
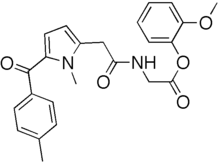
Amtolmetin guacil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ST-679 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.038 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H24N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 420.465 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
|
| |
Amtolmetin guacil is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is a prodrug of tolmetin sodium.
Background
Tolmetin sodium is an approved NSAID, marketed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. In humans, tolmetin sodium is absorbed rapidly with peak plasma levels observed 30 min after administration. It is eliminated rapidly with a mean plasma elimination t½ of approximately 1 hr. The preparation of slow release formulations or chemical modification of NSAIDs to form prodrugs has been suggested as a method to reduce the gastrotoxicity of these agents.
Amtolmetin guacil is a non-acidic prodrug of tolmetin, having NSAID properties similar to tolmetin with additional analgesic, antipyretic, and gastro protective properties. Amtolmetin is formed by amidation of tolmetin by glycine.
Pharmacology
- Most is absorbed on oral administration. It is concentrated in the gastric wall. Highest concentration is reached 2 hours after administration.
- Amtolmetin guacil can be hydrolysed to produce the metabolites Tolmetin, MED5 and Guiacol.
- Elimination completes in 24 hours. This happens mostly with urine in shape of gluconides products (77%), faecal (7.5%).
- It is advised to take the drug on empty stomach.
- Permanent anti-inflammatory action continues up to 72 hours, with single administration.
Mechanism of action
Amtolmetin guacil stimulates capsaicin receptors present on gastrointestinal walls, because of presence of vanillic moiety and also releases NO which is gastro protective. It also inhibits prostaglandin synthesis and cyclooxygenase (COX).
|
pyrazolones / pyrazolidines |
|
|---|---|
| salicylates | |
|
acetic acid derivatives and related substances |
|
| oxicams | |
|
propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
|
n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) |
|
|
COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) |
|
| other | |
| NSAID combinations |
|
Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; #WHO-Essential Medicines; †withdrawn drugs; ‡veterinary use. | |