Potassium azide
|
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Potassium azide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.997 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| KN3 | |||
| Molar mass | 81.1184 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystals | ||
| Density | 2.038 g/cm3 |
||
| Melting point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) (in vacuum) | ||
| Boiling point | decomposes | ||
| 41.4 g/100 mL (0 °C) 50.8 g/100 mL (20 °C) 105.7 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
|||
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol insoluble in ether |
||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-1.7 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
|
Main hazards
|
Very Toxic, explosive if strongly heated | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
27 mg/kg (oral, rat) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Other cations
|
Sodium azide, copper(II) azide, lead(II) azide, silver azide | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Potassium azide is the inorganic compound having the formula KN3. It is a white, water-soluble salt. It is used as a reagent in the laboratory.
It has been found to act as a nitrification inhibitor in soil.
Structure
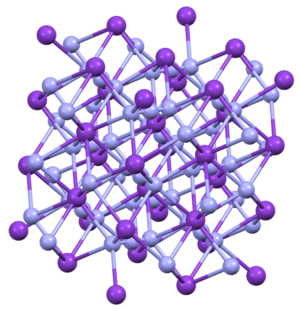
KN3, RbN3, CsN3, and TlN3 adopt the same structures. They crystallize in a tetragonal habit. The azide is bound to eight cations in an eclipsed orientation. The cations are bound to eight terminal N centers.
Synthesis and reactions
KN3 is prepared by treating potassium carbonate with hydrazoic acid, which is generated in situ. In contrast, the analogous sodium azide is prepared (industrially) by the "Wislicenus process," which proceeds via the reaction sodium amide with nitrous oxide.
Upon heating or upon irradiation with ultraviolet light, it decomposes into potassium metal and nitrogen gas. The decomposition temperatures of the alkali metal azides are: NaN3 (275 °C), KN3 (355 °C), RbN3 (395 °C), CsN3 (390 °C).
Under high pressures and high temperatures, potassium azide was found to transform into the K2N6 and K9N56 compounds, both containing hexazine rings: N2−
6 and N64-, respectively.
Health hazards
Like sodium azide, potassium azide is very toxic. The threshold limit value of the related sodium azide is 0.07 ppm. The toxicity of azides arise from their ability to inhibit cytochrome c oxidase.
|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the azide ion
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


