Gaseous signaling molecules
Gaseous signaling molecules are gaseous molecules that are either synthesized internally (endogenously) in the organism, tissue or cell or are received by the organism, tissue or cell from outside (say, from the atmosphere or hydrosphere, as in the case of oxygen) and that are used to transmit chemical signals which induce certain physiological or biochemical changes in the organism, tissue or cell. The term is applied to, for example, oxygen, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, methane, hydrogen, ethylene, etc.
Select gaseous signaling molecules behave as neurotransmitters and are called gasotransmitters. These include nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
Historically, the study of gases and physiological effects was categorized under factitious airs.
The biological roles of each of the gaseous signaling molecules are outlined below.
Gasotransmitters
Gasotransmitters are a class of neurotransmitters. Only three gases are accepted to be classified as gasotransmitters including nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
Gaseous Signaling Molecules
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide, CO2, is one of the mediators of local autoregulation of blood supply. If its levels are high, the capillaries expand to allow a greater blood flow to that tissue.
Bicarbonate, HCO3−, ions are crucial for regulating blood pH. A person's breathing rate influences the level of CO2 in their blood. Breathing that is too slow or shallow causes respiratory acidosis, while breathing that is too rapid leads to hyperventilation, which can cause respiratory alkalosis.
Although the body requires oxygen for metabolism, low oxygen levels normally do not stimulate breathing. Rather, breathing is stimulated by higher carbon dioxide levels.
The respiratory centers try to maintain an arterial CO2 pressure of 40 mm Hg. With intentional hyperventilation, the CO2 content of arterial blood may be lowered to 10–20 mm Hg (the oxygen content of the blood is little affected), and the respiratory drive is diminished. This is why one can hold one's breath longer after hyperventilating than without hyperventilating. This carries the risk that unconsciousness may result before the need to breathe becomes overwhelming, which is why hyperventilation is particularly dangerous before free diving.
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, NO, is a key vertebrate biological messenger important in many physiological and pathological processes, acting, for instance, as a powerful vasodilator in humans (see Biological functions of nitric oxide).
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, N2O, in biological systems can be formed by an enzymatic or non-enzymatic reduction of nitric oxide. In vitro studies have shown that endogenous nitrous oxide can be formed by the reaction between nitric oxide and thiol. Some authors have shown that this process of NO reduction to N2O takes place in hepatocytes, specifically in their cytoplasm and mitochondria, and suggested that the N2O can possibly be produced in mammalian cells. It is well known that N2O is produced by some bacteria during process called denitrification.
In 1981, it was first suggested from clinical work with nitrous oxide (N2O) that a gas had a direct action at pharmacological receptors and thereby acted as a neurotransmitter. In vitro experiments confirmed these observations which were replicated at NIDA later.
Apart from its direct and indirect actions at opioid receptors, it was also shown that N2O inhibits NMDA receptor-mediated activity and ionic currents and diminishes NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Nitrous oxide also inhibits methionine synthase and slows the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, increases homocysteine concentration and decreases methionine concentration. This effect was shown in lymphocyte cell cultures and in human liver biopsy samples.
Nitrous oxide does not bind as a ligand to the heme and does not react with thiol-containing proteins. Nevertheless, studies have shown that nitrous oxide can reversibly and non-covalently "insert" itself into the inner structures of some heme-containing proteins such as hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochrome oxidase and alter their structure and function. The ability of nitrous oxide to alter the structure and function of these proteins was demonstrated by shifts in infrared spectra of cysteine thiols of hemoglobin and by partial and reversible inhibition of cytochrome oxidase.
Endogenous nitrous oxide can possibly play a role in modulating endogenous opioid and NMDA systerosclerosis, severe sepsis, severe malaria, or autoimmunity. Clinical tests involving humans have been performed, but the results have not yet been released.
Carbon suboxide
Carbon suboxide, C3O2, can be produced in small amounts in any biochemical process that normally produces carbon monoxide, CO, for example, during heme oxidation by heme oxygenase-1. It can also be formed from malonic acid. It has been shown that carbon suboxide in an organism can quickly polymerize into macrocyclic polycarbon structures with the common formula (C3O2)n (mostly (C3O2)6 and (C3O2)8), and that those macrocyclic compounds are potent inhibitors of Na+/K+-ATP-ase and Ca-dependent ATP-ase, and have digoxin-like physiological properties and natriuretic and antihypertensive actions. Those macrocyclic carbon suboxide polymer compounds are thought to be endogenous digoxin-like regulators of Na+/K+-ATP-ases and Ca-dependent ATP-ases, and endogenous natriuretics and antihypertensives. Other than that, some authors think also that those macrocyclic compounds of carbon suboxide can possibly diminish free radical formation and oxidative stress and play a role in endogenous anticancer protective mechanisms, for example in the retina.
Sulfur dioxide
The role of sulfur dioxide, SO2, in mammalian biology is not yet well understood. Sulfur dioxide blocks nerve signals from the pulmonary stretch receptors and abolishes the Hering–Breuer inflation reflex.
It was shown that endogenous sulfur dioxide plays a role in diminishing an experimental lung damage caused by oleic acid. Endogenous sulfur dioxide lowered lipid peroxidation, free radical formation, oxidative stress and inflammation during an experimental lung damage. Conversely, a successful lung damage caused a significant lowering of endogenous sulfur dioxide production, and an increase in lipid peroxidation, free radical formation, oxidative stress and inflammation. Moreover, blockade of an enzyme that produces endogenous SO2 significantly increased the amount of lung tissue damage in the experiment. Conversely, adding acetylcysteine or glutathione to the rat diet increased the amount of endogenous SO2 produced and decreased the lung damage, the free radical formation, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.
It is considered that endogenous sulfur dioxide plays a significant physiological role in regulating cardiac and blood vessel function, and aberrant or deficient sulfur dioxide metabolism can contribute to several different cardiovascular diseases, such as arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, pulmonary arterial hypertension, stenocardia.
It was shown that in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension due to congenital heart diseases the level of homocysteine is higher and the level of endogenous sulfur dioxide is lower than in normal control children. Moreover, these biochemical parameters strongly correlated to the severity of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Authors considered homocysteine to be one of useful biochemical markers of disease severity and sulfur dioxide metabolism to be one of potential therapeutic targets in those patients.
Endogenous sulfur dioxide also has been shown to lower the proliferation rate of endothelial smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, via lowering the MAPK activity and activating adenylyl cyclase and protein kinase A. Smooth muscle cell proliferation is one of important mechanisms of hypertensive remodeling of blood vessels and their stenosis, so it is an important pathogenetic mechanism in arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis.
Endogenous sulfur dioxide in low concentrations causes endothelium-dependent vasodilation. In higher concentrations it causes endothelium-independent vasodilation and has a negative inotropic effect on cardiac output function, thus effectively lowering blood pressure and myocardial oxygen consumption. The vasodilating effects of sulfur dioxide are mediated via ATP-dependent calcium channels and L-type ("dihydropyridine") calcium channels. Endogenous sulfur dioxide is also a potent antiinflammatory, antioxidant and cytoprotective agent. It lowers blood pressure and slows hypertensive remodeling of blood vessels, especially thickening of their intima. It also regulates lipid metabolism.
Endogenous sulfur dioxide also diminishes myocardial damage, caused by isoproterenol adrenergic hyperstimulation, and strengthens the myocardial antioxidant defense reserve.
Hydrogen cyanide
Some authors have shown that neurons can produce hydrogen cyanide, HCN, upon activation of their opioid receptors by endogenous or exogenous opioids. They have also shown that neuronal production of HCN activates NMDA receptors and plays a role in signal transduction between neuronal cells (neurotransmission). Moreover, increased endogenous neuronal HCN production under opioids was seemingly needed for adequate opioid analgesia, as analgesic action of opioids was attenuated by HCN scavengers. They considered endogenous HCN to be a neuromodulator.
It was also shown that, while stimulating muscarinic cholinergic receptors in cultured pheochromocytoma cells increases HCN production, in a living organism (in vivo) muscarinic cholinergic stimulation actually decreases HCN production.
Leukocytes generate HCN during phagocytosis.
The vasodilatation, caused by sodium nitroprusside, has been shown to be mediated not only by NO generation, but also by endogenous cyanide generation, which adds not only toxicity, but also some additional antihypertensive efficacy compared to nitroglycerine and other non-cyanogenic nitrates which do not cause blood cyanide levels to rise.
Ammonia
Ammonia, NH3, also plays a role in both normal and abnormal animal physiology. It is biosynthesised through normal amino acid metabolism, but is toxic in high concentrations. The liver converts ammonia to urea through a series of reactions known as the urea cycle. Liver dysfunction, such as that seen in cirrhosis, may lead to elevated amounts of ammonia in the blood (hyperammonemia). Likewise, defects in the enzymes responsible for the urea cycle, such as ornithine transcarbamylase, lead to hyperammonemia. Hyperammonemia contributes to the confusion and coma of hepatic encephalopathy, as well as the neurologic disease common in people with urea cycle defects and organic acidurias.
Ammonia is important for normal animal acid/base balance. After formation of ammonium from glutamine, α-ketoglutarate may be degraded to produce two molecules of bicarbonate, which are then available as buffers for dietary acids. Ammonium is excreted in the urine, resulting in net acid loss. Ammonia may itself diffuse across the renal tubules, combine with a hydrogen ion, and thus allow for further acid excretion.
Methane
Some authors have shown that endogenous methane, CH4, is produced not only by the intestinal flora and then absorbed into the blood, but also is produced - in small amounts - by eukaryotic cells (during process of lipid peroxidation). And they have also shown that the endogenous methane production rises during an experimental mitochondrial hypoxia, for example, sodium azide intoxication. They thought that methane could be one of intercellular signals of hypoxia and stress.
Other authors have shown that cellular methane production also rises during sepsis or bacterial endotoxemia, including an experimental imitation of endotoxemia by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration.
Some other researchers have shown that methane, produced by the intestinal flora, is not fully "biologically neutral" to the intestine, and it participates in the normal physiologic regulation of peristalsis. And its excess causes not only belching, flatulence and belly pain, but also functional constipation.
Ethylene

Ethylene, H2C=CH2, serves as a hormone in plants. It acts at trace levels throughout the life of the plant by stimulating or regulating the ripening of fruit, the opening of flowers, and the abscission (or shedding) of leaves. Commercial ripening rooms use "catalytic generators" to make ethylene gas from a liquid supply of ethanol. Typically, a gassing level of 500 to 2,000 ppm is used, for 24 to 48 hours. Care must be taken to control carbon dioxide levels in ripening rooms when gassing, as high temperature ripening (20 °C; 68 °F) has been seen to produce CO2 levels of 10% in 24 hours.
Ethylene has been used since the ancient Egyptians, who would gash figs in order to stimulate ripening (wounding stimulates ethylene production by plant tissues). The ancient Chinese would burn incense in closed rooms to enhance the ripening of pears. In 1864, it was discovered that gas leaks from street lights led to stunting of growth, twisting of plants, and abnormal thickening of stems. In 1901, a Russian scientist named Dimitry Neljubow showed that the active component was ethylene. Sarah Doubt discovered that ethylene stimulated abscission in 1917. It wasn't until 1934 that Gane reported that plants synthesize ethylene. In 1935, Crocker proposed that ethylene was the plant hormone responsible for fruit ripening as well as senescence of vegetative tissues.
Ethylene is produced from essentially all parts of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, fruits, tubers, and seeds. Ethylene production is regulated by a variety of developmental and environmental factors. During the life of the plant, ethylene production is induced during certain stages of growth such as germination, ripening of fruits, abscission of leaves, and senescence of flowers. Ethylene production can also be induced by a variety of external aspects such as mechanical wounding, environmental stresses, and certain chemicals including auxin and other regulators.
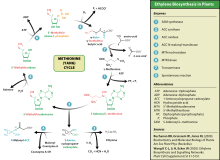
Ethylene is biosynthesized from the amino acid methionine to S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM, also called Adomet) by the enzyme Met Adenosyltransferase. SAM is then converted to 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) by the enzyme ACC synthase (ACS). The activity of ACS determines the rate of ethylene production, therefore regulation of this enzyme is key for the ethylene biosynthesis. The final step requires oxygen and involves the action of the enzyme ACC-oxidase (ACO), formerly known as the ethylene forming enzyme (EFE). Ethylene biosynthesis can be induced by endogenous or exogenous ethylene. ACC synthesis increases with high levels of auxins, especially indole acetic acid (IAA) and cytokinins.
Ethylene is perceived by a family of five transmembrane protein dimers such as the ETR1 protein in Arabidopsis. The gene encoding an ethylene receptor has been cloned in Arabidopsis thaliana and then in tomato. Ethylene receptors are encoded by multiple genes in the Arabidopsis and tomato genomes. Mutations in any of the gene family, which comprises five receptors in Arabidopsis and at least six in tomato, can lead to insensitivity to ethylene.DNA sequences for ethylene receptors have also been identified in many other plant species and an ethylene binding protein has even been identified in Cyanobacteria.
Environmental cues such as flooding, drought, chilling, wounding, and pathogen attack can induce ethylene formation in plants. In flooding, roots suffer from lack of oxygen, or anoxia, which leads to the synthesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC). ACC is transported upwards in the plant and then oxidized in leaves. The ethylene produced causes nastic movements (epinasty) of the leaves, perhaps helping the plant to lose water.
Ethylene in plant induces such responses:
- Seedling triple response, thickening and shortening of hypocotyl with pronounced apical hook.
- In pollination, when the pollen reaches the stigma, the precursor of the ethene, ACC, is secreted to the petal, the ACC releases ethylene with ACC oxidase.
- Stimulates leaf and flower senescence
- Stimulates senescence of mature xylem cells in preparation for plant use
- Induces leaf abscission
- Induces seed germination
- Induces root hair growth — increasing the efficiency of water and mineral absorption through rhizosheath formation
- Induces the growth of adventitious roots during flooding
- Stimulates survival under low-oxygen conditions (hypoxia) in submerged plant tissues
- Stimulates epinasty — leaf petiole grows out, leaf hangs down and curls into itself
- Stimulates fruit ripening
- Induces a climacteric rise in respiration in some fruit which causes a release of additional ethylene.
- Affects gravitropism
- Inhibits root growth in response to soil compaction, shade and flooding
- Stimulates nutational bending
- Inhibits stem growth and stimulates stem and cell broadening and lateral branch growth outside of seedling stage (see Hyponastic response)
- Interference with auxin transport (with high auxin concentrations)
- Inhibits shoot growth and stomatal closing except in some water plants or habitually flooded ones such as some rice varieties, where the opposite occurs (conserving CO
2 and O
2) - Induces flowering in pineapples
- Inhibits short day induced flower initiation in Pharbitus nil and Chrysanthemum morifolium
Small amounts of endogenous ethylene are also produced in mammals, including humans, due to lipid peroxidation. Some of endogenous ethylene is then oxidized to ethylene oxide, which is able to alkylate DNA and proteins, including hemoglobin (forming a specific adduct with its N-terminal valine, N-hydroxyethyl-valine). Endogenous ethylene oxide, just as like environmental (exogenous) one, can alkylate guanine in DNA, forming an adduct 7-(2-hydroxyethyl)-guanine, and this poses an intrinsic carcinogenic risk. It is also mutagenic.
External links
-
 Media related to Gaseous signaling molecules at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Gaseous signaling molecules at Wikimedia Commons