Histopathology of dermatitis can be performed in uncertain cases of inflammatory skin condition that remain uncertain after history and physical examination.
Sampling
Generally a skin biopsy:
- For punch biopsies, a size of 4 mm is preferred for most inflammatory dermatoses.
- Panniculitis or cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: 6 mm punch biopsy or skin excision.
A superficial or shave biopsy is regarded as insufficient.
Fixation
Staining
Generally 3 sections for H&E staining and one section with periodic acid Schiff (PAS)
- If suspected bacterial and fungal microorganisms, consider Gram stain and Gomori methenamine silver stain.
Microscopic evaluation
One approach is to classify into mainly either of the following, primarily based on depth of involvement:
- Epidermis, papillary dermis, and superficial vascular plexus:
-
- Vesiculobullous lesions
- Pustular dermatosis
- Non vesicullobullous, non-pustular
-
- With epidermal changes
- Without epidermal changes. These characteristically have a superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate, and can be classified by type of cell infiltrate:
- Lymphocytic (most common)
- Lymphoeosinophilic
- Lymphoplasmacytic
- Mast cell
- Lymphohistiocytic
- Neutrophilic
Continue in corresponding section:
Non vesicullobullous, non-pustular lesions with epidermal changes
Spongiotic dermatitis
It is characterized by epithelial intercellular edema.
|
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Acute |
Subacute |
Chronic
|
| Generally/Not otherwise specified |
Typical findings:
- Variable degree of epidermal spongiosis and vesicle formation, filled with proteinaceous fluid containing lymphocytes and histiocytes.
- Usually superficial dermal edema with perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate, with exocytosis.
- No acanthosis or parakeratosis.
|
Typical findings:
- Mild to moderate spongiosis and exocytosis of inflammatory cells
- Irregular acanthosis and parakeratosis.
- Superficial dermal perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate
- Swelling of endothelial cells
- Papillary dermal edema are present
|
Typical findings:
- The spongiosis is mild to absent
- Pronounced irregular acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and parakeratosis
- Minimal dermal inflammation and exocytosis of inflammatory cells are present.
- Possibly fibrosis of papillary dermis
PAS stain is essential to exclude fungal infection.
|
 Subacute Subacute
|
|
| Allergic/contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis
|
As above. Eosinophils may be present in the dermis and epidermis (eosinophilic spongiosis). |
|
|
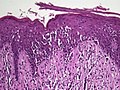
 Allergic dermatitis Allergic dermatitis
|
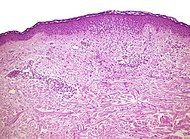
 Atopic dermatitis Atopic dermatitis
|
| Seborrheic dermatitis
|
Typical findings:
- Focal, usually mild, spongiosis with overlying scale crust, with a few neutrophils
- The crust is often centered on a follicle
- The papillary dermis is generally mildly edematous
- Dilated blood vessels in the superficial vascular plexus
- Mild superficial perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes, histiocytes and occasional neutrophils. There is some exocytosis of inflammatory cells but not as prominent as in nummular dermatitis
|
Typical findings:
- Psoriasiform hyperplasia, initially slight, with mild spongiosis
- Usually numerous yeast-like organisms in the surface keratin
- Same changes as seen in acute stage.
|
Typical findings:
- More pronounced psoriasiform hyperplasia
- Only minimal spongiosis
- Presence of scaling crusts in a folliculocentric distribution, distinguishes from psoriasis.
|
|

|
In addition to above, an unspecific spongiotic dermatitis can be consistent with nummular dermatitis, dyshidrotic dermatitis, Id reaction, dermatophytosis, miliaria, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and pityriasis rosea.
Interface dermatitis
These are sorted into either:
- Interface dermatitis with vacuolar change
- Interface dermatitis with lichenoid inflammation
Interface dermatitis with vacuolar change
Causes of vacuolar interface dermatitis
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Generally/Not otherwise specified
|
Typical findings, called "vacuolar interface dermatitis":
- Mild inflammatory cell infiltrate along the dermoepidermal junction (black arrow in image)
- Vacuolization within the basal keratinocytes (white arrow in image)
- Often necrotic, predominantly basal, individual keratinocytes, manifesting as colloid or Civatte bodies
|

|
|
| Acute graft-versus-host-disease
|
- Vacuolar alteration of various severity, from focal or diffuse vacuolation of the basal keratinocytes (grade I), to separation at the dermoepidermal junction (grade III)
- Involvement of the hair follicle
- Rarely eosinophils
|
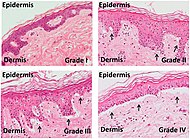
|
|
| Allergic drug reaction
|
- Rarely involvement of hair follicles.
- Frequently eosinophils
|

