
Benazepril
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /bəˈnæzəprɪl/ |
| Trade names | Lotensin, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a692011 |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 96.7% |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 10-11 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney and bile duct |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
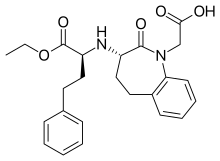
| Formula | C24H28N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 424.497 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Benazepril, sold under the brand name Lotensin among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth. Versions are available as the combinations benazepril/hydrochlorothiazide and benazepril/amlodipine.
Common side effects include feeling tired, dizziness, cough, and light-headedness with standing. Serious side effects may include kidney problems, low blood pressure, high blood potassium, and angioedema. Use in pregnancy may harm the baby, while use when breastfeeding may be safe. It is an ACE inhibitor and works by decreasing renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity.
Benazepril was patented in 1981 and came into medical use in 1990. It was created by the chemist Mahesh Desai. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 141st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 4 million prescriptions.
Structure Activity Relationship
Benazepril Hydrochloride's OCh2Ch3 group must be metabolized in order to inhibit the ACE Enzyme to form Benazeprilat, which is the active form of the molecule. The bulky cyclic structure is resistant to hydrolysis. A special note about the molecule is that the nitrogen within the ring makes the bulky cyclic structure especially harder to break down, and can account for the drug's PK profile, in which the duration of action is 24 hours.
Medical uses
It is useful for high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. Other reasonable initial options include angiotensin II receptor antagonists, calcium-channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics.
Side effects
The most common side effects patients experience are a headache or a chronic cough. The chronic cough develops in about 20% of patients treated, and those patients that experience it find it develops after a few months of use. Anaphylaxis, angioedema, and elevation of potassium levels are more serious side effects that can also occur.
Contraindications
Benazepril should be discontinued during pregnancy and in women planning to become pregnant, as it can harm the fetus.
Dosage forms
It is also available in combination with hydrochlorothiazide, under the trade name Lotensin HCT, and with amlodipine (Lotrel).
Veterinary use
Under the brand names Fortekor (Novartis) and VetACE (Jurox Animal Health), benazepril is used to treat congestive heart failure in dogs and chronic kidney failure in cats and dogs.
External links
- "Benazepril". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
|
ACE inhibitors ("-pril") |
|
|---|---|
|
AIIRAs ("-sartan") |
|
|
Renin inhibitors ("-kiren") |
|
| Dual ACE/NEP inhibitors | |
| Neprilysin inhibitors | |
| |