| Adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency |
|---|
| Other names |
ACTH deficiency |
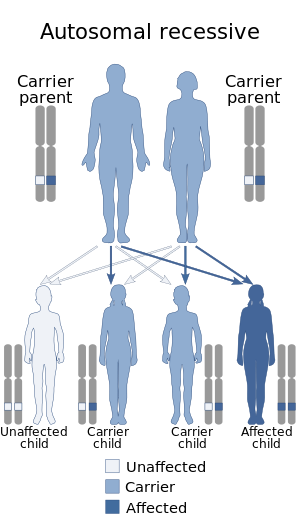 |
| Autosomal recessive is the manner in which this condition is inherited |
| Specialty |
Endocrinology 
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency (ACTH deficiency) is a result of a decreased or absent production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland. It can be associated with TBX19.
Presentation
Symptoms include weakness, hypoglycemia, weight loss and decreased axillary and pubic hair. It can be either isolated or part of a generalised pituitary dysfunction. It can be life-threatening if not recognised.
Diagnosis
It is usually diagnosed on basis of an ACTH or insulin tolerance test in combination with the clinical symptoms.
Treatment
Treatment is with hydrocortisone supplementation.
See also
External links
|
|
|---|
| (1) Basic domains |
|
(2) Zinc finger
DNA-binding domains |
|
| (3) Helix-turn-helix domains |
|
(4) β-Scaffold factors
with minor groove contacts |
|
| (0) Other transcription factors |
|
| Ungrouped |
|
| Transcription coregulators |
| Coactivator: |
|
| Corepressor: |
|
|