|
|
|
Lichen sclerosus
|
Hyperkeratosis, atrophic epidermis, sclerosis of dermis and dermal lymphocytes. |

|
| Erythema multiforme
|
|
|
|
|
| Lupus erythematosis
|
Typical findings in systemic lupus erythematosus:
- Fibrinoid necrosis at the dermoepidermal junction
- Liquefactive degeneration and atrophy of the epidermis
- Mucin deposition in the reticular dermis
- Edema, small hemorrhages
- Mild and mainly lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper dermis
- Fibrinoid material in the dermis around capillary blood vessels, on collagen and in the interstitium
- In non-bullous cases, perivascular and interstitial neutrophils are sometimes present in the upper dermis, with damage to blood vessels
|

|

|
An interface dermatitis with vacuolar alteration, not otherwise specified, may be caused by viral exanthems, phototoxic dermatitis, acute radiation dermatitis, erythema dyschromicum perstans, lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis.
Interface dermatitis with lichenoid inflammation
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Generally/Not otherwise specified
|
Typical findings:
- In the papillary dermis: a confluent, band-like, dense inflammation of mainly small lymphocytes and a few histiocytes, along or hugging the dermoepidermal junction.
- Often vacuolar degeneration of basal keratinocytes and apoptotic bodies (colloid or Civatte bodies).
|
|
|
| Lichen planus
|
Irregular epidermal hyperplasia with a jagged “sawtooth” appearance, compact hyperkeratosis or orthokeratosis, foci of wedge-shaped hypergranulosis, basilar vacuolar degeneration, slight spongiosis in the spinous layer, and squamatization. The dermal papillae between the elongated rete ridges are frequently dome shaped. Necrotic keratinocytes can be observed in the basal layer of the epidermis and at the dermal-epidermal junction. Eosinophilic remnants of anucleate apoptotic basal cells may also be found in the dermis and are referred to as “colloid or civatte bodies”. Whickham striae are usually seen in the areas of hypergranulosis. Vacuolar degeneration at the basal layer may be noted leading to focal subepidermal clefts (Max Joseph spaces). Squamatization occurs as a result of maturation and flattening of cells in the basal layer. It happens in areas of marked hypergranulosis with prominence of the sawtooth pattern of rete ridges. Wedge-shaped hypergranulosis can occur in the eccrine ducts (acrosyringia) or hair follicles (acrotrichia). In the hypertrophic subtype, the associated hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, hypergranulosis, papillomatosis, acanthosis, and hyperplasia markedly increased with thicker collagen bundles forming in the dermis. Moreover, the rete ridges are more elongated and rounded as opposed to the typical sawtooth pattern. In atrophic LP, loss of the rete ridges and dermal fibrosis is prominent. In vesiculobullous LP, the disease progression is quicker. Hence, some of the distinctive features such as hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, or dense lymphocytic dermal-epidermal infiltrate may not be present. LP lesion may resolve with residual hyperpigmentation caused by a persistent increase in the number of melanophages in the papillary dermis. |
 |

|
| Lichenoid drug reaction
|
Can virtually be indistinguishable from cutaneous LP both clinically and histopathologically.
- Typically, lesions have a photodistribution in the absence of oral mucosal involvement.
- Characteristically parakeratosis, a dermal eosinophilic infiltrate, and a perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate affecting the reticular dermis.
- Epidermal changes are less common in lichenoid drug eruptions when compared to classic lichen planus. However, a higher concentration of necrotic keratinocyte and eosinophils in the infiltrate can be helpful in distinguishing lichenoid drug reaction from cutaneous lichen planus. A lengthy interval between the commencement of drug therapy and the onset of lesions does not exclude a diagnosis of lichenoid drug reaction. Resolution of the lesions often occurs within weeks to months after discontinuation of the offending drug.
|
 |
|
| Lichen nitidus
|
- Localized granulomatous lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in an expanded dermal papilla
- Thinning of overlying epidermis and downward extension of the rete ridges at the lateral margin of the infiltrate, resulting in a typical "claw clutching a ball" appearance.
|
 |

