therapy and have received at least one prior anti-CD20-based therapy.
In August 2017, the FDA approved a new indication for ibrutinib to treat graft-versus-host disease. It was the first drug approved by the FDA for this condition.
In February 2018, a tablet formulation of ibrutinib was approved for use in the United States.
In August 2018, ibrutinib in combination with rituximab was approved in the United States for the treatment of adults with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM), a rare and incurable type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL).
In January 2019, ibrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab was approved for the treatment of adults with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
In April 2020, the FDA expanded the indication of ibrutinib to include its combination with rituximab for the initial treatment of adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Approval was based on the E1912 trial (NCT02048813), a 2:1 randomized, multicenter, open-label, actively controlled trial of ibrutinib with rituximab compared to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in 529 adult subjects 70 years or younger with previously untreated CLL or SLL requiring systemic therapy.
Society and culture
Economics
Janssen Pharmaceutica and Pharmacyclics introduced a new single dose tablet formulation with a flat pricing structure in the first half of 2018 and discontinued the capsule formulation. This caused an outcry as it was perceived to triple the cost of the drug to the average patient.
Janssen Pharmaceutica and Pharmacyclics have since reversed the decision to discontinue the capsule formulation with the drug currently available in both capsule and tablet forms.
Ibrutinib was added to the Australian Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme in 2018.
Generic ibrutinib was added to the Indian Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme in 2020.
Further reading
- Nocco S, Andriano TM, Bose A, Chilov M, Godwin K, Dranitsaris G, et al. (June 2022). "Ibrutinib-associated dermatologic toxicities: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 174: 103696. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103696. PMID 35523374. S2CID 248554326.
- Ran F, Liu Y, Wang C, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Liu Y, et al. (February 2022). "Review of the development of BTK inhibitors in overcoming the clinical limitations of ibrutinib". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 229: 114009. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114009. PMID 34839996. S2CID 244502431.
External links
- "Ibrutinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Ibrutinib, National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary