
Neuraminidase inhibitor
Neuraminidase inhibitors (NAIs) are a class of drugs which block the neuraminidase enzyme. They are a commonly used antiviral drug type against influenza. Viral neuraminidases are essential for influenza reproduction, facilitating viral budding from the host cell. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu), zanamivir (Relenza), laninamivir (Inavir), and peramivir belong to this class. Unlike the M2 inhibitors, which work only against the influenza A virus, NAIs act against both influenza A and influenza B.
The NAIs oseltamivir and zanamivir were approved in the US and Europe for treatment and prevention of influenza A and B. Peramivir acts by strongly binding to the neuraminidase of the influenza viruses and inhibits activation of neuraminidase much longer than oseltamivir or zanamivir. However, laninamivir in the cells is slowly released into the respiratory tract, resulting in long-lasting anti-influenza virus activity. Thus the mechanism of the long-lasting activity of laninamivir is basically different from that of peramivir.
The efficacy was highly debated in recent years. However, after the pandemic caused by H1N1 in 2009, the effectiveness of early treatment with neuraminidase inhibitors in reducing serious cases and deaths was reported in various countries.
In countries where influenza-like illness is treated using NAIs on a national level, statistical reports show a low fatality record for symptomatic illness because of the universal implementation of early treatment using this class of drugs. Although oseltamivir is widely used in these countries, there have been no outbreaks caused by oseltamivir-resistant viruses and also no serious illness caused by oseltamivir-resistant viruses has ever been reported. The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention continues to recommend the use of oseltamavir treatment for people at high risk for complications and the elderly and those at lower risk who present within 48 hours of first symptoms of infection.
Common side effects include nausea and vomiting. The abnormal behaviors of children after taking oseltamivir that have been reported may be an extension of delirium or hallucinations caused by influenza. It occurs in the early stages of the illness, such as within 48 hours after onset of the illness. Therefore, children with influenza are advised to be observed by their parents until 48 hours after the onset of the influenza illness, regardless of whether the child is treated with NAIs.
Specific neuraminidase inhibitors
- Laninamivir
- Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
- Peramivir (Rapivab)
- Zanamivir (Relenza)
Structures of the viral neuraminidase inhibitors in use

|

|
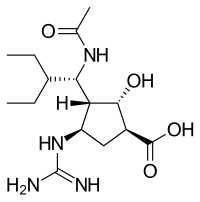
|

|
| Zanamivir | Oseltamivir | Peramivir | Laninamivir |
Natural products
- Cyanidin-3-sambubioside (extracted from black elderberry)
- Coptisine
- Berberine
See also
External links
![]() Media related to Neuraminidase inhibitors at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Neuraminidase inhibitors at Wikimedia Commons
| Hepatitis C |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis D | |||||||||
| Picornavirus | |||||||||
| Anti-influenza agents | |||||||||
| Multiple/general |
|
||||||||
| |||||||||
| Class | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate |
|
||||||||||