|
| Lichen amyloidosus
|
Presence of amyloid, possibly with direct immunofluorescence and Congo red staining. |
|
Interface dermatitis with lichenoid inflammation, not otherwise specified, can be caused by lichen planus-like keratosis, lichenoid actinic keratosis, lichenoid lupus erythematosus, lichenoid GVHD (chronic GVHD), pigmented purpuric dermatosis, pityriasis rosea, and pityriasis lichenoides chronica. Unusual conditions that can be associated with a lichenoid inflammatory cell infiltrate are HIV dermatitis, syphilis, mycosis fungoides, urticaria pigmentosa, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. In cases of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, it is important to exclude potentially harmful mimics such as a regressed melanocytic lesion or lichenoid pigmented actinic keratosis.
Psoriaform dermatitis
Examining multiple deeper levels is recommended if initial cuts do not correlate well with the clinical history.
Psoriaform dermatitis typically displays:
- Regular epidermal hyperplasia, elongation of the rete ridges, hyperkeratosis, and parakeratosis.
- Usually:A superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate
- Often: Thinning of epidermal cells overlying the tips of dermal papillae (suprapapillary plates), and dilated, tortuous blood vessels within these papillae
Further histopathologic diagnosis is performed by the following parameters:
Psoriasiform dermatitis
| Condition |
Hyperkeratosis |
Parakeratosis |
Acanthosis |
Suprapapillary plate |
Granular cell layer changes |
Spinous cell layer changes |
Basal cell layer changes |
Other distinctive feature |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
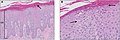
| Psoriasis
|
Present |
Diffuse |
Regular |
Thin |
Decreased or absent |
Increased mitoses; minimal spongiosis
Clubbed rete pegs |
Absent
|
|
 |

|
| Psoriasiform drug reaction
|
Present |
Focal |
Regular and irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Spongiosis; eosinophilic infiltrate |
Inflammatory cells; Civatte bodies |
|
| Chronic allergic/contact and atopic dermatitis
|
Present |
Focal; crust may be present |
Irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Spongiosis; eosinophilic infiltrate |
Absent |
|
| Fungal infection
|
Compact |
Focal; crust may be present |
Irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Occasional neutrophiles; |
Absent |
|
| Lichen simplex chronicus
|
Present |
Focal; thick crust |
Regular or irregular |
Thin or thick |
Thickened; hypergranulosis |
±minimal inflammatory infiltrate |
Absent |
|
| Scabies
|
Present |
Focal or diffuse |
Irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Inflammatory infiltrate; eosinophilic spongiosis |
Absent |
|
| Seborrheic dermatitis and HIV dermatitis
|
Present |
Focal |
Irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Spongiosis; lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltrate |
Absent |
|
| Pityriasis rubra pilaris
|
Compact |
Shoulder parakeratosis; alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis |
Regular or irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Spongiosis; lymphocytic infiltrate; rare acantholysis |
Occasional vacuolar change |
|
| Pityriasis rosea
|
Present |
Focal |
Irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Small foci of spongiosis; lymphocytic infiltrate |
Occasional necrotic keratinocytes |
|
| Syphilis
|
Present |
Focal |
Regular or irregular |
Normal or thick |
Normal |
Lymphocytes and neutrophils |
Interface change |
|
| Pityriasis lichenoides chronica
|
Present |
Caps of parakeratosis |
Irregular |
Normal |
Normal |
Mild spongiosis, lymphocytic infiltrate; necrotic keratinocytes |
Necrotic keratinocytes |
|
| Mycosis fungoides
|
Present |
Focal |
Regular or irregular |
Normal |
Normal |
Minimal or no spongiosis; ±Pautrier microabscess |
Atypical lymphoid cells lining the dermo–epidermal junction |
|
|
Non vesicullobullous, non-pustular lesions without epidermal changes
Lymphocytic infiltrate
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Urticaria, lymphocyte predominant
|
Perivascular location. Mast cells are relatively sparse, potentially demonstrated with special stains, preferably tryptase stain. Extravasated erythrocytes are present in about 50% of the cases. No vasculitis. |
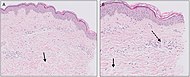 Dermal edema [solid arrows in (A,B)] and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils without signs of vasculitis (dashed arrow). Dermal edema [solid arrows in (A,B)] and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils without signs of vasculitis (dashed arrow). |
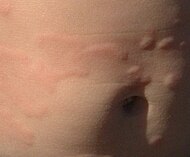
|
|
Fungal skin infection
|
Often visible fungus. Other signs depend on fungus species. |
|
|
| Pigmented purpuric dermatosis
|
- Perivascular infiltrate, but may involve the dermis, further away from blood vessels.
- Sometimes tendency for lichenoid infiltrate
- Mild vascular damage, mainly endothelial swelling and focal karyorrhectic debris.
- Red blood cell extravasation.
- The epidermis may be normal or may exhibit spongiosis, focal parakeratosis, exocytosis and/or vacuolar change.
|

|

|
| Erythema annulare centrifugum
|
- Mild spongiosis, parakeratosis and microvesiculation.
- "Coat-sleeve anomaly": tight lymphohistiocytic infiltrate surrounding superficial vessels
Deep lesions: Sharply demarcated perivascular mononuclear cell infiltrate in middle to deep dermis
|

