
Comparison of phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids (/kəˈnæbənɔɪdzˌ ˈkænəbənɔɪdz/) are compounds found in the cannabis plant or synthetic compounds that can interact with the endocannabinoid system. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (Delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis.Cannabidiol (CBD) is another major constituent of some cannabis plants. At least 113 distinct cannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis.
This article gives comparative structures of some of the more common natural and synthetic cannabinoids, as well as showing structures of legally banned and sanctioned cannabinoids.
Structures
| Cannabinoid | 2D Structure | 3D Structure |
|---|---|---|
| CBC |

|

|
| CBCV |

|

|
| CBD |

|
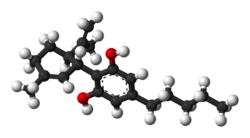
|
| CBDP |

|

|
| CBDV |

|

|
| CBE |

|

|
| CBG |

|

|
| CBGV |

|

|
| CBL |

|

|
| CBN |
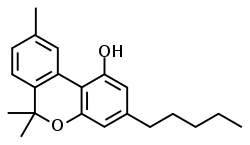
|
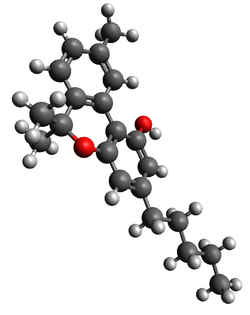
|
| CBND |

|

|
| CBTC |

|

|
| CBV |

|

|
| delta-8-THC |

|

|
| THC |

|
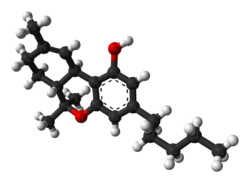
|
| THCC |

|

|
| THCH |

|

|
| THCP |

|

|
| THCV |

|

|
Legality
| Cannabinoid | Legal status |
|---|---|
| CBCA, CBC | Legal in most countries |
| CBCVA, CBCV | |
| CBDA, CBD | |
| CBDPA, CBDP | |
| CBDVA, CBDV | |
| CBEA, CBE | |
| CBGA, CBG | |
| CBGAM, CBGM | |
| CBGVA, CBGV | |
| CBLA, CBL | |
| CBNA, CBN | |
| CBNDA, CBND | |
| CBTA, CBT | |
| CBVA, CBV | |
| THCA, THC | UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances |
| THCCA, THCC | |
| THCH | Legal in most countries |
| THCPA, THCP | Legal in most countries |
| THCVA, THCV |
Thermal properties
Conversion temperatures
| Heated cannabinoid | Conversion temperature | Resulting cannabinoid |
|---|---|---|
| CBD | 250 °C (482 °F) to 300 °C (572 °F) | THC |
Decarboxylation temperatures
Upon heating, cannabinoid acids decarboxylate to give their psychoactive cannabinoid. For example, Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the main psychoactive compound found in cannabis and is responsible for the "high" feeling when consumed. However, cannabis does not naturally contain significant amounts of THC. Instead, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is found naturally in raw and live cannabis and is non-intoxicating. Over time, THCA slowly converts to THC through a process of decarboxylation over the course of roughly a year, but can be sped up with exposure to high temperatures. When heated under conditions of 110 °C, decarboxylation generally occurs in 30–45 minutes. The decarboxylated THCA (THC) is added to cannabis edibles, as THCA is not orally active. When consumed orally, the liver breaks down and metabolizes THC into the more potent 11-hydroxy-THC.
All cannabinoids listed here and their acids are found naturally in the plant to varying degrees.
| Decarboxylation reaction | Temperature |
|---|---|
| CBCA → CBC | |
| CBCVA → CBCV | |
| CBDA → CBD | |
| CBDPA → CBDP | |
| CBDVA → CBDV | |
| CBEA → CBE | |
| CBGA → CBG | |
| CBGAM → CBGM | |
| CBGVA → CBGV | |
| CBLA → CBL | |
| CBNA → CBN | |
| CBNDA → CBND | |
| CBTA → CBT | |
| CBVA → CBV | |
| THCA → THC | 110 °C (230 °F) |
| THCCA → THCC | |
| THCPA → THCP | |
| THCVA → THCV |
Vaporization temperatures
Dry-herb vaporizers can be used to inhale cannabis in its flower form. There are 483 identifiable chemical constituents known to exist in the cannabis plant, and at least 85 different cannabinoids have been isolated from the plant. The aromatic terpenoids begin to vaporize at 126.0 °C (258.8 °F), but the more bioactive tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and other cannabinoids also found in cannabis (often legally sold as cannabinoid isolates) like cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), do not vaporize until near their respective boiling points.
The cannabinoids listed here are found in the plant but only in trace amounts. However, they have also been extracted and sold as isolates online. Third party certification may help ensure buyers to avoid synthetic cannabinoids.
| Cannabinoid | Boiling point |
|---|---|
| CBC | 220 °C (428 °F) |
| CBCV | |
| CBD | 160 °C (320 °F)-180 °C (356 °F) |
| CBDP | |
| CBDV | |
| CBE | |
| CBG | |
| CBGM | |
| CBGV | |
| CBL | |
| CBN | 185 °C (365 °F) |
| CBT | |
| CBV | |
| delta-8-THC | 175 °C (347 °F)-178 °C (352 °F) |
| THC | 157 °C (315 °F) |
| THCC | |
| THCP | |
| THCV | <220 |
Structural scheduling
| Cannabigerol-type (CBG) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|

