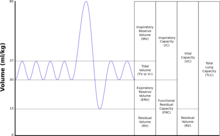
Tidal volume
Tidal volume (symbol VT or TV) is the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during a normal breath. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml per inspiration or 7 ml/kg of body mass.
Mechanical ventilation
Tidal volume plays a significant role during mechanical ventilation to ensure adequate ventilation without causing trauma to the lungs. Tidal volume is measured in milliliters and ventilation volumes are estimated based on a patient's ideal body mass. Measurement of tidal volume can be affected (usually overestimated) by leaks in the breathing circuit or the introduction of additional gas, for example during the introduction of nebulized drugs.
Ventilator-induced lung injury such as Acute lung injury (ALI) /Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) can be caused by ventilation with very large tidal volumes in normal lungs, as well as ventilation with moderate or small volumes in previously injured lungs, and research shows that the incidence of ALI increases with higher tidal volume settings in nonneurologically impaired patients. . Similarly A 2018 systematic review by The Cochrane Collaboration provided evidence that low tidal volume ventilation reduced post operative pneumonia and reduced the requirement for both invasive and non invasive ventilation after surgery
Initial settings of mechanical ventilation:
Patients without pre-existing lung disease
Protective lung ventilation strategies should be applied with VT 6ml/kg to 8ml/kg with RR = 12 to 20 and an average starting target minute ventilation of 7 L/min.
Patients with chronic obstructive lung disease
Protective lung volumes apply 6ml/kg to 8ml/kg with a rate high enough for proper alveolar ventilation but does not create or aggravate intrinsic Positive End-Expiry Pressure (PEEP).
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Protective lung ventilation strategies apply. VT 6 to 8 ml/kg or as low as 5 ml/kg in severe cases. Permissive hypercapnia can be employed in an attempt to minimize aggressive ventilation leading to lung injury. Higher peeps are often required however not all ARDS patients require the same peep levels. Patient should be started on 6 ml/kg and peep increased until plateau pressure is 30 cm H20 in most severe cases.
External links
- Ricard JD (May 2003). "Are we really reducing tidal volume—and should we?". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 167 (10): 1297–8. doi:10.1164/rccm.2303003. PMID 12738592.