
- Autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- Bartter syndrome
- Benign familial neonatal seizures
- Calciumopathy
- Channelome
- Channelopathy
- Childhood absence epilepsy
- Congenital hyperinsulinism
- Congenital insensitivity to pain
- Congenital stationary night blindness
- Cystic fibrosis
- Dent's disease
- Episodic ataxia
- Erythromelalgia
- Familial atrial fibrillation
- Familial hemiplegic migraine
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- Generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus
- Hemiplegic migraine
- Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis
- Hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia
- Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Mucolipidosis type IV
- Myotonia congenita
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Paramyotonia congenita
- Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder
- Periodic paralysis
- Potassium-aggravated myotonia
- Pseudohypoaldosteronism
- Rolandic epilepsy
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type 6
- Sporadic hemiplegic migraine
- Template:Channelopathy
- Timothy syndrome
Channelopathy
| Channelopathy | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Sodium channel, implicated in channelopathies including Brugada syndrome, Long QT syndrome, Dravet syndrome, Paramyotonia congenita | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics, Neuromuscular medicine, Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Dependent on type. Include: Syncope, muscle weakness, seizures, breathlessness |
| Complications | Dependent on type. Include: Sudden death |
| Causes | Genetic variants |
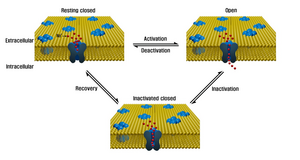
Channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by the dysfunction of ion channel subunits or their interacting proteins. These diseases can be inherited or acquired by other disorders, drugs, or toxins. Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, which impair channel function, are the most common cause of channelopathies. There are more than 400 genes that encode ion channels, found in all human cell types and are involved in almost all physiological processes. Each type of channel is a multimeric complex of subunits encoded by a number of genes. Depending where the mutation occurs it may affect the gating, conductance, ion selectivity, or signal transduction of the channel.
Channelopathies can be categorized based on the organ system which they are associated with. In the cardiovascular system, the electrical impulse needed for each heartbeat is made possible by the electrochemical gradient of each heart cell. Because the heartbeat is dependent on the proper movement of ions across the surface membrane, cardiac channelopathies make up a key group of heart diseases.Long QT syndrome, the most common form of cardiac channelopathy, is characterized by prolonged ventricular repolarization, predisposing to a high risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., torsade de pointes), syncope, and sudden cardiac death.
The channelopathies of human skeletal muscle include hyper- and hypokalemic (high and low potassium blood concentrations) periodic paralysis, myotonia congenita and paramyotonia congenita.
Channelopathies affecting synaptic function are a type of synaptopathy.
Causes
Genetic type
Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, which cause defects in channel function, are the most common cause of channelopathies.
Acquired type
Acquired channelopathies are caused by acquired disorders, drug use, toxins, etc.
Types
The types in the following table are commonly accepted. Channelopathies currently under research, like Kir4.1 potassium channel in multiple sclerosis, are not included.
Bibliography
External links
VIDEO Channel Surfing in Pediatrics by Carl E. Stafstrom, M.D., at the UW-Madison Health Sciences Learning Center.
- "The Weiss Lab". The Weiss Lab is investigating the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying human diseases caused by dysfunction of ion channels.
- The Channelopathy Foundation - Foundation for Ion Channel diseases
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation
- Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network
|
Neuromuscular- junction disease |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myopathy |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calcium channel |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium channel |
|
||||
| Potassium channel |
|
||||
| Chloride channel | |||||
| TRP channel | |||||
| Connexin | |||||
| Porin | |||||
See also: ion channels | |||||