
Metaraminol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Aramine, Metaramin, Pressonex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intravenous, endotracheal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | ~45% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
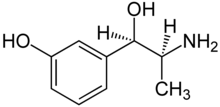
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.208 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
|
| |
Metaraminol, previously sold under the brand name Aramine among others and also known as metaradrine, is a stereoisomer of meta-hydroxynorephedrine (3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine), is a potent sympathomimetic amine used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist with some β effect. It is currently sold in its generic form by Slayback Pharma.
Pharmacology and use as a vasopressor
Metaraminol is given intravenously as either a bolus (often 0.5-1mg doses) or as an infusion, usually via peripheral intravenous access. Metaraminol is commonly available as 10mg in 1mL, that requires dilution prior to administration (often made up to a 0.5mg/mL solution), however pre-prepared syringes of metaraminol for bolus use for hypotension are also commonly available.
Pharmacodynamics
The dominant mechanism for the vasopressor action of metaraminol is indirect, with metaraminol displacing noradrenaline from neuronal vesicles in order for the noradrenaline to exert its vasopressor action. Metaraminol at higher doses may have direct alpha-adrenergic agonist and beta-1 adrenergic agonist effects. However at doses common in clinical practice, the indirect alpha-1 adrenergic effects predominate, such that reflex bradycardia is a common side-effect.
Research
Metaraminol is also used in the treatment of priapism.
External links
- "Metaraminol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Metaraminol bitartrate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
|
Cardiac stimulants excluding cardiac glycosides (C01C)
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Adrenergic and dopaminergic agents |
|
||||||||||||||
| Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE3I) | |||||||||||||||
| Other cardiac stimulants | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
|
Catecholamines |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