|
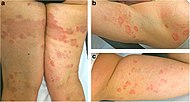
|
| Not otherwise specified |
A lesion with superficial lymphocytic infiltrate without additional histopathologic characteristics can be due to for example drug reactions and insect bites. |
Lymphoeosinophilic infiltrate
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
| Urticaria, lymphocyte predominant
|
Perivascular location. Mast cells are relatively sparse, potentially demonstrated with special stains, preferably tryptase stain. Extravasated erythrocytes are present in about 50% of the cases. No vasculitis. |
 Dermal edema (solid arrows) and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils (dashed arrow) Dermal edema (solid arrows) and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils (dashed arrow)
|

|
| Prevesicular stage of bullous pemphigoid
|
Image at right shows influx of inflammatory cells including eosinophils and neutrophils in the dermis (solid arrow) and blister cavity (dashed arrows), and deposition of fibrin (asterisks). However, the diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid consist of at least 2 positive results out of 3 criteria:
- Pruritus and/or predominant cutaneous blisters
- Linear IgG and/or C3c deposits (in an n- serrated pattern) by direct immunofluorescence microscopy (DIF)
- Positive epidermal side staining by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy on human salt-split skin (IIF SSS) on a serum sample.
|

|
|
| Not otherwise specified |
A lesion with superficial lymphoeosinophilic infiltrate without additional histopathologic characteristics can be due to for example drug reactions and insect bites. |
|
|
Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
Mastocytosis
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
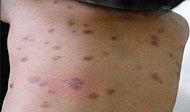
| Urticaria pigmentosa
|
Mastocytosis with a clinical picture of darkish spots.
|

|
|
| Not otherwise specified |
Includes the rare disease of primary mastocytosis. |
|
|
Lymphohistiocytic infiltrate
These include bacterial infections including leprosy, and the sample should therefore be stained with Ziel-Neelsen, acid fast stains, Gomori methenamine silver, PAS, and Fite stains. If negative, an unspecific lymphohistocytic dermatosis may be caused by drug reactions and viral infections.
Neutrophilic infiltrate
| Main conditions |
Characteristics |
Micrograph |
Photograph
|
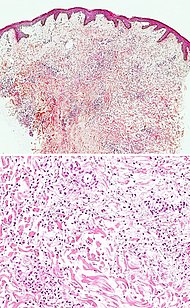
| Urticaria, neutrophil predominant
|
- Interstitial location
- Relatively dense infiltrate
- Mast cells are relatively sparse, potentially demonstrated with special stains, preferably tryptase stain.
- Extravasated erythrocytes are present in about 50% of the cases
- No vasculitis.
|
|
|
| Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
- Subepidermal vesicles and blisters associated with accumulation of neutrophils at the papillary tips.
- Sometimes presence of eosinophils, giving an appearance similar to bullous pemphigoid.
- The histopathology is unspecific in approximately 35%–40% of the cases, and direct immunofluorescence is needed, showing deposition of IgA in the papillary dermis in a granular or fibrillar pattern.
|

|

|
| Early linear IgA bullous dermatosis
|
Subepidermal blister formation. |

|

|
| Early febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet's syndrome)
|
Neutrophilic and lymphohistiocytic infiltrate and edema. |

|

|
| Connective tissue disorders
|
- Usually associated with epidermal changes. (Systemic lupus erythematosis pictured)
|

|

|
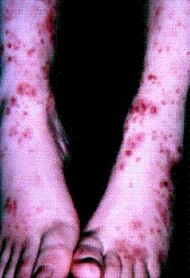
| Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis
|
- Neutrophils with nuclear dust (dashed arrows in image), with high affinity for postcapillary venules.
- Features of vascular injury: fibrinoid necrosis (asterisks) and erytrocyt extravasation (solid arrows)
|

|
|
Multinucleated giant cells

Suture granuloma, with multinucleated giant cells surrounding (grey) suture material.
-
Foreign bodies indicate a foreign body granuloma.
- Specific forms of multinucleated giant cells include the Touton giant cell, which contains a ring of nuclei surrounding a central homogeneous cytoplasm, with foamy cytoplasm surrounding the nuclei. The central cytoplasm (surrounded by the nuclei) may be both amphophilic and eosinophilic.
This article incorporates material from the article Dermatitis at Patholines, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.







 Dermal edema [solid arrows in (A,B)] and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils without signs of vasculitis (dashed arrow).
Dermal edema [solid arrows in (A,B)] and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils without signs of vasculitis (dashed arrow).




 Dermal edema (solid arrows) and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils (dashed arrow)
Dermal edema (solid arrows) and a sparse superficial predominantly perivascular and interstitial infiltrate of lymphocytes and eosinophils (dashed arrow)