
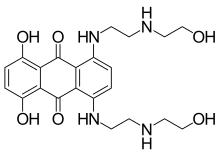
Mitoxantrone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Novantrone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608019 |
| Routes of administration |
Mainly intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | 78% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2E1) |
| Elimination half-life | 75 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H28N4O6 |
| Molar mass | 444.488 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Mitoxantrone (INN, BAN, USAN; also known as Mitozantrone in Australia; trade name Novantrone) is an anthracenedione antineoplastic agent.
Uses
Mitoxantrone is used to treat certain types of cancer, mostly acute myeloid leukemia. It improves the survival rate of children suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse.
The combination of mitoxantrone and prednisone is approved as a second-line treatment for metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Until recently this combination was the first line of treatment; however, a combination of docetaxel and prednisone improves survival rates and lengthens the disease-free period.
Mitoxantrone is also used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), most notably the subset of the disease known as secondary-progressive MS. In the absence of a cure, mitoxantrone is effective in slowing the progression of secondary-progressive MS and extending the time between relapses in both relapsing-remitting MS and progressive-relapsing MS.
Side effects
Mitoxantrone, as with other drugs in its class, may cause adverse reactions of varying severity, including nausea, vomiting, hair loss, heart damage and immunosuppression, possibly with delayed onset. Cardiomyopathy is a particularly concerning effect as it is irreversible; thus regular monitoring with echocardiograms or MUGA scans is recommended for patients.
Because of the risk of cardiomyopathy, mitoxantrone carries a limit on the cumulative lifetime dose (based on body surface area) in MS patients.
Mechanism of action
Mitoxantrone is a type II topoisomerase inhibitor; it disrupts DNA synthesis and DNA repair in both healthy cells and cancer cells by intercalation between DNA bases. It is also classified as an antibiotic.
See also
- Pixantrone, a mitoxantrone analogue under development
- Losoxantrone
External links
- "Mitoxantrone". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
|
Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signs and symptoms | |||||||||
| Investigations and diagnosis | |||||||||
| Approved treatment | |||||||||
| Other treatments | |||||||||
| Demyelinating diseases |
|
||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Products | |
|---|---|
| Related | |