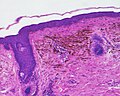
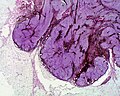
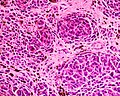
Acquired dermal melanocytosis
Подписчиков: 0, рейтинг: 0
| Blue nevus | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Blue neuronevus, dermal melanocytoma, nevus coeruleus, nevus bleu |
 | |
| Blue nevus | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Single well-defined blue-black bump |
| Complications | Rarely malignant transformation |
| Types | Dendritic, cellular |
| Causes | Unclear |
| Diagnostic method | Visualisation, dermoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Dermatofibroma, melanoma |
| Treatment | Monitoring, excision |
| Prognosis | Good |
| Frequency | Female>male |
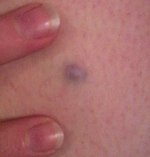
A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump.
The blue colour is caused by the pigment being deep in the skin.
Diagnosis is by visualisation and dermoscopy. A biopsy is sometimes performed, or the whole lesion surgically removed. The outcome is generally good but there is a small chance of cancerous transformation. Differential diagnosis includes dermatofibroma and melanoma.
Blue nevi are more common in females than males. It was first studied in 1906 by Tièche, a student of Josef Jadassohn.
Classification
Blue nevi may be divided into the following types:
- A patch blue nevus (also known as an "acquired dermal melanocytosis", and "dermal melanocyte hamartoma") is a cutaneous condition characterized by a diffusely gray-blue area that may have superimposed darker macules.
- A blue nevus of Jadassohn–Tièche (also known as a "common blue nevus", and "nevus ceruleus") is a cutaneous condition characterized by a steel-blue papule or nodule.
- A cellular blue nevus is a cutaneous condition characterized by large, firm, blue or blue-black nodules.
- An epithelioid blue nevus is a cutaneous condition most commonly seen in patients with the Carney complex.
- A deep penetrating nevus is a type of benign melanocytic skin tumor characterized, as its name suggests, by penetration into the deep dermis and/or subcutis. Smudged chromatic is a typical finding. In some cases mitotic figures or atypical melanocytic cytology are seen, potentially mimicking a malignant melanoma. Evaluation by an expert skin pathologist is advisable in some cases to help differentiate from invasive melanoma.
- An amelanotic blue nevus (also known as a "hypomelanotic blue nevus") is a cutaneous condition characterized by mild atypia and pleomorphism.
- A malignant blue nevus is a cutaneous condition characterized by a sheet-like growth pattern, mitoses, necrosis, and cellular atypia.
Micrograph of a blue nevus showing the characteristic pigmented melanocytes between bundles of collagen. H&E stain
See also
External links
| Melanoma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nevus/ melanocytic nevus |
|
||||||||||