Menthofuran
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
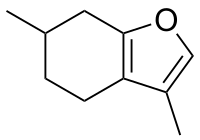
3,6-Dimethyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.087 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O | |
| Molar mass | 150.221 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 208 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 86 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Menthofuran is an organic compound found in a variety of essential oils including that of pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium). It is highly toxic and believed to be the primary toxin in pennyroyal responsible for its potentially fatal effects. After ingestion of menthofuran, it is metabolically activated to chemically reactive intermediates that are hepatotoxic.
Biosynthesis
Menthofuran is produced biosynthetically from pulegone by the enzyme menthofuran synthase.
Chemistry
Synthesis
Menthofuran can be synthesized from 5-methylcyclohexane-1,3-dione and allenyldimethylsulfonium bromide in two steps via a furannulation strategy consisting of enolate addition and rearrangement.
Pharmacology
Menthofuran is a metabolite of pulegone. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have found the pulegone metabolite menthofuran to be an inhibitor of CYP2A6.
Menthofuran may deplete glutathione levels, leaving hepatocytes vulnerable to free radical damage.