Cannabigerol |

Cannabigerol |
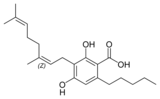
Cannabinerolic acid A |

Cannabigerovarin |
|
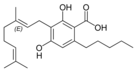
Cannabigerolic acid A |

Cannabigerolic acid A |

Cannabigerovarinic acid A |
||
| Cannabichromene-type (CBC) | ||||

(±)-Cannabichromene |

(±)-Cannabichromenic acid A |

(±)-Cannabivarichromene, (±)-Cannabichromevarin |

(±)-Cannabichromevarinic |
|
| Cannabidiol-type (CBD) | ||||
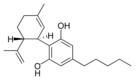
(−)-Cannabidiol |

Cannabidiol |

Cannabidiol-C4 |

(−)-Cannabidivarin |

Cannabidiorcol |
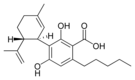
Cannabidiolic acid |

Cannabidivarinic acid |
|||
| Cannabinodiol-type (CBND) | ||||

Cannabinodiol |

Cannabinodivarin |
|||
| Tetrahydrocannabinol-type (THC) | ||||

Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol |

Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-C4 |

Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin |

Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol |
|

Δ9-Tetrahydro- |

Δ9-Tetrahydro- |

Δ9-Tetrahydro- |
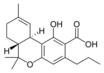
Δ9-Tetrahydro- |

Δ9-Tetrahydro- |

(−)-Δ8-trans-(6aR,10aR)- |

(−)-Δ8-trans-(6aR,10aR)- |

(−)-(6aS,10aR)-Δ9- |
||
| Cannabinol-type (CBN) | ||||
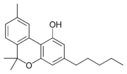
Cannabinol |

Cannabinol-C4 |

Cannabivarin |

Cannabinol-C2 |

Cannabiorcol |
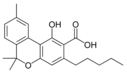
Cannabinolic acid A |

Cannabinol methyl ether |
|||
| Cannabitriol-type (CBT) | ||||

(−)-(9R,10R)-trans- |

(+)-(9S,10S)-Cannabitriol |

(±)-(9R,10S/9S,10R)- |

(−)-(9R,10R)-trans- |

(±)-(9R,10R/9S,10S)- |
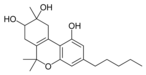
8,9-Dihydroxy-Δ6a(10a)- |

Cannabidiolic acid A |

(−)-(6aR,9S,10S,10aR)- |

(−)-6a,7,10a-Trihydroxy- |
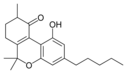
10-Oxo-Δ6a(10a)- |
| Cannabielsoin-type (CBE) | ||||

(5aS,6S,9R,9aR)- |
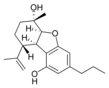
(5aS,6S,9R,9aR)- |
|||

(5aS,6S,9R,9aR)- |

(5aS,6S,9R,9aR)- |

(5aS,6S,9R,9aR)- |
||

Cannabiglendol-C3 |

Dehydrocannabifuran |

Cannabifuran |
||
| Isocannabinoids | ||||

(−)-Δ7-trans-(1R,3R,6R)- |

(±)-Δ7-1,2-cis- |

(−)-Δ7-trans-(1R,3R,6R)- |
||
| Cannabicyclol-type (CBL) | ||||
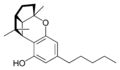
(±)-(1aS,3aR,8bR,8cR)- |

(±)-(1aS,3aR,8bR,8cR)- |

(±)-(1aS,3aR,8bR,8cR)- |
||
| Cannabicitran-type (CBT) | ||||

Cannabicitran |
||||
| Cannabichromanone-type (CBCN) | ||||

Cannabichromanone |

Cannabichromanone-C3 |

Cannabicoumaronone |
||