
Argon plasma coagulation
| Argon plasma coagulation | |
|---|---|
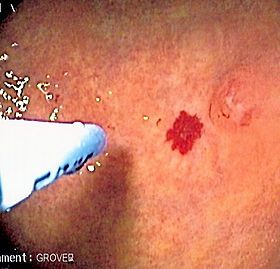
Argon plasma coagulation administered via probe through the colonoscope at an angiodysplasia in the colon. The patient had multiple colonic angiodysplasiae in the setting of aortic stenosis.
| |
| Other names | APC |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
Argon plasma coagulation (APC) is a medical endoscopic procedure used to control bleeding from certain lesions in the gastrointestinal tract. It is administered during esophagogastroduodenoscopy or colonoscopy.
Medical use
APC involves the use of a jet of ionized argon gas (plasma) directed through a probe passed through the endoscope. The probe is placed at some distance from the bleeding lesion, and argon gas is emitted, then ionized by a high-voltage discharge (approx 6kV). High-frequency electric current is then conducted through the jet of gas, resulting in coagulation of the bleeding lesion. As no physical contact is made with the lesion, the procedure is safe if the bowel has been cleaned of colonic gases, and can be used to treat bleeding in parts of the gastrointestinal tract with thin walls, such as the cecum. The depth of coagulation is usually only a few millimetres.
APC is used to treat the following conditions:
- angiodysplasias, anywhere in the GI tract
- gastric antral vascular ectasia, or watermelon stomach
- colonic polyps after polypectomy
- radiation proctitis
- esophageal cancer
See also
Further reading
- Peng Y, Wang H, Feng J, Fang S, Zhang M, Wang F, Chang Y, Shi X, Zhao Q, Liu J (2018). "Efficacy and Safety of Argon Plasma Coagulation for Hemorrhagic Chronic Radiation Proctopathy: A Systematic Review". Gastroenterology Research and Practice. 2018: 3087603. doi:10.1155/2018/3087603. PMC 5845516. PMID 29681929.