J wave

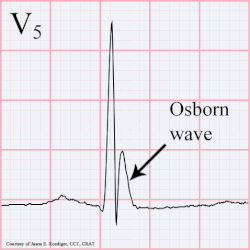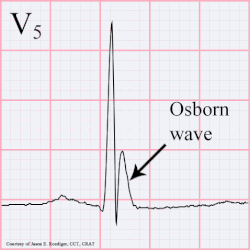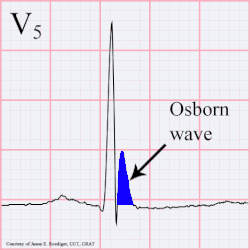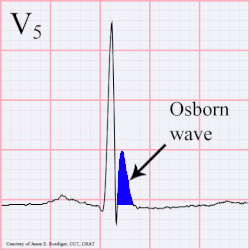
A J wave — also known as Osborn wave, camel-hump sign, late delta wave, hathook junction, hypothermic wave,K wave, H wave or current of injury — is an abnormal electrocardiogram finding.
J waves are positive deflections occurring at the junction between the QRS complex and the ST segment, where the S point, also known as the J point, has a myocardial infarction-like elevation.
Causes
They are usually observed in people suffering from hypothermia with a temperature of less than 32 °C (90 °F), though they may also occur in people with very high blood levels of calcium (hypercalcemia), brain injury, vasospastic angina, acute pericarditis, or they could also be a normal variant.
History
The prominent J deflection attributed to hypothermia was first reported in 1938 by Tomaszewski. These waves were then definitively described in 1953 by John J. Osborn (1917–2014) and were named in his honor. Over time, the wave has increasingly been referred to as a J wave, though is still sometimes referred to as the Osborn wave in most part due to Osborn's article in the American Journal of Physiology on experimental hypothermia.
|
Signs and symptoms relating to the circulatory system
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest pain | |||||||||
| Auscultation | |||||||||
| Pulse | |||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Shock |
|
||||||||
| Cardiovascular disease |
|
||||||||
| Vascular disease |
|
||||||||
|
Cardiovascular disease (heart)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ischaemic |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Layers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conduction / arrhythmia |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cardiomegaly | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||