Auer rod
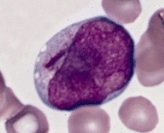
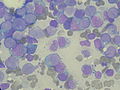
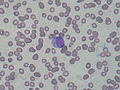
Auer rods (or Auer bodies) are large, crystalline cytoplasmic inclusion bodies sometimes observed in myeloid blast cells during acute myeloid leukemia, acute promyelocytic leukemia, high-grade myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders. Composed of fused lysosomes and rich in lysosomal enzymes, Auer rods are azurophilic and can resemble needles, commas, diamonds, rectangles, corkscrews, or (rarely) granules.
Eponym
Although Auer rods are named for American physiologist John Auer, they were first described in 1905 by Canadian physician Thomas McCrae, then at Johns Hopkins Hospital, as Auer himself acknowledged in his 1906 paper. Both McCrae and Auer mistakenly thought that the cells containing the rods were lymphoblasts.
Additional images
Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia with Auer rods in several blasts
External links
- Image at NIH/MedlinePlus
- Slides at wadsworth.org
- Image at University of Utah
|
Blood film findings
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red blood cells |
|
||||||||||
| White blood cells |
|
||||||||||