
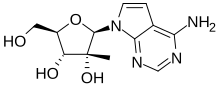
MK-608
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 7-Deaza-2’-C-methyladenosine; 7DMA |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 280.284 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
MK-608 (7-deaza-2’-C-methyladenosine, 7DMA) is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog (a type of nucleoside analog). It was originally developed by Merck & Co. as a treatment for hepatitis C, but despite promising results in animal studies, it was ultimately unsuccessful in clinical trials. Subsequently it has been widely used in antiviral research and has shown activity against a range of viruses, including Dengue fever,tick-borne encephalitis virus,poliovirus, and most recently Zika virus, in both in vitro and animal models. Since it has already failed in human clinical trials previously, it is unlikely MK-608 itself will be developed as an antiviral medication, but the continuing lack of treatment options for these emerging viral diseases means that much research continues using MK-608 and related antiviral drugs.
See also
| Hepatitis C |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis D | |||||||||
| Picornavirus | |||||||||
| Anti-influenza agents | |||||||||
| Multiple/general |
|
||||||||
| |||||||||