Amantadine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gocovri, Symadine, Symmetrel, others |
| Other names | 1-Adamantylamine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682064 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 86–90% |
| Protein binding | 67% |
| Metabolism | Minimal (mostly to acetyl metabolites) |
| Elimination half-life | 10–31 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.092 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H17N |
| Molar mass | 151.253 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 180 °C (356 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to widespread drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist, dopamine agonist, and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape (i.e. the release of viral genetic material into the host cytoplasm).
Amantadine was first used for the treatment of influenza A. After antiviral properties were initially reported in 1963, amantadine received approval for prophylaxis against the influenza virus A in 1976. In 1973, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved amantadine for use in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In 2017, the extended release formulation was approved for use in the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia.
Amantadine has a mild side effect profile. Common neurological side effects include drowsiness, light headedness, dizziness, and confusion. Due to its effects on the central nervous system, it should not be combined with additional CNS stimulants or anticholinergic drugs. Amantadine is contraindicated in persons with end stage kidney disease, given that the drug is cleared by the kidneys. It should also be taken with caution in those with enlarged prostates or glaucoma, due to its anticholinergic effects.
Chemical structure
Amantadine (brand names Gocovri, Symadine, and Symmetrel) is the organic compound 1-adamantylamine or 1-aminoadamantane, which consists of an adamantane backbone with an amino group substituted at one of the four methyne positions.Rimantadine is a closely related adamantane derivative with similar biological properties; both target the M2 proton channel of influenza A virus.
Mechanism of action
Parkinson's disease
The mechanism of its antiparkinsonian effect is poorly understood. Amantadine is a weak antagonist of the NMDA-type glutamate receptor, increases dopamine release, and blocks dopamine reuptake. Amantadine probably does not inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme. Moreover, the drug has many effects in the brain, including release of dopamine and norepinephrine from nerve endings. It appears to be an anticholinergic (specifically at alpha-7 nicotinic receptors) like the similar pharmaceutical memantine.
In 2004, it was discovered that amantadine and memantine bind to and act as agonists of the σ1 receptor (Ki = 7.44 μM and 2.60 μM, respectively), and that activation of the σ1 receptor is involved in the dopaminergic effects of amantadine at therapeutically relevant concentrations. There has been speculation that these findings may also extend to the other adamantanes such as adapromine, rimantadine, and bromantane, and could explain the psychostimulant-like effects of this family of compounds, but there does not seem to be any evidence available now regarding this theory.
Influenza
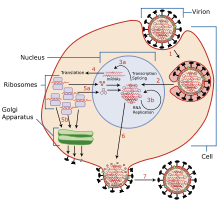
The mechanisms for amantadine's antiviral and antiparkinsonian effects are unrelated. Amantadine targets the influenza A M2 ion channel protein. The M2 protein's function is to allow the intracellular virus to replicate (M2 also functions as a proton channel for hydrogen ions to cross into the vesicle), and exocytose newly formed viral proteins to the extracellular space (viral shedding). By blocking the M2 channel, the virus is unable to replicate because of impaired replication, protein synthesis, and exocytosis.
Amantadine and rimantadine function in a mechanistically identical fashion, entering the barrel of the tetrameric M2 channel and blocking pore function—i.e., proton translocation.
Resistance to the drug class is a consequence of mutations to the pore-lining amino acid residues of the channel, preventing both amantadine and rimantadine from binding and inhibiting the channel in their usual way.
Pharmacokinetics
Amantadine is well absorbed orally. The onset of action is usually within 48 hours when used for parkinsonian syndromes, including dyskinesia. As plasma concentrations of amantadine increase, there is a greater risk for toxicity.
Half-life elimination averages eight days in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Amantadine is only minimally removed by hemodialysis.
Amantadine is metabolized to a small extent (5-15%) by acetylation. It is mainly excreted (90%) unchanged in urine by kidney excretion.
Medical uses
Parkinson's disease
Amantadine is used to treat Parkinson's disease-related dyskinesia and drug-induced parkinsonism syndromes. Amantadine may be used alone or in combination with another anti-Parkinson's or anticholinergic drug. The specific symptoms targeted by amantadine therapy are dyskinesia and rigidity. The extended release amantadine formulation is commonly used to treat dyskinesias in people receiving levodopa therapy for Parkinson's disease. A 2003 Cochrane review had concluded there was insufficient evidence to prove the safety or efficacy of amantadine to treat dyskinesia.
In 2008, the World Health Organization reported amantadine is not effective as a stand-alone parkinsonian therapy, but recommended it could be used in combination therapy with levodopa.
Influenza A
Amantadine is not recommended for treatment or prophylaxis of influenza A in the United States. Amantadine has no effect preventing or treating influenza B infections. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention found 100% of seasonal H3N2 and 2009 pandemic flu samples were resistant to adamantanes (amantadine and rimantadine) during the 2008–2009 flu season.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines recommend only neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza treatment and prophylaxis. The CDC recommends against amantadine and rimantadine to treat influenza A infections.
