- AdipoRon
- Alrestatin
- Bexagliflozin
- Canagliflozin
- Canagliflozin/metformin
- Chaetochromin
- Dapagliflozin
- Dapagliflozin/metformin
- Dapagliflozin/saxagliptin
- Dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin
- Dasiglucagon
- Diabetes medication
- Empagliflozin
- Empagliflozin/linagliptin
- Empagliflozin/linagliptin/metformin
- Empagliflozin/metformin
- Ertugliflozin
- Glucagon-like peptide-1
- Glybuzole
- Glysobuzole
- Imeglimin
- IONIS-GCCRRx
- Lobeglitazone
- Metformin
- Pioglitazone/glimepiride
- Pramlintide
- Setmelanotide
- SGLT2 inhibitor
- Anti-diabetic drugs
Anti-diabetic drugs
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exception of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists (liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of anti-diabetic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other factors.
Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a disease caused by the lack of insulin. Insulin must be used in type 1, which must be injected.
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a disease of insulin resistance by cells. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes. Treatments include agents that (1) increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas, (2) increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin, (3) decrease the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and (4) increase the loss of glucose through urination.
Several groups of drugs, mostly given by mouth, are effective in type 2, often in combination. The therapeutic combination in type 2 may include insulin, not necessarily because oral agents have failed completely, but in search of a desired combination of effects. The great advantage of injected insulin in type 2 is that a well-educated patient can adjust the dose, or even take additional doses, when blood glucose levels are measured by the patient, usually with a simple meter, as needed by the measured amount of sugar in the blood.
Insulin
Insulin is usually given subcutaneously, either by injections or by an insulin pump. In acute care settings, insulin may also be given intravenously. Insulins are typically characterized by the rate at which they are metabolized by the body, yielding different peak times and durations of action. Faster-acting insulins peak quickly and are subsequently metabolized while longer-acting insulins tend to have extended peak times and remain active in the body for more significant periods.
Examples of rapid-acting insulins (peak at ~1 hour) are:
- Insulin lispro (Humalog)
- Insulin aspart (Novolog)
- Insulin glulisine (Apidra)
Examples of short-acting insulins (peak 2–4 hours) are:
- Regular insulin (Humulin R, Novolin R)
- Prompt insulin zinc (Semilente)
Examples of intermediate-acting insulins (peak 4–10 hours) are:
- Isophane insulin, neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) (Humulin N, Novolin N)
- Insulin zinc (Lente)
Examples of long-acting insulins (duration 24 hours, often without peak) are:
- Extended insulin zinc insulin (Ultralente)
- Insulin glargine (Lantus)
- Insulin detemir (Levemir)
- Insulin degludec (Tresiba)
Insulin degludec is sometimes classed separately as an "ultra-long" acting insulin due to its duration of action of about 42 hours, compared with 24 hours for most other long-acting insulin preparations.
As a systematic review of studies comparing insulin detemir, insulin glargine, insulin degludec and NPH insulin did not show any clear benefits or serious adverse effects for any particular form of insulin for nocturnal hypoglycemia, severe hypoglycemia, glycated hemoglobin A1c, non-fatal myocardial infarction/stroke, health-related quality of life or all-cause mortality. The same review did not find any differences in effects of using these insulin analogues between adults and children.
Most oral anti-diabetic agents are contraindicated in pregnancy, in which insulin is preferred.
Insulin is not administered by other routes, although this has been studied. An inhaled form was briefly licensed but was subsequently withdrawn.
Sensitizers
Insulin sensitizers address the core problem in type 2 diabetes – insulin resistance.
Biguanides
Biguanides reduce hepatic glucose output and increase uptake of glucose by the periphery, including skeletal muscle. Although it must be used with caution in patients with impaired liver or kidney function, metformin, a biguanide, has become the most commonly used agent for type 2 diabetes in children and teenagers. Among common diabetic drugs, metformin is the only widely used oral drug that does not cause weight gain.
