
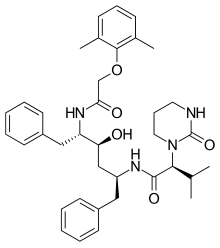
Lopinavir
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ABT-378 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a602015 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Protein binding | 98-99% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 6 hours |
| Excretion | Mostly fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.281.362 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C37H48N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 628.814 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir).
It was patented in 1995 and approved for medical use in 2000.
Side effects
Side effects, interactions, and contraindications have only been evaluated in the drug combination lopinavir/ritonavir.
Pharmacology
Lopinavir is highly bound to plasma proteins (98–99%).
Reports are contradictory regarding lopinavir penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Anecdotal reports state that lopinavir cannot be detected in the CSF; however, a study of paired CSF-plasma samples from 26 patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir found lopinavir CSF levels above the IC50 in 77% of samples.
Research
A 2014 study indicates that lopinavir is effective against the human papilloma virus (HPV). The study used the equivalent of one tablet twice a day applied topically to the cervices of women with high-grade and low-grade precancerous conditions. After three months of treatment, 82.6% of the women who had high-grade disease had normal cervical conditions, confirmed by smears and biopsies. Lopinavir has been shown to impair protein synthesis via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and eEF2 kinase (eEF2K) activation, a mechanism that is similar to the antiviral effect of protein phosphatase 1 inhibitors.
Lopinavir was found to inhibit MERS-CoV replication in the low-micromolar range in cell cultures. In 2020, lopinavir/ritonavir was found not to work in severe COVID-19. In this trial the medication was started typically around 13 days after the start of symptoms.
External links
- "Lopinavir". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.