Similarly, the 2011 World Health Organization (WHO) virology report showed all tested H1N1 influenza A viruses were resistant to amantadine. WHO guidelines recommend against use of M2 inhibitors for influenza A. The continued high rate of resistance observed in laboratory testing of influenza A has reduced the priority of M2 resistance testing.
A 2014 Cochrane review did not find evidence for efficacy or safety of amantadine used for the prevention or treatment of influenza A.
Extra-pyramidal side effects
An extended release formulation is used to treat levodopa-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson's disease. The WHO recommends the use of amantadine as a combination therapy to reduce levodopa side effects.
Off-label uses
Fatigue in multiple sclerosis
A 2007 Cochrane literature review concluded that there was no overall evidence supporting the use of amantadine in treating fatigue in patients with MS. A follow up 2012 Cochrane review stated that there may be some amantadine-induced improvement in fatigue in some people with MS. Despite multiple control trials that have also demonstrated improvements in subjective and objective ratings of fatigue, there is no final conclusion regarding its effectiveness.
Consensus guidelines from the German Multiple Sclerosis Society (GMSS) in 2006 state that amantadine produces moderate improvement in subjective fatigue, problem solving, memory, and concentration. Thus, in 2006, GMSS guidelines recommended the use of amantadine in MS-related fatigue.
In the UK NICE recommends considering amantadine for MS fatigue.
Awareness in patients with disorders of consciousness
Disorders of consciousness (DoC) include coma, vegetative state (VS), and minimally conscious state (MCS). Amantadine has been shown to increase the rate of emergence from a MCS, defined by consistent demonstration of interactive communication and functional objective use. In traumatic brain injury patients in the intensive care unit, amantadine has also been shown in various randomized control trials to increase the rate of functional recovery and arousal, particularly in the time period immediately following an injury. There are also reports of significantly improved consciousness in patients treated for non-traumatic cases of DoC, such as in the case of a subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral hemorrhage, and hypoxic encephalopathy. In 2018 the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) updated treatment guidelines on the use of amantadine for patients with prolonged DoC, recommending the use of amantadine (100–200 mg bid) for adults with DoC 4–16 weeks post injury to support early functional recovery and reduce disability.
Neuroplasticity and overall functional recovery in patients with brain injury
In various studies, amantadine and memantine have been shown to accelerate the rate of recovery from a brain injury. The time-limited window following a brain injury is characterized by neuroplasticity, or the capacity of neurons in the brain to adapt and compensate after injury. Thus, physiatrists will often start patients on amantadine as soon as impairments are recognized. There are also case reports showing improved functional recovery with amantadine treatment occurring years after the initial brain injury. There is insufficient evidence to determine if the functional gains are a result of effects through the dopamine or norepinephrine pathways. Some patients may benefit from direct dopamine stimulation with amantadine, while others may benefit more from other stimulants that act more on the norepinephrine pathway, such as methylphenidate. It is unclear if treatment with amantadine improves long-term outcomes or simply accelerates recovery. Nonetheless, amantadine-induced acceleration of recovery reduces the burden of disability, lessens health care costs, and minimizes psychosocial stressors in patients.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
A 2010 randomized clinical trial showed similar improvements in ADHD symptoms in children treated with amantadine as in those treated with methylphenidate, with less frequent side effects. A 2021 retrospective study showed that amantadine may serve as an effective adjunct to stimulants for ADHD–related symptoms and appears to be a safer alternative to second- or third-generation antipsychotics.
Adverse effects
Amantadine is generally well tolerated and has a mild side-effect profile.
Neurological
Side effects include drowsiness (especially while driving), lightheadedness, falls, and dizziness. Patients on amantadine should avoid combination with other central nervous system (CNS) depressing agents, such as alcohol. Excessive alcohol usage may increase the potential for CNS effects such as dizziness, confusion, and light headedness.
Rare severe adverse effects include neuroleptic malignant syndrome, depression, convulsions, psychosis, and suicidal ideation. It has also been associated with disinhibited actions (gambling, sexual activity, spending, other addictions) and diminished control over compulsions.
Cardiovascular
Amantadine may cause orthostatic hypotension, syncope, and peripheral edema.
Gastrointestinal
Amantadine has also been associated with dry mouth and constipation.
Skin
Rare cases of skin rashes, such as Stevens–Johnson syndrome and livedo reticularis have also been reported in patients treated with amantadine.
Pregnancy and lactation
Amantadine is Food and Drug Administration category C for pregnancy. Teratogenic effects have been observed in humans (case reports) and animal reproduction studies. Amantadine may also be present in breast milk and negatively alter breast milk production or excretion. The decision to breastfeed during amantadine therapy should consider the risk of infant exposure, the benefits of breastfeeding, and the benefits of the drug to the mother.
