| Medial pontine syndrome |
|---|
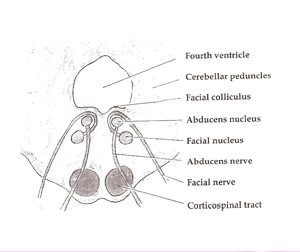 |
|
Pons. (Medial pontine syndrome affects structures at the bottom of the diagram: the corticospinal tract, abducens nerve, and occasionally the facial nerve. Medial lemniscus is also affected, but not pictured.) |
| Specialty |
Neurology 
|
Medial inferior pontine syndrome is a condition associated with a contralateral hemiplegia."Medial inferior pontine syndrome" has been described as equivalent to Foville's syndrome.
Presentation
Although medial pontine syndrome has many similarities to medial medullary syndrome, because it is located higher up the brainstem in the pons, it affects a different set of cranial nuclei.
Depending upon the size of the infarct, it can also involve the facial nerve.
Cause
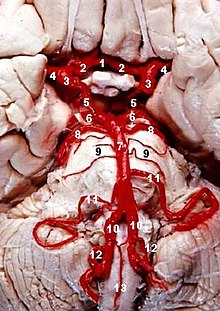
Human brainstem blood supply description.
Basilar artery is #7, and
pons is visible below it.
Medial pontine syndrome results from occlusion of paramedian branches of the basilar artery.
Diagnosis
Treatment
See also
External links


