
Osazone
Подписчиков: 0, рейтинг: 0

Ball-and-stick model of glucosazone
Osazones are a class of carbohydrate derivatives found in organic chemistry formed when reducing sugars are reacted with excess of phenylhydrazine at boiling temperatures.
Formation
Osazone formation was developed by Emil Fischer, who used the reaction as a test to identify monosaccharides.
The formation of a pair of hydrazone functionalities involves both oxidation and condensation reactions. Since the reaction requires a free carbonyl group, only "reducing sugars" participate. Sucrose, which is nonreducing, does not form an osazone.
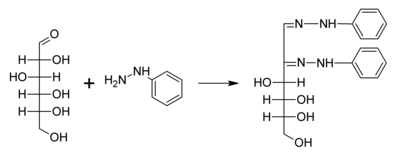 A typical reaction showing the formation of an osazone. D-glucose reacts with phenylhydrazine to give glucosazone. The same product is obtained from fructose and mannose.
A typical reaction showing the formation of an osazone. D-glucose reacts with phenylhydrazine to give glucosazone. The same product is obtained from fructose and mannose.
Appearance
Osazones are highly coloured and crystalline compounds. Osazones are readily distinguished.
- Maltosazone (from maltose) forms petal-shaped crystals.
- Lactosazone (from lactose) forms powder puff-shaped crystals.
- Galactosazone (from galactose) forms rhombic-plate shaped crystals.
- Glucosazone (from glucose, fructose or mannose) forms broomstick or needle-shaped crystals.
- Fischer, Emil (1908). "Schmelzpunkt des Phenylhydrazins und einiger Osazone". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 41: 73–77. doi:10.1002/cber.19080410120.
- Fischer, Emil (1894). "Ueber einige Osazone und Hydrazone der Zuckergruppe". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 27 (2): 2486–2492. doi:10.1002/cber.189402702249.
- Barry, VINCENT C.; Mitchell, PW (1955). "Mechanism of Osazone Formation". Nature. 175 (4448): 220. Bibcode:1955Natur.175..220B. doi:10.1038/175220a0. PMID 13235861.

