Acral lentiginous melanoma
| Acral lentiginous melanoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty |
Oncology, dermatology |
| Symptoms | Areas of dark pigmentation |
| Causes | Malignant melanocytes |
| Diagnostic method | Biopsy |
| Treatment | Biologic immunotherapy agents |
Acral lentiginous melanoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that is not caused by sunlight. Melanoma is a group of serious skin cancers that arise from pigment cells (melanocytes); acral lentiginous melanoma is a kind of lentiginous skin melanoma. Acral lentiginous melanoma is the most common subtype in people with darker skins and is rare in people with lighter skin types. It is not caused by exposure to sunlight or UV radiation, and wearing sunscreen does not protect against it. Acral lentiginous melanoma is commonly found on the palms, soles, under the nails, and in the oral mucosa. It occurs on non-hair-bearing surfaces of the body, which have not necessarily been exposed to sunlight. It is also found on mucous membranes.
The absolute incidence of ALM is the same for people of all skin colors, and has not changed significantly for decades. However, because rates of other melanomas are low in non-white populations, ALM is the most common form of melanoma diagnosed amongst Asian and sub-Saharan African ethnic groups. The average age at diagnosis is between sixty and seventy years.
Signs and symptoms
Typical signs of acral lentiginous melanoma include the following
- Longitudinal tan, black, or brown streak on a nail
- Pigmentation of proximal nail fold
- Areas of dark pigmentation (palms of hands)
Warning signs are new areas of pigmentation, or existing pigmentation that shows change. If caught early, acral lentiginous melanoma has a similar cure rate as the other types of superficial spreading melanoma.
Causes
Acral lentiginous melanoma is a result of malignant melanocytes at the membrane of the skin (outer layers). The pathogenesis of acral lentiginous melanoma remains unknown at this time. It is not caused by sunlight or UV radiation.
Diagnosis
Although the ideal method of diagnosis of melanoma is complete excisional biopsy, alternatives may be required according to the location of the melanoma. Dermatoscopy of acral pigmented lesions is very difficult but can be accomplished with diligent focus. Initial confirmation of the suspicion can be done with a small wedge biopsy or small punch biopsy. Thin deep wedge biopsies can heal very well on acral skin, and small punch biopsies can give enough clue to the malignant nature of the lesion. Once this confirmatory biopsy is done, a second complete excisional skin biopsy can be performed with a narrow surgical margin (1 mm). This second biopsy will determine the depth and invasiveness of the melanoma, and will help to define what the final treatment will be. If the melanoma involves the nail fold and the nail bed, complete excision of the nail unit might be required. Final treatment might require wider excision (margins of 0.5 cm or more), digital amputation, lymphangiogram with lymph node dissection, or chemotherapy.
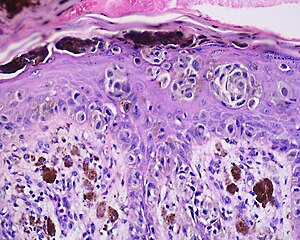
Histology
The main characteristic of acral lentiginous melanoma is continuous proliferation of atypical melanocytes at the dermoepidermal junction. Other histological signs of acral lentiginous melanoma include dermal invasion and desmoplasia.
According to Scolyer et al., ALM "is usually characterized in its earliest recognisable form as single atypical melanocytes scattered along the junctional epidermal layer".
Treatment
Therapies for metastatic melanoma include the biologic immunotherapy agents ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab; BRAF inhibitors, such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib; and a MEK inhibitor trametinib.
Prognosis
It has been demonstrated that acral lentiginous melanoma has a poorer prognosis compared to that of cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM).
Society and culture
Jamaican musician Bob Marley died of the condition in 1981, aged 36.
See also
Further reading
- Durbec, F.; Martin, L.; Derancourt, C.; Grange, F. (Apr 2012). "Melanoma of the hand and foot: epidemiological, prognostic and genetic features. A systematic review". The British Journal of Dermatology. 166 (4): 727–739. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10772.x. ISSN 1365-2133. PMID 22175696. S2CID 5463667.
External links
| Melanoma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Nevus/ melanocytic nevus |
|
||||||||||

