Propylene glycol

| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Propane-1,2-diol | |||
| Other names
Propylene glycol
α-Propylene glycol 1,2-Propanediol 1,2-Dihydroxypropane Methyl ethyl glycol Methylethylene glycol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider |
|
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.307 | ||
| EC Number |
|
||
| E number | E1520 (additional chemicals) | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
|
||
| UNII |
|
||
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.095 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | odorless | ||
| Density | 1.036 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −59 °C (−74 °F; 214 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 188.2 °C (370.8 °F; 461.3 K) | ||
| Miscible | |||
| Solubility in ethanol | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in acetone | Miscible | ||
| Solubility in chloroform | Miscible | ||
| log P | -1.34 | ||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.34 W/m-K (50% H2O @ 90 °C (194 °F)) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.042 Pa·s | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| QA16QA01 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
|
Related glycols
|
Ethylene glycol, 1,3-propanediol | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid, which is nearly odorless but possesses a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. Containing two alcohol groups, it is classed as a diol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.
It is produced on a large scale primarily for the production of polymers. In the European Union, it has E-number E1520 for food applications. For cosmetics and pharmacology, the number is E490. Propylene glycol is also present in propylene glycol alginate, which is known as E405. Propylene glycol is a compound which is GRAS (generally recognized as safe) by the US Food and Drug Administration under 21 CFR x184.1666, and is also approved by the FDA for certain uses as an indirect food additive. Propylene glycol is approved and used as a vehicle for topical, oral, and some intravenous pharmaceutical preparations in the U.S. and in Europe.
Structure
The compound is sometimes called (alpha) α-propylene glycol to distinguish it from the isomer propane-1,3-diol, known as (beta) β-propylene glycol. Propylene glycol is chiral. Commercial processes typically use the racemate. The S-isomer is produced by biotechnological routes.
Production
Industrial
Industrially, propylene glycol is mainly produced from propylene oxide (for food-grade use). According to a 2018 source, 2.16 M tonnes are produced annually. Manufacturers use either non-catalytic high-temperature process at 200 °C (392 °F) to 220 °C (428 °F), or a catalytic method, which proceeds at 150 °C (302 °F) to 180 °C (356 °F) in the presence of ion exchange resin or a small amount of sulfuric acid or alkali.
Final products contain 20% propylene glycol, 1.5% of dipropylene glycol, and small amounts of other polypropylene glycols. Further purification produces finished industrial grade or USP/JP/EP/BP grade propylene glycol that is typically 99.5% or greater. Use of USP (US Pharmacopoeia) propylene glycol can reduce the risk of Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) rejection.
Propylene glycol can also be obtained from glycerol, a byproduct from the production of biodiesel. This starting material is usually reserved for industrial use because of the noticeable odor and taste that accompanies the final product.
Laboratory
S-Propanediol is synthesized via fermentation methods. Lactic acid and lactaldehyde are common intermediates. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate, one of the two products of breakdown (glycolysis) of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, is a precursor to methylglyoxal. This conversion is the basis of a potential biotechnological route to the commodity chemical 1,2-propanediol. Three-carbon deoxysugars are also precursor to the 1,2-diol.
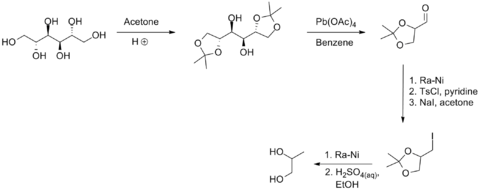
A small-scale, nonbiological route from D-mannitol is illustrated in the following scheme:
Applications
Polymers
Forty-five percent of propylene glycol produced is used as a chemical feedstock for the production of unsaturated polyester resins. In this regard, propylene glycol reacts with a mixture of unsaturated maleic anhydride and isophthalic acid to give a copolymer. This partially unsaturated polymer undergoes further crosslinking to yield thermoset plastics. Related to this application, propylene glycol reacts with propylene oxide to give oligomers and polymers that are used to produce polyurethanes. Propylene glycol is used in water-based acrylic architectural paints to extend dry time which it accomplishes by preventing the surface from drying due to its slower evaporation rate compared to water.
