
Indoprofen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High (rapid and complete absorption) |
| Metabolism | Glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 2.3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.197 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
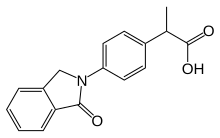
| Formula | C17H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 281.311 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
|
| |
Indoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It was withdrawn worldwide in the 1980s after postmarketing reports of severe gastrointestinal bleeding.
A 2004 study using high-throughput screening found indoprofen to increase production of the survival of motor neuron protein, suggesting it may provide insight into treatments for spinal muscular atrophies.
Synthesis
The isoindolone ring system forms the nucleus for one of the more traditional "profen" NSAIDs.
Reduction of the nitro group in arylpropionic acid (1) gives the corresponding aniline (2). Reaction of the intermediate with the imide (3) from phthalic anhydride (i.e. phthalimide) gives the product (4) in which the aniline nitrogen has exchanged with ammonia (apparently phthalic anhydride was not used directly). Treatment of the new imide with zinc in acetic acid leads to reduction of but one of the carbonyl groups to afford indolone, indoprofen.
|
pyrazolones / pyrazolidines |
|
|---|---|
| salicylates | |
|
acetic acid derivatives and related substances |
|
| oxicams | |
|
propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
|
n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) |
|
|
COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) |
|
| other | |
| NSAID combinations |
|
Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; #WHO-Essential Medicines; †withdrawn drugs; ‡veterinary use. | |
