
Perineum
| Perineum | |
|---|---|
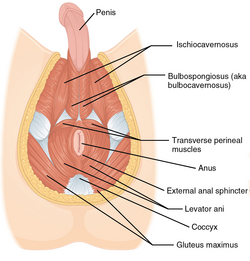 The muscles of the male perineum
| |
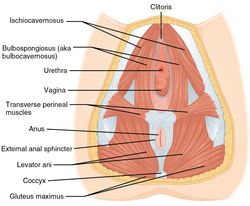 The muscles of the female perineum
| |
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | /ˌpɛrɪˈniːəm/; |
| System | Musculoskeletal system |
| Artery | Perineal artery, dorsal artery of the penis and deep artery of the penis |
| Nerve | Perineal nerve, posterior scrotal nerves, dorsal nerve of the penis or dorsal nerve of clitoris |
| Lymph | Primarily superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Perineum, perinaeum |
| MeSH | D010502 |
| TA98 | A09.5.00.001 |
| TA2 | 131 |
| FMA | 9579 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone.
The word entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος perinaios, perineos, itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς perís 'penis' through influence from πηρίς pērís 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the corresponding lack of distance in women. As a result of folk etymologies (such as ἰνάω ináō, "to carry off by evacuations"), it is contemporaneously extended to both sexes.
Structure
The perineum is generally defined as the surface region between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx. The perineum is below the pelvic diaphragm and between the legs. It is a diamond-shaped area that includes the anus and, in females, the vagina. Its definition varies: it can refer to only the superficial structures in this region, or it can be used to include both superficial and deep structures. The perineum corresponds to the outlet of the pelvis.
A line drawn across the surface connecting the ischial tuberosities divides the space into two triangles:
- The anterior urogenital triangle, contains the penis (males) or vagina (females)
- The posterior anal triangle containing the anus
The formal anatomical boundaries of the perineum may be said to be:
- in front: the pubic arch and the arcuate ligament of the pubis
- behind: the tip of the coccyx
- on either side: the inferior rami of the pubis and ischial tuberosity, and the sacrotuberous ligament
- superiorly: pelvic floor
- inferiorly: skin and fascia
Body
The perineal body (or central tendon of perineum) is a pyramidal fibromuscular mass in the middle line of the perineum at the junction between the urogenital triangle and the anal triangle. In males, it is found between the bulb of the penis and the anus; in females, it is found between the vagina and anus, and about 1.25 cm (0.49 in) in front of the latter.
The perineal body is essential for the integrity of the pelvic floor, particularly in females. Its rupture during vaginal birth leads to widening of the gap between the anterior free borders of levator ani muscle of both sides, thus predisposing the woman to prolapse of the uterus, rectum, or even the urinary bladder. Perineal tears and episiotomy often occur in childbirth with first-time deliveries, but the risk of these injuries can be reduced by preparing the perineum, often through massage.
At this point, the following muscles converge and are attached:
- External anal sphincter
- Bulbospongiosus muscle
- Superficial transverse perineal muscle
- Anterior fibers of the levator ani
- Fibers from male or female external urinary sphincter
- Deep transverse perineal muscle
Fascia
The terminology of the perineal fascia can be confusing, and there is some controversy over the nomenclature. This stems from the fact that there are two parts to the fascia, the superficial and deep parts, and each of these can be subdivided into superficial and deep parts.
The layers and contents are as follows, from superficial to deep:
- skin
- superficial perineal fascia: Subcutaneous tissue divided into two layers: (a) A superficial fatty layer, and (b) Colles' fascia, a deeper, membranous layer
- deep perineal fascia and muscles:
Superficial perineal pouch Contains superficial perineal muscles: transversus perinei superficialis, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus Inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm, or perineal membrane A membranous layer of the deep fascia Deep perineal pouch Contains the deep perineal muscles: transversus perinei profundus, sphincter urethrae membranaceae Superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm Considered hypothetical by some modern anatomists, but still commonly used to logically divide the contents of the region - fascia and muscles of pelvic floor (levator ani, coccygeus)
Areas
The region of the perineum can be considered a distinct area from pelvic cavity, with the two regions separated by the pelvic diaphragm. The perianal area (peri- and anal) is a subset of the perineum. The following areas are thus classified as parts of the perineal region:
- perineal pouches: superficial and deep (see above for details)
-
ischioanal fossa – a fat-filled space at the lateral sides of anal canal, bounded laterally by the obturator internus muscle, and medially by the pelvic diaphragm and anal canal; its base is the skin
- anal canal
- pudendal canal – contains internal pudendal artery and the pudendal nerve
Clinical significance
Extensive deformation of the pelvic floor occurs during a vaginal delivery. Approximately 85% of women have some perineal tear during a vaginal delivery and in about 69% suturing is required. Obstetric perineal trauma contributes to postpartum morbidity and frustration of women after delivery. In many women the childbirth trauma is manifested in advanced age when the compensatory mechanisms of the pelvic floor become weakened making the problem more serious among the aged population.
The anogenital distance is a measure of the distance between the midpoint of the anus and the underside of the scrotum or the vagina. Studies show that the human perineum is twice as long in males as in females. Measuring the anogenital distance in neonatal humans has been suggested as a noninvasive method to determine male feminisation and thereby predict neonatal and adult reproductive disorders.
There are claims that sometimes the perineum is excessively repaired after childbirth, using a so-called "husband stitch" and that this can increase vaginal tightness or result in pain during intercourse.
Society and culture
Perineum sunning is a wellness practice that involves exposing the perineum (area between the genitals and anus) to sunlight. Adherents claim various unproven health benefits such as improved libido, circulation, sleep, and longevity. There is no scientific evidence that this behavior promotes any of the alleged benefits. The practice of exposing a sensitive area of skin to sunlight also increases the risk of skin cancers such as melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal-cell carcinoma. Doctors recommend safer alternative options such as relaxation, meditation, and mindfulness, which can also achieve the same desired benefits.
Gallery
See also
- Deep perineal pouch
- Erogenous zone
- Intimate part
- Mula Bandha
- Pelvic floor
- Perineal raphe
- Perineal tear classification
- 101 Vagina
- Femalia
External links
| Perineum |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fascia |
|
||||||||||||||
| National | |
|---|---|
| Other | |