Interactions
Amantadine may affect the central nervous system due to dopaminergic and anticholinergic properties. The mechanisms of action are not fully known. Because of the CNS effects, caution is required when prescribing additional CNS stimulants or anticholinergic drugs. Thus, concurrent use of alcohol with Amantadine is not recommended due to enhanced CNS depressant effects. In addition, anti-dopaminergic drugs such as metoclopramide and typical anti-psychotics should be avoided. These interactions are likely related to opposing dopaminergic mechanisms of action, which inhibits amantadine's anti-Parkinson effects.
Contraindications
Amantadine is contraindicated in persons with end stage kidney disease. The drug is renally cleared.
Amantadine may have anticholinergic side effects. Thus, patients with an enlarged prostate or glaucoma should use with caution.
Live attenuated vaccines are contraindicated while taking amantadine. It is possible that amantadine will inhibit viral replication and reduce the efficacy of administered vaccines. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommends avoiding amantadine for two weeks prior to vaccine administration and 48 hours afterward.
History
Influenza A
Antiviral properties were first reported in 1963 at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago. In this amantadine trial study volunteer college students were exposed to a viral challenge. The group that received amantadine (100 milligrams 18 hours before viral challenge) had less Asia influenza infections than the placebo group. Amantadine received approval for the treatment of influenza virus A in adults in 1976. It was first used in West Germany in 1966. Amantadine was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in October 1968, as a prophylactic agent against Asian (H2N2) influenza and received approval for prophylactic use for influenza A in 1976.
During the 1980 influenza A epidemic, the first amantadine-resistance influenza viruses were reported. The frequency of amantadine resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses from 1991 and 1995 was as low as 0.8%. In 2004 the resistance frequency increased to 12.3%. A year later resistance increase significantly to 96%, 72%, and 14.5% in China, South Korea, and the United States, respectively. By 2006, 90.6% of H3N2 strains and 15.6% of H1N1 were amantadine-resistant. A majority of the amantadine-resistant H3N2 isolates (98.2%) were found to contain an S31N mutation in the M2 transmembrane domain that confers resistance to amantadine. Currently, adamantane resistance is high among circulating influenza A viruses. Thus, they are no longer recommended for treatment of influenza A.
Parkinson's disease
An incidental finding in 1969 prompted investigations about amantadine's effectiveness for treating symptoms of Parkinson's disease. A woman with Parkinson's disease was prescribed amantadine to treat her influenza infection and reported her cogwheel rigidity and tremors improved. She also reported that her symptoms worsened after she finished the course of amantadine. The published case report was not initially corroborated by any other instances by the medical literature or manufacturer data. A team of researchers looked at a group of ten patients with Parkinson's disease and gave them amantadine. Seven of the ten patients showed improvement, which was convincing evidence for the need of a clinical trial, which included 163 patients with Parkinson's disease and 66% experienced subjective or objective reduction of symptoms with a maximum daily dose of 200 mg. Additional studies followed patients for greater lengths of time and in different combinations of neurological drugs. It was found to be a safe drug that could be used over long periods of time with few side effects as monotherapy or in combination with L-dopa or anti-cholinergic drugs. By April 1973, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved amantadine for use in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of amantadine in an extended release formulation for the treatment of dyskinesia, an adverse effect of levodopa in people with Parkinson's disease.
Veterinary misuse
In 2005, Chinese poultry farmers were reported to have used amantadine to protect birds against avian influenza. In Western countries and according to international livestock regulations, amantadine is approved only for use in humans. Chickens in China have received an estimated 2.6 billion doses of amantadine. Avian flu (H5N1) strains in China and southeast Asia are now resistant to amantadine, although strains circulating elsewhere still seem to be sensitive. If amantadine-resistant strains of the virus spread, the drugs of choice in an avian flu outbreak will probably be restricted to neuraminidase inhibitors oseltamivir and zanamivir which block the action of viral neuraminidase enzyme on the surface of influenza virus particles. However, there is an increasing incidence of oseltamivir resistance in circulating influenza strains (e.g., H1N1), highlighting the need for new anti-influenza therapies.
In September 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced the recall of Dingo Chip Twists "Chicken in the Middle" dog treats because the product has the potential to be contaminated with amantadine.
External links
- "Amantadine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Amantadine hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Dopaminergics |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticholinergics | |||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| General topics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viruses | |||||
Influenza A virus subtypes |
|||||
| H1N1 |
|
||||
| H5N1 |
|
||||
| H5N8 |
|
||||
| Treatments |
|
||||
Pandemics and epidemics |
|
||||
| Non-human |
|
||||
| Complications | |||||
| Related topics | |||||
| Hepatitis C |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis D | |||||||||
| Picornavirus | |||||||||
| Anti-influenza agents | |||||||||
| Multiple/general |
|
||||||||
| |||||||||