Food and drug
Propylene glycol is also used in various edible items such as coffee-based drinks, liquid sweeteners, ice cream, whipped dairy products and soda.Vaporizers used for delivery of pharmaceuticals or personal-care products often include propylene glycol among the ingredients. In alcohol-based hand sanitizers, it is used as a humectant to prevent the skin from drying. Propylene glycol is used as a solvent in many pharmaceuticals, including oral, injectable, and topical formulations. Many pharmaceutical drugs which are insoluble in water utilize propylene glycol as a solvent and carrier; benzodiazepine tablets are one example. Propylene glycol is also used as a solvent and carrier for many pharmaceutical capsule preparations. Additionally, certain formulations of artificial tears use propylene glycol as an ingredient.

Antifreeze
The freezing point of water is depressed when mixed with propylene glycol. It is used as aircraft de-icing and anti-icing fluid. A 50% water-diluted and heated solution is used for removal of icing accretions from the fuselages of commercial aircraft on the ground (de-icing), and 100% undiluted cold solution is used only on wings and tail surfaces of an aircraft in order to prevent ice accretion from forming during a specific period of time before takeoff (anti-icing). Normally, such time-frame is limited to 15–90 minutes, depending on the severity of snowfall and outside air temperature. Water-propylene glycol mixtures dyed pink to indicate the mixture is relatively nontoxic are sold under the name of RV or marine antifreeze. Propylene glycol is frequently used as a substitute for ethylene glycol in low toxicity, environmentally friendly automotive antifreeze. It is also used to winterize the plumbing systems in vacant structures. The eutectic composition/temperature is 60:40 propylene glycol:water/−60 °C. The −50 °F/−45 °C commercial product is, however, water rich; a typical formulation is 40:60.
Electronic cigarettes liquid

Propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, or a mixture of both, are the main ingredients in e-liquid used in electronic cigarettes. They are aerosolized to resemble smoke and serve as carriers for substances such as nicotine and flavorants.
Miscellaneous applications
- As a solvent for many substances, both natural and synthetic.
- As a humectant (E1520).
- As a freezing point depressant for slurry ice.
- In veterinary medicine as an oral treatment for hyperketonaemia in ruminants.
- In the cosmetics industry, where propylene glycol is very commonly used as a carrier or base for various types of makeup.
- For trapping and preserving insects (including as a DNA preservative).
- For the creation of theatrical smoke and fog in special effects for film and live entertainment. So-called 'smoke machines' or 'hazers' vaporize a mixture of propylene glycol and water to create the illusion of smoke. While many of these machines use a propylene glycol-based fuel, some use oil. Those which use propylene glycol do so in a process that is identical to how electronic cigarettes work; utilizing a heating element to produce a dense vapor. The vapor produced by these machines has the aesthetic look and appeal of smoke, but without exposing performers and stage crew to the harms and odors associated with actual smoke.
- As an additive in PCR to reduce the melting temperature of nucleic acids for targeting of GC rich sequences.
- as a surfactant, it is used to prevent water from beading up on objects. It is used in photography for this purpose to reduce the risk of water spots, or deposits of minerals from water used to process film or paper.
Safety in humans
When used in average quantities, propylene glycol has no measurable effect on development and/or reproduction on animals and probably does not adversely affect human development or reproduction without active use. The safety of electronic cigarettes—which utilize propylene glycol-based preparations of nicotine or THC and other cannabinoids—is the subject of much controversy.Vitamin E acetate has also been identified in this controversy.
