Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1
| Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 | |
|---|---|
| Other names |
Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis–ectodermal dystrophy/dysplasia (APECED),
Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1, Whitaker syndrome, Candidiasis-hypoparathyroidism–Addison's disease syndrome |
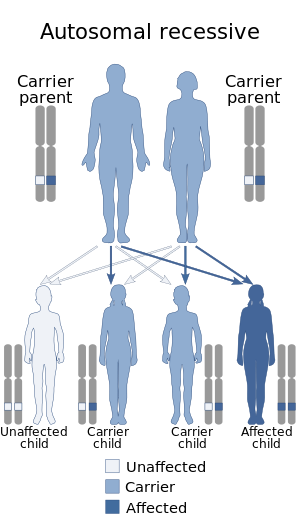 | |
| Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 is autosomal recessive | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, medical genetics |
| Symptoms | chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis |
| Causes | mutation in AIRE gene |
| Diagnostic method | CT scan, biopsy |
| Treatment | hormone therapy, antifungals, immunosuppression |
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1), is a subtype of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (autoimmune polyglandular syndrome). It causes the dysfunction of multiple endocrine glands due to autoimmunity. It is a genetic disorder, inherited in autosomal recessive fashion due to a defect in the AIRE gene (autoimmune regulator), which is located on chromosome 21 and normally confers immune tolerance.
Signs and symptoms
APS-1 tends to cause severe symptoms. These are present from early in life, usually around 3.5 years of age. Common symptoms of APS-1 include:
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.
- Hypoparathyroidism.
- Addison's disease.
- Ectodermal dystrophy (skin, dental enamel, and nails).
APS-1 may also cause:
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Hypogonadism.
- Vitiligo.
- Alopecia.
- Malabsorption.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Cataract.
- Cerebellar ataxia.
Cause
APS-1 is caused by a mutation in the AIRE gene, encoding a protein called autoimmune regulator. This is found on the 21q22.3 chromosome location, hence chromosome 21. The AIRE gene may be affected by any of at least 90 mutations. Mutations may be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
Different mutations are more common in different geographic regions. R139X is a common mutation in Sardinia. R257* is a common mutation in Finland.
Pathophysiology
APS-1 is due to problems with immune tolerance. APS-1 causes considerable reactions with both interferon omega and interferon alpha. There may also be a reaction against interleukin 22. This leads to damage to endocrine organs. Common problems include hypercalcaemia and nephrocalcinosis (due to a lack of calcitonin from the thyroid), and pituitary problems (such as growth hormone deficiency). Antibodies against NLRP5 may lead to hypoparathyroidism.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of APS-1 is based on a number of tests, including endoscopy, a CT scan, a biopsy (with histological testing), and serum endocrine autoantibody screening.
Treatment
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 treatment is based on the symptoms that are presented by the affected individual. Treatments may involve hormone therapy, systemic antifungal treatments, and immunosuppression.
History
APS-1 may also be known as autoimmunity endocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy / dysplasia (APECED), autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1, Whitaker syndrome, or candidiasis-hypoparathyroidism-Addison's disease syndrome.
See also
Further reading
- De Martino L, Capalbo D, Improda N, Lorello P, Ungaro C, Di Mase R, et al. (1 January 2016). "Novel Findings into AIRE Genetics and Functioning: Clinical Implications". Frontiers in Pediatrics. 4: 86. doi:10.3389/fped.2016.00086. PMC 4992815. PMID 27597936.
- Peterson P, Pitkänen J, Sillanpää N, Krohn K (March 2004). "Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy (APECED): a model disease to study molecular aspects of endocrine autoimmunity". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 135 (3): 348–57. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02384.x. PMC 1808970. PMID 15008965.
- Capalbo D, De Martino L, Giardino G, Di Mase R, Di Donato I, Parenti G, et al. (2012). "Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy: insights into genotype-phenotype correlation". International Journal of Endocrinology. 2012: 353250. doi:10.1155/2012/353250. PMC 3485503. PMID 23133448.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
Disorders involving multiple endocrine glands
| |
|---|---|
|
Type I/allergy/atopy (IgE) |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Type II/ADCC |
|
||||||||
|
Type III (Immune complex) |
|
||||||||
|
Type IV/cell-mediated (T cells) |
|
||||||||
| Unknown/ multiple |
|
||||||||
|
Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Basic domains |
|
||||||||
| (2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains |
|
||||||||
| (3) Helix-turn-helix domains |
|
||||||||
| (4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts |
|
||||||||
| (0) Other transcription factors |
|
||||||||
| Ungrouped | |||||||||
| Transcription coregulators |
|
||||||||