
HIDEA syndrome
| HIDEA syndrome | |
|---|---|
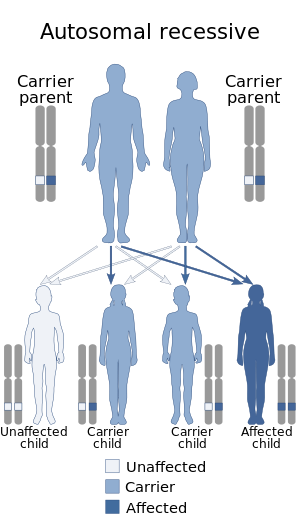 | |
| HIDEA syndrome is inherited via an autosomal recessive manner. | |
| Causes | Mutation in P4HTM gene |
HIDEA syndrome is a syndrome characterised by hypotonia, hypoventilation, intellectual disability, dysautonomia, epilepsy, and eye abnormalities. It is caused by the mutation of the P4HTM gene on chromosome 3.
Presentation
This syndrome causes intellectual disability and affects the eyes, musculoskeletal system, and face.
Eyes
- Difficulty fixing the eyes on an object
Face
Facial features gradually become coarser during childhood.
Musculoskeletal system
- Hypotonia
- Planovalgus
- Contractures in elbow joints
- Interphalangeal joint hypermobility
Other associated features include hypoventilation, obstructive and central sleep apnea and dysautonomia.
Genetics
This condition is caused by mutations in the Prolyl 4-hydroxylase, transmembrane (P4HTM) gene. This gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 3 (3p21.3).
The inheritance of this condition is autosomal recessive.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis may be suspected on clinical grounds.
It is made by sequencing the P4HTM gene.
Management
There is presently no curative treatment. Management is supportive.
Epidemiology
The prevalence is not known but this is considered to be a rare disease. Only 12 patients have been reported to date.
History
This condition was first described in 2014. The causative mutation was discovered in 2019.