
Apixaban
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eliquis, others |
| Other names | BMS-562247-01 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a613032 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~50% |
| Protein binding | ~87% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP1A2 and others |
| Elimination half-life | 9–14 h |
| Excretion | Bile duct (75%), kidney (25%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.167.332 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
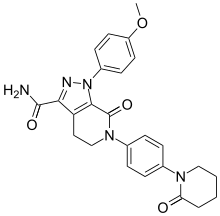
| Formula | C25H25N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 459.506 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Apixaban, sold under the brand name Eliquis, is an anticoagulant medication used to treat and prevent blood clots and to prevent stroke in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation through directly inhibiting factor Xa. Specifically, it is used to prevent blood clots following hip or knee replacement and in those with a history of prior clots. It is used as an alternative to warfarin and does not require monitoring by blood tests or dietary restrictions. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include bleeding and nausea. Other side effects may include bleeding around the spine and allergic reactions. Use is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Use appears to be relatively safe in those with mild kidney problems. Compared to warfarin it has fewer interactions with other medications. It is a direct factor Xa inhibitor.
In 2007, Pfizer and Bristol-Myers Squibb began development of apixaban as an anticoagulant. Apixaban was approved for medical use in the European Union in May 2011, and in the United States in December 2012. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, it was the 48th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States with more than 13 million prescriptions. It is available as a generic medication.
Medical uses
Apixaban is indicated for the following:
- To lower the risk of stroke and embolism in people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prevention. DVTs may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE) in knee or hip replacement surgery patients.
- Treatment of both DVT and PE.
- To reduce the risk of recurring DVT and PE after initial therapy.
In the EU, apixaban is indicated for the prevention of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in adults who have undergone elective hip or knee replacement surgery, the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adults with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) with one or more risk factors, for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in adults, and for the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults.
Atrial fibrillation
Apixaban is recommended by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in people with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and at least one of the following risk factors: prior stroke or transient ischemic attack, age 75 years or older, diabetes mellitus, or symptomatic heart failure.
Apixaban and other anticoagulants (dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban) appear equally effective as warfarin in preventing non-hemorrhagic stroke in people with atrial fibrillation and are associated with lower risk of intracranial bleeding.
While apixaban may be used in people with severely decreased kidney function and those on hemodialysis it has not been studied in these groups.
Side effects
Bleeding
Apixaban can increase the risk of bleeding which may be serious and potentially fatal. Concurrent use with other medications that affect blood clotting can further increase this risk. This includes medications such as other anticoagulants, heparin, aspirin, antiplatelet medications, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Andexanet alfa is a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved antidote for apixaban in people with uncontrolled and life-threatening bleeding events.
Spinal puncture
Following spinal anesthesia or puncture, people who are being treated with anti-thrombotic agents are at higher risk for developing a hematoma, which causes long-term or permanent paralysis. The risk of this may be increased by using epidural or intrathecal catheters after a surgical operation or from the concurrent use of medicinal agents that affect hemostasis.
Mechanism of action
Apixaban is a highly selective, orally bioavailable, and reversible direct inhibitor of free and clot-bound factor Xa. Factor Xa catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, the final enzyme in the coagulation cascade that is responsible for fibrin clot formation. Apixaban has no direct effect on platelet aggregation, but by inhibiting factor Xa, it indirectly decreases clot formation induced by thrombin.
History
Apixaban was approved for medical use in the European Union in May 2011.
A new drug application (NDA) for the approval of apixaban was submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) by Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) and Pfizer jointly after conclusion of the ARISTOTLE clinical trial in 2011. Apixaban was approved for the prevention of stroke in people with atrial fibrillation on 28 December 2012. On 13 March 2014, it was approved for the additional indication of preventing deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in people who have recently undergone knee or hip replacement. On 21 August 2014, the FDA approved apixaban for the additional indication of the treatment of recurring deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. During its development the drug was known as BMS-562247-01. By late 2019, sales of the product by BMS accounted for thirty-percent of their quarterly revenue.
In December 2019, the US FDA approved a generic version of apixaban produced jointly by Mylan and Micro Labs. BMS and Pfizer worked quickly to block generics from being created, and in August 2020, they won a patent infringement lawsuit against Sigmapharm, Sunshine Lake, and Unichem, after previously settling patent cases against 25 other companies. In September 2021, a Federal Circuit Court upheld the ruling. The result is that apixaban generics will most likely not be available in the United States until at least 2026, but possibly 2031.
In mid-2022, the Canadian generic drug company, Apotex Inc., obtained approval for marketing of apixaban.
Research
Use in the COVID-19 pandemic
The UK National Health Service (NHS) is testing the use of apixaban in treating post-recovery COVID-19.
External links
- "Apixaban". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Antiplatelet drugs |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Thrombolytic drugs/ fibrinolytics |
|||||||||||||||
| Non-medicinal | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||