
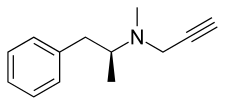
D-Deprenyl
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H17N |
| Molar mass | 187.286 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
|
| |
d-Deprenyl, also known as or dextro-N-propargyl-N-methylamphetamine, is an MAO-B inhibitor that metabolizes into d-amphetamine and d-methamphetamine and is therefore also a norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent. It is the opposite enantiomer of l-deprenyl (selegiline).
l-Deprenyl, also an MAO-B inhibitor, metabolizes to l-amphetamine and l-methamphetamine, which are both norepinephrine releasing agents. In contrast, d-deprenyl additionally has dopaminergic effects and has been found to be reinforcing in scientific research, whereas l-deprenyl is not known to have any appreciable psychological reinforcement.
In addition to its actions as an MAO-B inhibitor and NDRA, d-deprenyl has been found to bind with high affinity to the σ1 receptor (Ki = 79 nM) similarly to various other amphetamine derivatives. Its l-isomer, selegiline, binds with 3.5-fold lower affinity in comparison.
See also
| DRAs |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAs |
|
||||||||||||||
| SRAs |
|
||||||||||||||
| Others |
|
||||||||||||||
| σ1 |
|
|---|---|
| σ2 | |
| Unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
|
Catecholamines |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|