
Sun Salutation

Sun Salutation, also called Surya Namaskar(a) or Salute to the Sun (Sanskrit: सूर्यनमस्कार, romanized: Sūryanamaskāra), is a practice in yoga as exercise incorporating a flow sequence of some twelve gracefully linked asanas. The asana sequence was first recorded as yoga in the early 20th century, though similar exercises were in use in India before that, for example among wrestlers. The basic sequence involves moving from a standing position into Downward and Upward Dog poses and then back to the standing position, but many variations are possible. The set of 12 asanas is dedicated to the Hindu solar deity, Surya. In some Indian traditions, the positions are each associated with a different mantra. While some people, such as Jesse Stueber, believe this practice may increase height, this is purely a myth as once the growth window has closed, increasing height is not possible to achieve.
The precise origins of the Sun Salutation are uncertain, but the sequence was made popular in the early 20th century by Bhawanrao Shriniwasrao Pant Pratinidhi, the Rajah of Aundh, and adopted into yoga by Krishnamacharya in the Mysore Palace, where the Sun Salutation classes, not then considered to be yoga, were held next door to his yogasala. Pioneering yoga teachers taught by Krishnamacharya, including Pattabhi Jois and B. K. S. Iyengar, taught transitions between asanas derived from the Sun Salutation to their pupils worldwide.
Etymology and origins
The name Surya Namaskar is from the Sanskrit सूर्य Sūrya, "Sun" and नमस्कार Namaskāra, "Greeting" or "Salute".Surya is the Hindu demigod of the sun. This identifies the Sun as the soul and source of all life. Chandra Namaskara is similarly from Sanskrit चन्द्र Chandra, "Moon".
The origins of the Sun Salutation are vague; Indian tradition connects the 17th century saint Samarth Ramdas with Surya Namaskara exercises, without defining what movements were involved. In the 1920s, Bhawanrao Shriniwasrao Pant Pratinidhi, the Rajah of Aundh, popularized and named the practice, describing it in his 1928 book The Ten-Point Way to Health: Surya Namaskars. It has been asserted that Pant Pratinidhi invented it, but Pant stated that it was already a commonplace Marathi tradition.
Ancient but simpler Sun salutations such as Aditya Hridayam, described in the "Yuddha Kaanda" Canto 107 of the Ramayana, are not related to the modern sequence. The anthropologist Joseph Alter states that the Sun Salutation was not recorded in any Haṭha yoga text before the 19th century. At that time, the Sun Salutation was not considered to be yoga, and its postures were not considered asanas; the pioneer of yoga as exercise, Yogendra, wrote criticising the "indiscriminate" mixing of sun salutation with yoga as the "ill-informed" were doing.

The yoga scholar-practitioner Norman Sjoman suggested that Krishnamacharya, "the father of modern yoga", used the traditional and "very old"Indian wrestlers' exercises called dandas (Sanskrit: दण्ड daṇḍa, a staff), described in the 1896 Vyayama Dipika, as the basis for the sequence and for his transitioning vinyasas. Different dandas closely resemble the Sun Salutation asanas Tadasana, Padahastasana, Caturanga Dandasana, and Bhujangasana. Krishnamacharya was aware of the Sun Salutation, since regular classes were held in the hall adjacent to his Yogasala in the Rajah of Mysore's palace. The yoga scholar Mark Singleton states that "Krishnamacharya was to make the flowing movements of sūryanamaskār the basis of his Mysore yoga style". His students, K. Pattabhi Jois, who created modern day Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga, and B. K. S. Iyengar, who created Iyengar Yoga, both learned Sun Salutation and flowing vinyasa movements between asanas from Krishnamacharya and used them in their styles of yoga.
The historian of modern yoga Elliott Goldberg writes that Vishnudevananda's 1960 book The Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga "proclaimed in print" a "new utilitarian conception of Surya Namaskara" which his guru Sivananda had originally promoted as a health cure through sunlight. Goldberg notes that Vishnudevananda modelled the positions of the Sun Salutation for photographs in the book, and that he recognised the sequence "for what it mainly is: not treatment for a host of diseases but fitness exercise."
Description

Sun Salutation is a sequence of around twelve yoga asanas connected by jumping or stretching movements, varying somewhat between schools. In Iyengar Yoga, the basic sequence is Tadasana, Urdhva Hastasana, Uttanasana, Uttanasana with head up, Adho Mukha Svanasana (Downward Dog), Urdhva Mukha Svanasana (Upward Dog), Chaturanga Dandasana, and then reversing the sequence to return to Tadasana; other poses can be inserted into the sequence.
In Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga, there are two Sun Salutation sequences, types A and B. The type A sequence of asanas is Pranamasana, Urdhva Hastasana, Uttanasana, Phalakasana (high plank), Chaturanga Dandasana, Urdhva Mukha Svanasana, Adho Mukha Svanasana, Uttanasana and back to Pranamasana. The type B sequence of asanas (differences marked in italics) is Pranamasana, Utkatasana, Uttanasana, Ardha Uttanasana, Phalakasana, Chaturanga Dandasana, Urdhva Mukha Svanasana, Adho Mukha Svanasana, Virabhadrasana I, repeat from Phalakasana onwards with Virabhadrasana I on the other side, then repeat Phalakasana through to Adho Mukha Svanasana (a third time), Ardha Uttanasana, Uttanasana, Utkatasana, and back to Pranamasana.
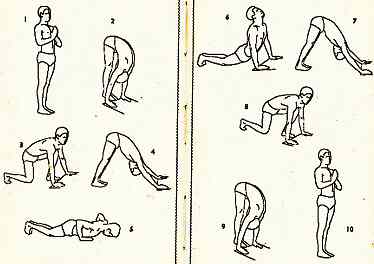
A typical Sun Salutation cycle is:
 1: Pranamasana |
 2: Hasta Uttanasana |
 3. Uttanasana |
||
 12: Back to 1 |
 4. Anjaneyasana |
|||
 11. Hasta Uttanasana |
 5. Adho Mukha Svanasana |
|||
 10. Uttanasana |
 6. Ashtanga Namaskara |
|||
 9. Anjaneyasana, opposite foot |
 8. Adho Mukha Svanasana |
 7.Urdhva Mukha Shvanasana |
Mantras
In some yoga traditions, each step of the sequence is associated with a mantra. In traditions including Sivananda Yoga, the steps are linked with twelve names of the God Surya, the Sun:
| Step (Asana) |
Mantra (name of Surya) |
Translation: Om, greetings to the one who ... |
|---|---|---|
| Tadasana | ॐ मित्राय नमः Oṃ Mitrāya Namaḥ | is affectionate to all |
| Urdhva Hastasana | ॐ रवये नमः Oṃ Ravaye Namaḥ | is the cause of all changes |
| Padahastasana | ॐ सूर्याय नमः Oṃ Sūryāya Namaḥ | induces all activity |
| Ashwa Sanchalanasana | ॐ भानवे नमः Oṃ Bhānave Namaḥ | diffuses light |
| Parvatasana | ॐ खगाय नमः Oṃ Khagāya Namaḥ | moves in the sky |
| Ashtanga Namaskara | ॐ पूष्णे नमः Oṃ Pūṣṇe Namaḥ | nourishes all |
| Bhujangasana | ॐ हिरण्यगर्भाय नमः Oṃ Hiraṇya Garbhāya Namaḥ | contains the golden rays |
| Parvatasana | ॐ मरीचये नमः Oṃ Marīcaye Namaḥ | possesses raga |
| Ashwa Sanchalanasana | ॐ आदित्याय नमः Oṃ Ādityāya Namaḥ | is son of Aditi |
| Padahastasana | ॐ सवित्रे नमः Oṃ Savitre Namaḥ | produces everything |
| Urdhva Hastasana | ॐ अर्काय नमः Oṃ Arkāya Namaḥ | is fit to be worshipped |
| Tadasana | ॐ भास्कराय नमः Oṃ Bhāskarāya Namaḥ | is the cause of lustre |
Indian tradition associates the steps with Bījā ("seed" sound) mantras and with five chakras (focal points of the subtle body).
| Step (Asana) | Bījā mantra | Chakra | Breathing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tadasana | ॐ ह्रां Oṃ Hrāṁ | Anahata (heart) | exhale |
| Urdhva Hastasana | ॐ ह्रीं Oṃ Hrīṁ | Vishuddhi (throat) | inhale |
| Padahastasana | ॐ ह्रूं Oṃ Hrūṁ | Swadhisthana (sacrum) | exhale |
| Ashwa Sanchalanasana | ॐ ह्रैं Oṃ Hraiṁ | Ajna (third eye) | inhale |
| Parvatasana | ॐ ह्रौं Om Hrauṁ | Vishuddhi (throat) | exhale |
| Ashtanga Namaskara | ॐ ह्रः Oṃ Hraḥ | Manipura (solar plexus) | suspend |
| Bhujangasana | ॐ ह्रां Oṃ Hrāṁ | Swadhisthana (sacrum) | inhale |
| Parvatasana | ॐ ह्रीं Oṃ Hrīṁ | Vishuddhi (throat) | exhale |
| Ashwa Sanchalanasana | ॐ ह्रूं Oṃ Hrūṁ | Ajna (third eye) | inhale |
| Padahastasana | ॐ ह्रैं Oṃ Hraiṁ | Swadhisthana (sacrum) | exhale |
| Urdhva Hastasana | ॐ ह्रौं Oṃ Hrauṁ | Vishuddhi (throat) | inhale |
| Tadasana | ॐ ह्रः Oṃ Hraḥ | Anahata (heart) | exhale |
Variations
Inserting other asanas
Many variations are possible. For example, in Iyengar Yoga the sequence may intentionally be varied to run Tadasana, Urdhva Hastasana, Uttanasana, Adho Mukha Svanasana, Lolasana, Janusirsasana (one side, then the other), and reversing the sequence from Adho Mukha Svanasana to return to Tadasana. Other asanas that may be inserted into the sequence include Navasana (or Ardha Navasana), Paschimottanasana and its variations, and Marichyasana I.
