Phonocardiogram
| Phonocardiogram | |
|---|---|
 Phonocardiogram and jugular venous pulse tracing from a middle-aged man with pulmonary hypertension (pulmonary artery pressure 70 mm Hg) caused by cardiomyopathy. The jugular venous pulse tracing demonstrates a prominent a wave without a c or v wave being observed. The phonocardiograms (fourth left interspace and cardiac apex) show a murmur of tricuspid insufficiency and ventricular and atrial gallops.
| |
| Synonyms | PCG |
| ICD-9-CM | 89.55 |
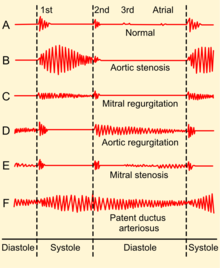
A phonocardiogram (or PCG) is a plot of high-fidelity recording of the sounds and murmurs made by the heart with the help of the machine called the phonocardiograph; thus, phonocardiography is the recording of all the sounds made by the heart during a cardiac cycle.
Medical use
Heart sounds result from vibrations created by the closure of the heart valves. There are at least two; the first (S1) is produced when the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) close at the beginning of systole and the second (S2) when the aortic valve and pulmonary valve (semilunar valves) close at the end of systole. Phonocardiography allows the detection of subaudible sounds and murmurs and makes a permanent record of these events. In contrast, the stethoscope cannot always detect all such sounds or murmurs and provides no record of their occurrence. The ability to quantitate the sounds made by the heart provides information not readily available from more sophisticated tests and provides vital information about the effects of certain drugs on the heart. It is also an effective method for tracking the progress of a patient's disease.
Discrete and the packet wavelet transform
According to a review by Cherif et al., discrete wavelet transform DWT is better at not affecting S1 or S2 while filtering heart murmurs. Packet wavelet transform affects internal components structure much more than DWT does.
History

Awareness of the sounds made by the heart dates to ancient times. The idea of developing an instrument to record it may date back to Robert Hooke (1635–1703), who wrote: "There may also be a possibility of discovering the internal motions and actions of bodies - whether animal, vegetable, or mineral, by the sound they make". The earliest known examples of phonocardiography date to the 1800s.
Monitoring and recording equipment for phonocardiography was developed through the 1930s and 1940s. Standardization began by 1950, when the first international conference was held in Paris.
A phonocardiogram system manufactured by Beckman Instruments was used on at least one of the Project Gemini manned spaceflights (1965-1966) to monitor the heartbeat of astronauts on the flight. It was one of many Beckman Instruments specialized for and used by NASA.
John Keefer filed a patent for a phonocardiogram simulator in 1970 while he was an employee of the U.S. government. The original patent description indicates that it is a device which via electrical voltage mimics the human heart's sounds.
See also
Further reading
- Almasi, Ali; Shamsollahi, Mohammad-Bagher; Senhadji, Lotfi (2011-08-01). A dynamical model for generating synthetic Phonocardiogram signals. Conference Proceedings. Vol. 2011. pp. 5686–5689. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6091376. ISBN 978-1-4577-1589-1. ISSN 1557-170X. PMC 3390312. PMID 22255630.
- Mizuno, Atsushi; Niwa, Koichiro; Shirai, Takeaki; Shiina, Yumi (1 January 2015). "Phonocardiogram in adult patients with tetralogy of Fallot". Journal of Cardiology. 65 (1): 82–86. doi:10.1016/j.jjcc.2014.03.011. ISSN 0914-5087. PMID 24842232. Retrieved 2 June 2016.
- Chernecky, Cynthia C.; Berger, Barbara J. (2007). Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1416066835. Retrieved 27 November 2016.
|
Tests and procedures involving the heart
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery |
|
||||||
| Tests |
|
||||||
| Function tests | |||||||
| Pacing | |||||||