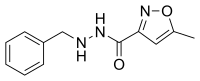
Isocarboxazid (Marplan, Marplon, Enerzer) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.
Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat mood and anxiety disorders. It has also been investigated in the treatment of schizophrenia,Parkinson's disease and other dementia-related disorders.
Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, melatonin, phenethylamine in the brain.
Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are used only rarely due to prominent food and drug interactions and have been largely superseded by newer antidepressants such as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The cause of the interactions is because MAOIs inhibit the metabolism of dietary amines (e.g., tyramine) and the monoamine neurotransmitters. In combination with other drugs that increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters such as the SSRIs, or with certain foods high in dietary amines such as aged cheeses, MAOIs can produce dangerous elevations of monoamine neurotransmitters resulting in potentially life-threatening syndromes such as hypertensive crisis and serotonin syndrome.
See also
|
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Non-selective |
|
|
MAOA-selective |
|
|
MAOB-selective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|