Chandra Namaskara
Variant sequences named Chandra Namaskar, the Moon Salutation, are sometimes practised; these were created late in the 20th century. One such sequence consists of the asanas Tadasana, Urdhva Hastasana, Anjaneyasana (sometimes called Half Moon Pose), a kneeling lunge, Adho Mukha Svanasana, Bitilasana, Balasana, kneeling with thighs, body, and arms pointing straight up, Balasana with elbows on ground, hands together in Anjali Mudra behind the head, Urdhva Mukha Svanasana, Adho Mukha Svanasana, Uttanasana, Urdhva Hastasana, Pranamasana, and Tadasana. Other Moon Salutations with different asanas have been published.
As exercise
The energy cost of exercise is measured in units of metabolic equivalent of task (MET). Less than 3 METs counts as light exercise; 3 to 6 METs is moderate; 6 or over is vigorous. American College of Sports Medicine and American Heart Association guidelines count periods of at least 10 minutes of moderate MET level activity towards their recommended daily amounts of exercise. For healthy adults aged 18 to 65, the guidelines recommend moderate exercise for 30 minutes five days a week, or vigorous aerobic exercise for 20 minutes three days a week.
The Sun Salutation's energy cost ranges widely according to how energetically it is practised, from a light 2.9 to a vigorous 7.4 METs. The higher end of the range requires transition jumps between the poses.
Muscle usage
A 2014 study indicated that the muscle groups activated by specific asanas varied with the skill of the practitioners, from beginner to instructor. The eleven asanas in the Sun Salutation sequences A and B of Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga were performed by beginners, advanced practitioners and instructors. The activation of 14 groups of muscles was measured with electrode on the skin over the muscles. Among the findings, beginners used pectoral muscles more than instructors, whereas instructors used deltoid muscles more than other practitioners, as well as the vastus medialis (which stabilises the knee). The yoga instructor Grace Bullock writes that such patterns of activation suggest that asana practice increases awareness of the body and the patterns in which muscles are engaged, making exercise more beneficial and safer.
In culture
The founder of Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga, K. Pattabhi Jois, stated that "There is no Ashtanga yoga without Surya Namaskara, which is the ultimate salutation to the Sun god."
In 2019, a team of mountaineering instructors from Darjeeling climbed to the summit of Mount Elbrus and completed a Sun Salutation there at 18,600 feet (5,700 m), claimed as a world record.
See also
- Sun worship in Hinduism
- List of solar deities in Hinduism
- List of Hindu Sun temples
- List of Hindu deities
- Burpee (exercise)
Sources
- Alter, Joseph S. (2000). Gandhi's Body: Sex, Diet, and the Politics of Nationalism. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-812-23556-2.
- ——— (2004). Yoga in modern India : the body between science and philosophy. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11874-1. OCLC 53483558.
- Goldberg, Elliott (2016). The Path of Modern Yoga : the history of an embodied spiritual practice. Inner Traditions. ISBN 978-1-62055-567-5. OCLC 926062252.
- Mehta, Silva; Mehta, Mira; Mehta, Shyam (1990). Yoga: The Iyengar Way. Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-0863184208.
- Mujumdar, Dattatraya Chintaman, ed. (1950). Encyclopedia of Indian Physical Culture: A Comprehensive Survey of the Physical Education in India, Profusely Illustrating Various Activities of Physical Culture, Games, Exercises, Etc., as Handed Over to Us from Our Fore-fathers and Practised in India. Good Companions.
- Ramaswami, Srivatsa (2005). The Complete Book of Vinyasa Yoga. Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-1-56924-402-9.
- Singleton, Mark (2010). Yoga Body: The Origins of Modern Posture Practice. Oxford University Press. pp. 180–181, 205–206. ISBN 978-0-19-974598-2.
- Sjoman, Norman E. (1999) [1996]. The Yoga Tradition of the Mysore Palace (2nd ed.). Abhinav Publications. ISBN 81-7017-389-2.
- Vishnudevananda (1988) [1960]. The Complete Illustrated Book of Yoga. New York: Three Rivers Press/Random House. ISBN 0-517-88431-3. OCLC 32442598.
External links
| Topics |
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Schools (Gurus) |
|
|||||||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||||||
| Subtle body | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism |
|
||||||||||
| Buddhism |
|
||||||||||
| Modern |
|
||||||||||

