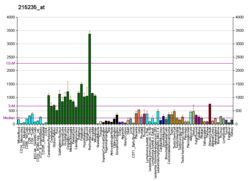
Fodrin
| SPTAN1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SPTAN1, EIEE5, NEAS, SPTA2, spectrin alpha, non-erythrocytic 1, DEE5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 182810 MGI: 98386 HomoloGene: 2353 GeneCards: SPTAN1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alpha II-spectrin, also known as Spectrin alpha chain, brain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTAN1 gene. Alpha II-spectrin is expressed in a variety of tissues, and is highly expressed in cardiac muscle at Z-disc structures, costameres and at the sarcolemma membrane. Mutations in alpha II-spectrin have been associated with early infantile epileptic encephalopathy-5, and alpha II-spectrin may be a valuable biomarker for Guillain–Barré syndrome and infantile congenital heart disease.
Structure
Alternate splicing of alpha II-spectrin has been documented and results in multiple transcript variants; specifically, cardiomyocytes have four identified alpha II-spectrin splice variants. As opposed to alpha I-spectrin that is principally found in erythrocytes, alpha II-spectrin is expressed in most tissues. In cardiac tissue, alpha II-spectrin is found in myocytes at Z-discs, costameres, and the sarcolemma membrane, and in cardiac fibroblasts along the surface of the cytoskeletal network. Alpha II-spectrin most commonly exists in a heterodimer with alpha II and beta II spectrin subunits; and dimers typically self-associate and heterotetramerize.
Function
The spectrins are a family of widely distributed cytoskeletal proteins which are involved in actin crosslinking, cell adhesion, intercellular communication and cell cycle regulation. Though a role in cardiac muscle is not well understood, it is likely that alpha II-spectrin is involved in organizing sub-sarcolemmal domains and stabilizing sarcolemmal membranes against the stresses associated with continuous cardiac contraction. Functional diversity of alpha II-spectrin is manifest through its four splice variants. First, a cardiac-specific, 21 amino acid sequence insert in the 21st spectrin repeat, termed alpha II-cardi+, was identified as an insert that modulates affinity of alpha II-spectrin for binding beta-spectrins and regulates myocyte growth and differentiation. Secondly, another insert of 20 amino acids in the 10th spectrin repeat, termed SH3i+, contains protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylation sites and modulates Ca2+-dependent cleavage of spectrin and protein-protein interaction properties. Thirdly, an insert of five amino acids in the fifteenth spectrin motif bears a highly antigenic epitope resembling an ankyrin-like p53 binding protein binding site. Fourthly, a six amino acid insert in the twenty-first spectrin motif with unknown function has been reported.
Alpha II-spectrin gene expression has been shown to be upregulated in cardiac fibroblasts in response to Angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling.
In animal models of disease and injury, alpha II-spectrin has been implicated in diverse functions. In a canine model of hypothermic circulatory arrest, alpha II-spectrin breakdown products have shown to be relevant markers of neurologic injury post-cardiac surgery.
Clinical significance
Mutations in SPTAN1 are the cause of early infantile epileptic encephalopathy-5.
Alpha II-spectrin has shown promising utility as a biomarker for brain necrosis and apoptosis in infants with congenital heart disease; breakdown products of alpha II-spectrin have been detected in the serum of neonates in the perioperative period and following open-heart surgery. Elevated protein expression of alpha II-spectrin has been detected in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with Guillain–Barré syndrome.
Interactions
SPTAN1 has been shown to interact with:
See also
Further reading
- Chow CW (1999). "Regulation and intracellular localization of the epithelial isoforms of the Na+/H+ exchangers NHE2 and NHE3". Clinical and Investigative Medicine. 22 (5): 195–206. PMID 10579058.
- Hayashi Y, Arakaki R, Ishimaru N (2003). "The role of caspase cascade on the development of primary Sjögren's syndrome". J. Med. Invest. 50 (1–2): 32–8. PMID 12630566.
- Bennett V (1979). "Immunoreactive forms of human erythrocyte ankyrin are present in diverse cells and tissues". Nature. 281 (5732): 597–9. Bibcode:1979Natur.281..597B. doi:10.1038/281597a0. PMID 492324. S2CID 263106.