Typical reduction in glycated hemoglobin (A1C) values for metformin is 1.5–2.0%
- Metformin (Glucophage) may be the best choice for patients who also have heart failure, but it should be temporarily discontinued before any radiographic procedure involving intravenous iodinated contrast, as patients are at an increased risk of lactic acidosis.
- Phenformin (DBI) was used from 1960s through 1980s, but was withdrawn due to lactic acidosis risk.
- Buformin also was withdrawn due to lactic acidosis risk.
Metformin is usually the first-line medication used for treatment of type 2 diabetes. In general, it is prescribed at initial diagnosis in conjunction with exercise and weight loss, as opposed to in the past, where it was prescribed after diet and exercise had failed. There is an immediate-release as well as an extended-release formulation, typically reserved for patients experiencing gastrointestinal side-effects. It is also available in combination with other oral diabetic medications.
Thiazolidinediones
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), also known as "glitazones," bind to PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ, a type of nuclear regulatory protein involved in transcription of genes regulating glucose and fat metabolism. These PPARs act on peroxisome proliferator responsive elements (PPRE). The PPREs influence insulin-sensitive genes, which enhance production of mRNAs of insulin-dependent enzymes. The final result is better use of glucose by the cells. These drugs also enhance PPAR-α activity and hence lead to a rise in HDL and some larger components of LDL.
Typical reductions in glycated hemoglobin (A1C) values are 1.5–2.0%. Some examples are:
- Rosiglitazone (Avandia): the European Medicines Agency recommended in September 2010 that it be suspended from the EU market due to elevated cardiovascular risks.
- Pioglitazone (Actos): remains on the market but has also been associated with increased cardiovascular risks.
- Troglitazone (Rezulin): used in 1990s, withdrawn due to hepatitis and liver damage risk.
Multiple retrospective studies have resulted in a concern about rosiglitazone's safety, although it is established that the group, as a whole, has beneficial effects on diabetes. The greatest concern is an increase in the number of severe cardiac events in patients taking it. The ADOPT study showed that initial therapy with drugs of this type may prevent the progression of disease, as did the DREAM trial. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE), which provides clinical practice guidelines for management of diabetes, retains thiazolidinediones as recommended first, second, or third line agents for type 2 diabetes mellitus, as of their 2019 executive summary, over sulfonylureas and α-glucosidase inhibitors. However, they are less preferred than GLP-1 agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors, especially in patients with cardiovascular disease (which liraglutide, empagliflozin, and canagliflozin are all FDA approved to treat).
Concerns about the safety of rosiglitazone arose when a retrospective meta-analysis was published in the New England Journal of Medicine. There have been a significant number of publications since then, and a Food and Drug Administration panel voted, with some controversy, 20:3 that available studies "supported a signal of harm", but voted 22:1 to keep the drug on the market. The meta-analysis was not supported by an interim analysis of the trial designed to evaluate the issue, and several other reports have failed to conclude the controversy. This weak evidence for adverse effects has reduced the use of rosiglitazone, despite its important and sustained effects on glycemic control. Safety studies are continuing.
In contrast, at least one large prospective study, PROactive 05, has shown that pioglitazone may decrease the overall incidence of cardiac events in people with type 2 diabetes who have already had a heart attack.
Lyn kinase activators
The LYN kinase activator tolimidone has been reported to potentiate insulin signaling in a manner that is distinct from the glitazones. The compound has demonstrated positive results in a Phase 2a clinical study involving 130 diabetic subjects.
Secretagogues
Secretagogues are drugs that increase output from a gland, in the case of insulin from the pancreas.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas were the first widely used oral anti-hyperglycemic medications. They are insulin secretagogues, triggering insulin release by inhibiting the KATP channel of the pancreatic beta cells. Eight types of these pills have been marketed in North America, but not all remain available. The "second-generation" drugs are now more commonly used. They are more effective than first-generation drugs and have fewer side-effects. All may cause weight gain.
