
Ferrous tartrate
Подписчиков: 0, рейтинг: 0
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
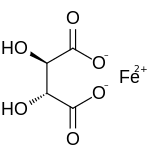
IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate; iron(2+)
| |
| Other names
Iron wine, Ferrous tartrate, Vinum Ferri
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.046 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4FeO6 | |
| Molar mass | 203.92 g/mol |
| Appearance | Reddish powder |
| Pharmacology | |
| B03AA08 (WHO) | |
|
|
| Oral | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| yes | |
| Legal status |
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ferrous tartrate is a chemical compound and the iron(II) salt of tartaric acid.
Historical uses
Ferrous tartrate has been used as a steel medicine. It was generally prescribed during the 19th and early 20th centuries. It is usually prepared by digesting for 30 days, 2 ounces (880 grains) tartarated iron in a pint of sherry. It can be difficult to prepare.
Historically, it was used as a stomachic and tonic, at a dose of 2 tbsp. It was also used to treat anemia, dose 1 to 2 fl. dr.
| Erythropoietins | |
|---|---|
| Iron supplements | |
|
Vitamin B12 and folic acid supplements |
|
| HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitors | |
| Other | |