Interleukin 7
Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL7 gene.
IL-7 is a hematopoietic growth factor secreted by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. It is also produced by keratinocytes,dendritic cells,hepatocytes,neurons, and epithelial cells, but is not produced by normal lymphocytes. A study also demonstrate how the autocrine production of the IL-7 cytokine mediated by T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) can be involved in the oncogenic development of T-ALL and offer novel insights into T-ALL spreading.
Structure
The three-dimensional structure of IL-7 in complex with the ectodomain of IL-7 receptor has been determined using X-ray diffraction.
Function
Lymphocyte maturation
IL-7 stimulates the differentiation of multipotent (pluripotent) hematopoietic stem cells into lymphoid progenitor cells (as opposed to myeloid progenitor cells where differentiation is stimulated by IL-3). It also stimulates proliferation of all cells in the lymphoid lineage (B cells, T cells and NK cells). It is important for proliferation during certain stages of B-cell maturation, T and NK cell survival, development and homeostasis.
IL-7 is a cytokine important for B and T cell development. This cytokine and the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) form a heterodimer that functions as a pre-pro-B cell growth-stimulating factor. This cytokine is found to be a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta (TCRß) during early T cell development. This cytokine can be produced locally by intestinal epithelial and epithelial goblet cells, and may serve as a regulatory factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes.Knockout studies in mice suggested that this cytokine plays an essential role in lymphoid cell survival.
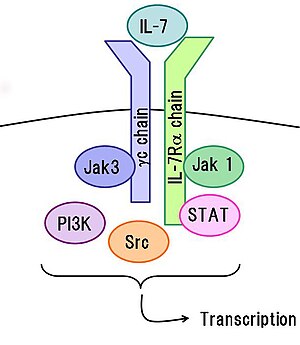
IL-7 signaling
IL-7 binds to the IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of Interleukin-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor. Binding results in a cascade of signals important for T-cell development within the thymus and survival within the periphery. Knockout mice which genetically lack IL-7 receptor exhibit thymic atrophy, arrest of T-cell development at the double positive stage, and severe lymphopenia. Administration of IL-7 to mice results in an increase in recent thymic emigrants, increases in B and T cells, and increased recovery of T cells after cyclophosphamide administration or after bone marrow transplantation.
Disease
Cancer
IL-7 promotes hematological malignancies (acute lymphoblastic leukemia, T cell lymphoma).
Viral Infections
Elevated levels of IL-7 have also been detected in the plasma of HIV-infected patients.
Clinical application
IL-7 as an immunotherapy agent has been examined in many pre-clinical animal studies and more recently in human clinical trials for various malignancies and during HIV infection.
Cancer
Recombinant IL-7 has been safely administered to patients in several phase I and II clinical trials. A human study of IL-7 in patients with cancer demonstrated that administration of this cytokine can transiently disrupt the homeostasis of both CD8+ and CD4+ T cells with a commensurate decrease in the percentage of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. No objective cancer regression was observed, however a dose limiting toxicity (DLT) was not reached in this study due to the development of neutralizing antibodies against the recombinant cytokine.
HIV infection
Associated with antiretroviral therapy, IL-7 administration decreased local and systemic inflammations in patients that had incomplete T-cell reconstitution. These results suggest that IL-7 therapy can possibly improve the quality of life of those patients.
Transplantation
IL-7 could also be beneficial in improving immune recovery after allogenic stem cell transplant.
Further reading
- Möller P, Böhm M, Czarnetszki BM, Schadendorf D (1997). "Interleukin-7. Biology and implications for dermatology". Exp. Dermatol. 5 (3): 129–37. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00107.x. PMID 8840152. S2CID 20874926.
- Appasamy PM (1999). "Biological and clinical implications of interleukin-7 and lymphopoiesis". Cytokines Cell. Mol. Ther. 5 (1): 25–39. PMID 10390077.
- Al-Rawi MA, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2004). "Interleukin-7 (IL-7) and IL-7 receptor (IL-7R) signalling complex in human solid tumours". Histol. Histopathol. 18 (3): 911–23. PMID 12792903.
- Aspinall R, Henson S, Pido-Lopez J, Ngom PT (2004). "Interleukin-7: an interleukin for rejuvenating the immune system". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1019 (1): 116–22. Bibcode:2004NYASA1019..116A. doi:10.1196/annals.1297.021. PMID 15247003. S2CID 8931092.
- Sica D, Rayman P, Stanley J, et al. (1993). "Interleukin 7 enhances the proliferation and effector function of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from renal-cell carcinoma". Int. J. Cancer. 53 (6): 941–7. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910530613. PMID 8473051. S2CID 41223517.
- Kim JH, Loveland JE, Sitz KV, et al. (1997). "Expansion of restricted cellular immune responses to HIV-1 envelope by vaccination: IL-7 and IL-12 differentially augment cellular proliferative responses to HIV-1". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 108 (2): 243–50. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.d01-1006.x. PMC 1904649. PMID 9158092.
| By family |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By function/ cell |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IL-1 |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-2 | |||||
| IL-3 | |||||
| IL-4 |
|
||||
| IL-5 |
|
||||
| IL-6 |
|
||||
| IL-7 |
|
||||
| IL-8 |
|
||||
| IL-9 |
|
||||
| IL-10 |
|
||||
| IL-11 |
|
||||
| IL-12 |
|
||||
| IL-13 |
|
||||
| IL-15 |
|
||||
| IL-17 |
|
||||
| IL-18 |
|
||||
| IL-20 |
|
||||
| IL-21 |
|
||||
| IL-22 |
|
||||
| IL-23 |
|
||||
| IL-27 |
|
||||
| IL-28 | |||||
| IL-31 |
|
||||
| IL1RL1 |
|
||||
| IL1RL2 |
|
||||
| Others |
|
||||
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.