Current clinical practice guidelines from the AACE rate sulfonylureas (as well as glinides) below all other classes of antidiabetic drugs in terms of suggested use as first, second, or third line agents - this includes bromocriptine, the bile acid sequestrant colesevelam, α-glucosidase inhibitors, TZDs (glitazones), and DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins). The low cost of most sulfonylureas, however, especially when considering their significant efficacy in blood glucose reduction, tends to keep them as a more feasible option in many patients - neither SGLT2 inhibitors nor GLP-1 agonists, the classes most favored by the AACE guidelines after metformin, are currently available as generics.
Sulfonylureas bind strongly to plasma proteins. Sulfonylureas are useful only in type 2 diabetes, as they work by stimulating endogenous release of insulin. They work best with patients over 40 years old who have had diabetes mellitus for under ten years. They cannot be used with type 1 diabetes, or diabetes of pregnancy. They can be safely used with metformin or glitazones. The primary side-effect is hypoglycemia, which appears to happen more commonly with sulfonylureas than with other treatments.
A Cochrane systematic review from 2011 showed that treatment with Sulphonylurea did not improve control of glucose levels more than insulin at 3 nor 12 months of treatment. This same review actually found evidence that treatment with Sulphonylurea could lead to earlier insulin dependence, with 30% of cases requiring insulin at 2 years. When studies measured fasting C-peptide, no intervention influenced its concentration, but insulin maintained concentration better compared to Sulphonylurea. Still, it is important to highlight that the studies available to be included in this review presented considerable flaws in quality and design.
Typical reductions in glycated hemoglobin (A1C) values for second-generation sulfonylureas are 1.0–2.0%.
- First-generation agents
- Second-generation agents
- glipizide
- glyburide or glibenclamide
- glimepiride
- gliclazide
- glyclopyramide
- gliquidone
Nonsulfonylurea secretagogues
Meglitinides
Meglitinides help the pancreas produce insulin and are often called "short-acting secretagogues." They act on the same potassium channels as sulfonylureas, but at a different binding site. By closing the potassium channels of the pancreatic beta cells, they open the calcium channels, thereby enhancing insulin secretion.
They are taken with or shortly before meals to boost the insulin response to each meal. If a meal is skipped, the medication is also skipped.
Typical reductions in glycated hemoglobin (A1C) values are 0.5–1.0%.
Adverse reactions include weight gain and hypoglycemia.
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are "diabetes pills" but not technically hypoglycemic agents because they do not have a direct effect on insulin secretion or sensitivity. These agents slow the digestion of starch in the small intestine, so that glucose from the starch of a meal enters the bloodstream more slowly, and can be matched more effectively by an impaired insulin response or sensitivity. These agents are effective by themselves only in the earliest stages of impaired glucose tolerance, but can be helpful in combination with other agents in type 2 diabetes.
Typical reductions in glycated hemoglobin (A1C) values are 0.5–1.0%.
These medications are rarely used in the United States because of the severity of their side-effects (flatulence and bloating). They are more commonly prescribed in Europe. They do have the potential to cause weight loss by lowering the amount of sugar metabolized.
Peptide analogs
Injectable incretin mimetics
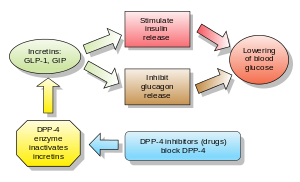
Incretins are insulin secretagogues. The two main candidate molecules that fulfill criteria for being an incretin are glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory peptide (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, GIP). Both GLP-1 and GIP are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
Injectable glucagon-like peptide analogs and agonists
Glucagon-like peptide (GLP) agonists bind to a membrane GLP receptor. As a consequence, insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells is increased. Endogenous GLP has a half-life of only a few minutes, thus an analogue of GLP would not be practical. As of 2019, the AACE lists GLP-1 agonists, along with SGLT2 inhibitors, as the most preferred anti-diabetic agents after metformin. Liraglutide in particular may be considered first-line in diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease, as it has received FDA approval for reduction of risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. In a 2011 Cochrane review, GLP-1 agonists showed approximately a 1% reduction in HbA1c when compared to placebo. GLP-1 agonists also show improvement of beta-cell function, but this effect does not last after treatment is stopped. Due to shorter duration of studies, this review did not allow for long-term positiver or negative effects to be assessed.
