Apolipoprotein H
β2-glycoprotein 1, also known as beta-2 glycoprotein 1 and Apolipoprotein H (Apo-H), is a 38 kDa multifunctional plasma protein that in humans is encoded by the APOH gene. One of its functions is to bind cardiolipin. When bound, the structure of cardiolipin and β2-GP1 both undergo large changes in structure. Within the structure of Apo-H is a stretch of positively charged amino acids (protein sequence positions 282-287), Lys-Asn-Lys-Glu-Lys-Lys, are involved in phospholipid binding (see image on right).
β2-GP1 has a complex involvement in agglutination. It appears to alter adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-mediated agglutination of platelets. Normally, β2-GP1 assumes an anticoagulation activity in serum (by inhibiting coagulation factors); however, changes in blood factors can result in a reversal of that activity.
Although previously referred to as apolipoprotein H, it is not present in appreciable quantities in the lipoprotein fractions, so ApoH is therefore thought to be a misnomer.
Inhibitory activities
β2-GP1 appears to completely inhibit serotonin release by the platelets and prevents subsequent waves of the ADP-induced aggregation. The activity of β2-GP1 appears to involve the binding of agglutinating, negatively charged compounds, and inhibits agglutination by the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. β2-GP1 causes a reduction of the prothrombinase binding sites on platelets and reduces the activation caused by collagen when thrombin is present at physiological serum concentrations of β2-GP1 suggesting a regulatory role of β2-GP1 in coagulation.
β2-GP1 also inhibits the generation of factor Xa in the presence of platelets. β2-GP1 also inhibits that activation of factor XIIa.
In addition, β2-GP1 inhibits the activation of protein C blocking its activity on phosphatidylserine:phosphatidylcholine vesicles however once protein C is activated, Apo-H fails to inhibit activity. Since protein C is involved in factor Va degradation Apo-H indirectly inhibits the degradation of factor Va. This inhibitory activity is diminished by adding phospholipids suggesting the Apo-H inhibition of protein C is phospholipid competitive. This indicates that under certain conditions Apo-H takes on procoagulation properties.
Pathology
Anti-β2-GP1 antibodies are found in both infectious and some systemic autoimmune diseases (eg. systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)). Positivity for anti-cardiolipin antibodies in diagnostic tests for autoimmune antiphospholipid syndrome requires the presence of β2-GP1in the cardiolipin extract. Anti-β2-GP1 antibodies are strongly associated with thrombotic forms of lupus.
Sushi 2 protein domain
| Sushi_2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
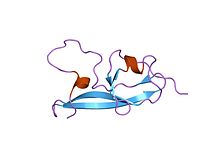 NMR structure of the fifth domain of human beta-2 glycoprotein 1
| |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Sushi_2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09014 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015104 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the protein domain Sushi 2 is also known as the fifth protein domain of beta-2 glycoprotein 1 (β2-GP1). This protein domain is only found in eukaryotes. The first four domains found in Apolipoprotein H resemble each other, however the fifth one appears to be different.
Structure
This protein domain is composed of four well-defined anti-parallel beta-strands and two short alpha-helices, as well as a long highly flexible loop. Additionally, the fifth protein domain appears to resemble the other four in Apolipoprotein with the exception of three internal disulfide bonds and an extra C-terminal loop.
Function
Its exact function remains to be fully elucidated; however it is known to play an important role in the binding of β2-GP1 to negatively charged compounds and subsequent capture for binding of anti-β2-GP1 antibodies. Development of antibodies against β2-GP1 can lead to Antiphospholipid syndrome which often leads to pregnancy complications.
External links
- Apolipoprotein+H at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Apolipoprotein H and Applied Research
- Human APOH genome location and APOH gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Apolipoprotein H (B2G1)
|
Lipids: lipoprotein particle metabolism
| |
|---|---|
| Lipoprotein particle classes and subclasses |
|
| Apolipoproteins | |
| Extracellular enzymes | |
| Lipid transfer proteins | |
| Cell surface receptors | |
| ATP-binding cassette transporter | |
| Mucoproteins |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteoglycans |
|
||||||||||
| Other |
|
||||||||||