
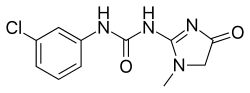
Fenobam
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
N-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N′-(1-methyl-4-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)urea | |
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.165.052 |
| MeSH | Fenobam |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H11ClN4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 266.684 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fenobam is an imidazole derivative developed by McNeil Laboratories in the late 1970s as a novel anxiolytic drug with an at-the-time-unidentified molecular target in the brain. Subsequently, it was determined that fenobam acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5, and it has been used as a lead compound for the development of a range of newer mGluR5 antagonists.
Fenobam has anxiolytic effects comparable to those of benzodiazepine drugs, but was never commercially marketed for the treatment of anxiety due to dose-limiting side effects such as amnesia and psychotomimetic symptoms. Following the discovery of its activity as a potent negative allosteric modulator of mGluR5, fenobam has been re-investigated for many applications, with its profile of combined antidepressant, anxiolytic, analgesic and anti-addictive effects potentially useful given the common co-morbidity of these symptoms. It has also shown promising initial results in the treatment of fragile X syndrome. It was developed by a team at McNeil Laboratories in the 1970s.
Chemistry
Fenobam is known to exist in five crystalline forms, all of them exhibiting a tautomeric structure with the proton attached to the five membered ring nitrogen.