- Exenatide (also Exendin-4, marketed as Byetta) is the first GLP-1 agonist approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Exenatide is not an analogue of GLP but rather a GLP agonist. Exenatide has only 53% homology with GLP, which increases its resistance to degradation by DPP-4 and extends its half-life. A 2011 Cochrane review showed a HbA1c reduction of 0.20% more with Exenatide 2 mg compared to insulin glargine, exenatide 10 µg twice daily, sitagliptin and pioglitazone. Exenatide, together with liraglutide, led to greater weight loss than glucagon-like peptide analogues.
- Liraglutide, a once-daily human analogue (97% homology), has been developed by Novo Nordisk under the brand name Victoza. The product was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMEA) on July 3, 2009, and by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on January 25, 2010. A 2011 Cochrane review showed a HbA1c reduction of 0.24% more with liraglutide 1.8 mg compared to insulin glargine, 0.33% more than exenatide 10 µg twice daily, sitagliptin and rosiglitazone. Liraglutide, together with exenatide, led to greater weight loss than glucagon-like peptide analogues.
- Taspoglutide is presently in Phase III clinical trials with Hoffman-La Roche.
- Lixisenatide (Lyxumia) Sanofi Aventis
- Semaglutide (Ozempic) (oral version is Rybelsus)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity) - once weekly
- Albiglutide (Tanzeum) - once weekly
These agents may also cause a decrease in gastric motility, responsible for the common side-effect of nausea, which tends to subside with time.
Gastric inhibitory peptide analogs
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
GLP-1 analogs resulted in weight loss and had more gastrointestinal side-effects, while in general dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors were weight-neutral and increased risk for infection and headache, but both classes appear to present an alternative to other antidiabetic drugs. However, weight gain and/or hypoglycemia have been observed when dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors were used with sulfonylureas; effects on long-term health and morbidity rates are still unknown.
DPP-4 inhibitors increase blood concentration of the incretin GLP-1 by inhibiting its degradation by DPP-4.
Examples are:
- vildagliptin (Galvus) EU Approved 2008
- sitagliptin (Januvia) FDA approved Oct 2006
- saxagliptin (Onglyza) FDA Approved July 2009
- linagliptin (Tradjenta) FDA Approved May 2, 2011
- alogliptin
- septagliptin
- teneligliptin
- gemigliptin (Zemiglo)
DPP-4 inhibitors lowered hemoglobin A1C values by 0.74%, comparable to other antidiabetic drugs.
A result in one RCT comprising 206 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HgbA1c of 7.8%) receiving either 50 or 100 mg/d of sitagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.7% (combined result of both doses). A combined result of 5 RCTs enlisting a total of 279 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HbA1c of 8%) receiving 5 mg/d of saxagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.73%. A combined result of 5 RCTs enlisting a total of 238 patients aged 65 or older (mean baseline HbA1c of 8.6%) receiving 100 mg/d of vildagliptin was shown to reduce HbA1c by 1.2%. Another set of 6 combined RCTs involving alogliptin (approved by FDA in 2013) was shown to reduce HbA1c by 0.73% in 455 patients aged 65 or older who received 12.5 or 25 mg/d of the medication.
Injectable amylin analogues
Amylin agonist analogues slow gastric emptying and suppress glucagon. They have all the incretins actions except stimulation of insulin secretion. As of 2007, pramlintide is the only clinically available amylin analogue. Like insulin, it is administered by subcutaneous injection. The most frequent and severe adverse effect of pramlintide is nausea, which occurs mostly at the beginning of treatment and gradually reduces. Typical reductions in A1C values are 0.5–1.0%.
