Pinolenic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
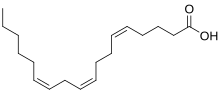
Preferred IUPAC name
(5Z,9Z,12Z)-Octadeca-5,9,12-trienoic acid | |
| Other names
Columbinic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H30O2 | |
| Molar mass | 278.4296 g/mol |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pinolenic acid (often misspelled as pinoleic acid) is a fatty acid contained in Siberian Pine nuts, Korean Pine nuts and the seeds of other pines (Pinus species). The highest percentage of pinolenic acid is found in Siberian pine nuts and the oil produced from them.
Chemistry and biochemistry
Pinolenic acid is formally designated as all-cis-5,9,12-18:3. Some sources also use the term columbinic acid for this substance. But columbinic acid sometimes designates an E-Z isomer (trans,cis,cis delta-5,9,12/18:3) in the biologic literature.
Pinolenic acid is an isomer of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA). GLA is an ω-6 essential fatty acid (EFA) but pinolenic acid is not. However, like the EFAs, it forms biologically active metabolites in the presence of cyclooxygenase or lipoxygenase. These metabolites can partially relieve some of the symptoms of EFA deficiency.
Physiology
Recent research has shown its potential use in weight loss by curbing appetite. Pinolenic acid causes the triggering of two hunger suppressants—cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Pinolenic acid may have LDL-lowering properties by enhancing hepatic LDL uptake.