- Frappier T, Stetzkowski-Marden F, Pradel LA (1991). "Interaction domains of neurofilament light chain and brain spectrin". Biochem. J. 275. ( Pt 2) (2): 521–7. doi:10.1042/bj2750521. PMC 1150082. PMID 1902666.
- Bennett AF, Hayes NV, Baines AJ (1991). "Site specificity in the interactions of synapsin 1 with tubulin". Biochem. J. 276. ( Pt 3) (3): 793–9. doi:10.1042/bj2760793. PMC 1151074. PMID 1905928.
- Davis LH, Bennett V (1990). "Mapping the binding sites of human erythrocyte ankyrin for the anion exchanger and spectrin". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (18): 10589–96. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)86987-3. PMID 2141335.
- Moon RT, McMahon AP (1990). "Generation of diversity in nonerythroid spectrins. Multiple polypeptides are predicted by sequence analysis of cDNAs encompassing the coding region of human nonerythroid alpha-spectrin". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (8): 4427–33. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)39582-1. PMID 2307671.
- Langley RC, Cohen CM (1986). "Association of spectrin with desmin intermediate filaments". J. Cell. Biochem. 30 (2): 101–9. doi:10.1002/jcb.240300202. PMID 2939097. S2CID 25080821.
- Cianci CD, Giorgi M, Morrow JS (1988). "Phosphorylation of ankyrin down-regulates its cooperative interaction with spectrin and protein 3". J. Cell. Biochem. 37 (3): 301–15. doi:10.1002/jcb.240370305. PMID 2970468. S2CID 42349239.
- Steiner JP, Bennett V (1988). "Ankyrin-independent membrane protein-binding sites for brain and erythrocyte spectrin". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (28): 14417–25. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)68236-5. PMID 2971657.
- Herrmann H, Wiche G (1987). "Plectin and IFAP-300K are homologous proteins binding to microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and to the 240-kilodalton subunit of spectrin". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (3): 1320–5. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)75789-5. PMID 3027087.
- McMahon AP, Giebelhaus DH, Champion JE, Bailes JA, Lacey S, Carritt B, Henchman SK, Moon RT (1987). "cDNA cloning, sequencing and chromosome mapping of a non-erythroid spectrin, human alpha-fodrin". Differentiation. 34 (1): 68–78. doi:10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00052.x. PMID 3038643.
- Frappier T, Regnouf F, Pradel LA (1988). "Binding of brain spectrin to the 70-kDa neurofilament subunit protein". Eur. J. Biochem. 169 (3): 651–7. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13657.x. PMID 3121319.
- McMahon AP, Moon RT (1988). "Structure and evolution of a non-erythroid spectrin, human alpha-fodrin". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 15 (5): 804–7. doi:10.1042/bst0150804. PMID 3691949.
- Lundberg S, Björk J, Löfvenberg L, Backman L (1995). "Cloning, expression and characterization of two putative calcium-binding sites in human non-erythroid alpha-spectrin". Eur. J. Biochem. 230 (2): 658–65. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.0658h.x. PMID 7607240.
- Hughes CA, Bennett V (1995). "Adducin: a physical model with implications for function in assembly of spectrin-actin complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (32): 18990–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.32.18990. PMID 7642559.
- Gregorio CC, Repasky EA, Fowler VM, Black JD (1994). "Dynamic properties of ankyrin in T lymphocytes: colocalization with spectrin and protein kinase C beta". J. Cell Biol. 125 (2): 345–58. doi:10.1083/jcb.125.2.345. PMC 2120020. PMID 8163551.
- Li X, Bennett V (1996). "Identification of the spectrin subunit and domains required for formation of spectrin/adducin/actin complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (26): 15695–702. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.26.15695. PMID 8663089.
- Stabach PR, Cianci CD, Glantz SB, Zhang Z, Morrow JS (1997). "Site-directed mutagenesis of alpha II spectrin at codon 1175 modulates its mu-calpain susceptibility". Biochemistry. 36 (1): 57–65. doi:10.1021/bi962034i. PMID 8993318.
|
PDB gallery
| |
|---|---|
|
Proteins of the cytoskeleton
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonhuman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: cytoskeletal defects | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||