Glycosurics
SGLT-2 inhibitors block the re-uptake of glucose in the renal tubules, promoting loss of glucose in the urine. This causes both mild weight loss, and a mild reduction in blood sugar levels with little risk of hypoglycemia. Oral preparations may be available alone or in combination with other agents. Along with GLP-1 agonists, they are considered preferred second or third agents for type 2 diabetics sub-optimally controlled with metformin alone, according to most recent clinical practice guidelines. Because they are taken by mouth, rather than injected (like GLP-1 agonists), patients who are injection-averse may prefer these agents over the former. They may be considered first line in diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease, especially heart failure, as these medications have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization in patients with such comorbidities. Because they are not available as generic medications, however, cost may limit their feasibility for many patients. Furthermore, there has been growing evidence that the effectiveness and safety of this drug class could depend on genetic variability of the patients.
Examples include:
The side effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors are derived directly from their mechanism of action; these include an increased risk of: ketoacidosis, urinary tract infections, candidal vulvovaginitis, and hypoglycemia.
Comparison
The following table compares some common anti-diabetic agents, generalizing classes, although there may be substantial variation in individual drugs of each class. When the table makes a comparison such as "lower risk" or "more convenient" the comparison is with the other drugs on the table.
| Comparison of anti-diabetic medication | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug class | Mechanism of action | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Sulfonylureas (glyburide, glimepiride, glipizide) | Stimulating insulin release by pancreatic beta cells by inhibiting the KATP channel |
|
|
|
| Metformin | Acts on the liver to reduce gluconeogenesis and causes a decrease in insulin resistance via increasing AMPK signalling. |
|
|
|
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (acarbose, miglitol, voglibose) | Inhibit carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine by inhibiting enzymes that break down polysaccharides |
|
|
|
| Thiazolidinediones (Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone) | Reduce insulin resistance by activating PPAR-γ in fat and muscle |
|
|
|
| SGLT2 inhibitors | ||||
Generic
Many anti-diabetes drugs are available as generics. These include:
- Sulfonylureas – glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide
- Biguanides – metformin
- Thiazolidinediones (Tzd) – pioglitazone, Actos generic
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors – Acarbose
- Meglitinides – nateglinide
- Combination of sulfonylureas plus metformin – known by generic names of the two drugs
No generics are available for dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (Januvia, Onglyza), the glifozins, the incretins and various combinations.
Alternative Medicine
The effect of Ayurvedic treatments has been researched, however due to methodological flaws of studies it has not been possible to draw conclusion regarding efficacy of these treatments and there is insufficient evidence to recommend them.
Further reading
- Lebovitz, Harold E. (2004). Therapy For Diabetes Mellitus and Related Disorders (4th ed.). Alexandria, VA: American Diabetes Association. ISBN 978-1-58040-187-6.
- Adams, Michael Ian; Holland, Norman Norwood (2003). Core Concepts in Pharmacology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-089329-1.
|
Major chemical drug groups – based upon the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System
| |
|---|---|
|
gastrointestinal tract / metabolism (A) |
|
|
blood and blood forming organs (B) |
|
|
cardiovascular system (C) |
|
| skin (D) | |
|
genitourinary system (G) |
|
|
endocrine system (H) |
|
|
infections and infestations (J, P, QI) |
|
|
malignant disease (L01–L02) |
|
|
immune disease (L03–L04) |
|
|
muscles, bones, and joints (M) |
|
|
brain and nervous system (N) |
|
|
respiratory system (R) |
|
| sensory organs (S) | |
| other ATC (V) | |
| Types | |
|---|---|
| Blood tests | |
| Management | |
| Complications |
|
| Advocacy & Organizations |
|
| Other | |