
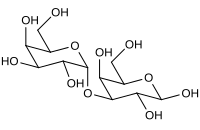
Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Systematic IUPAC name
3-O-α-D-Galactopyranosyl-D-galactopyranose | |
| Other names
Alpha-gal; 3-α-Galactobiose; Gal(α1-3)Gal; alpha-D-Gal-(1→3)-D-Gal
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.297 g·mol−1 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, commonly known as alpha gal and the Galili antigen, is a carbohydrate found in most mammalian cell membranes. It is not found in catarrhines, including humans, who have lost the GGTA1 gene. Their immune systems recognize it as a foreign body and produce xenoreactive immunoglobulin M antibodies, leading to organ rejection after transplantation.
Anti-alpha gal immunoglobulin G antibodies are some of the most common in humans. Regular stimulation from gut flora, typically initiated within the first six months of life, leads to an exceptionally high titre of around 1% of all circulating IgG. Alpha gal has also been suggested to play a role in an IgE-specific allergic response to some meats. While this allergic response is quite well documented, there is significant discrepancy between laboratory tests and clinical findings, indicating that much research must still be done on the alpha gal mechanism of action and related tests. Recent studies are showing increasing evidence that this allergy may be induced by the bite of the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) in North America and the castor bean tick (Ixodes ricinus) in Sweden.
A bacterial alpha-galactosidase that efficiently removes linear alpha-gal ends from molecules has been identified. It could be useful for xenotransplantation in the future. Human reaction to alpha-gal has beneficial uses as a vaccine adjuvant and for enhancing wound healing.
See also
External links
|
Types of carbohydrates
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||||||||||||||
| Geometry | |||||||||||||||
| Monosaccharides |
|
||||||||||||||
| Multiple |
|
||||||||||||||