Oral administration
The acute oral toxicity of propylene glycol is very low, and large quantities are required to cause perceptible health effects in humans; in fact, the toxicity of propylene glycol is one third of ethanol's. Propylene glycol is metabolized in the human body into pyruvic acid (a normal part of the glucose-metabolism process, readily converted to energy), acetic acid (handled by ethanol-metabolism), lactic acid (a normal acid generally abundant during digestion), and propionaldehyde (a potentially hazardous substance). According to the Dow Chemical Company, The LD50 (Lethal Dose that kills 50% of the test population) for rats is 20 g/kg (oral/rat).
Toxicity generally occurs at plasma concentrations over 4 g/L, which requires extremely high intake over a relatively short period of time, or when used as a vehicle for drugs or vitamins given intravenously or orally in large bolus doses. It would be nearly impossible to reach toxic levels by consuming foods or supplements, which contain at most 1 g/kg of PG, except for alcoholic beverages in the US which are allowed 5 percent = 50 g/kg. Cases of propylene glycol poisoning are usually related to either inappropriate intravenous administration or accidental ingestion of large quantities by children.
The potential for long-term oral toxicity is also low. In an NTP continuous breeding study, no effects on fertility were observed in male or female mice that received propylene glycol in drinking water at doses up to 10100 mg/kg bw/day. No effects on fertility were seen in either the first or second generation of treated mice. In a 2-year study, 12 rats were provided with feed containing as much as 5% propylene glycol, and showed no apparent ill effects. Because of its low chronic oral toxicity, propylene glycol was classified by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration as "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) for use as a direct food additive, including frozen foods such as ice cream and frozen desserts. The GRAS designation is specific to its use in food, and does not apply to other uses.
Skin, eye and inhalation contact

Propylene glycol may be non-irritating to the skin, see section Allergic Reaction below for details on allergic reactions. Undiluted propylene glycol is minimally irritating to the eye, producing slight transient conjunctivitis; the eye recovers after the exposure is removed. A 2018 human volunteer study found that 10 male and female subjects undergoing 4 hours exposures to concentrations of up to 442 mg/m3 and 30 minutes exposures to concentrations of up to 871 mg/m3 in combination with moderate exercise did not show pulmonary function deficits, or signs of ocular irritation, with only slight symptoms of respiratory irritation reported. Inhalation of propylene glycol vapors appears to present no significant hazard in ordinary applications. Due to the lack of chronic inhalation data, it is recommended that propylene glycol not be used in inhalation applications such as theatrical productions, or antifreeze solutions for emergency eye wash stations. Recently, propylene glycol (commonly alongside glycerol) has been included as a carrier for nicotine and other additives in e-cigarette liquids, the use of which presents a novel form of exposure. The potential hazards of chronic inhalation of propylene glycol or the latter substance as a whole are as-yet unknown.
According to a 2010 study, the concentrations of PGEs (counted as the sum of propylene glycol and glycol ethers) in indoor air, particularly bedroom air, has been linked to increased risk of developing numerous respiratory and immune disorders in children, including asthma, hay fever, eczema, and allergies, with increased risk ranging from 50% to 180%. This concentration has been linked to use of water-based paints and water-based system cleansers. However, the study authors write that glycol ethers and not propylene glycol are the likely culprit.
Propylene glycol has not caused sensitization or carcinogenicity in laboratory animal studies, nor has it demonstrated genotoxic potential.
Intravenous administration
Studies with intravenously administered propylene glycol have resulted in LD50 values in rats and rabbits of 7 mL/kg BW. Ruddick (1972) also summarized intramuscular LD50 data for rat as 13-20 mL/kg BW, and 6 mL/kg BW for the rabbit. Adverse effects to intravenous administration of drugs that use propylene glycol as an excipient have been seen in a number of people, particularly with large bolus dosages. Responses may include CNS depression, "hypotension, bradycardia, QRS and T abnormalities on the ECG, arrhythmia, cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, agitation, serum hyperosmolality, lactic acidosis, and haemolysis". A high percentage (12% to 42%) of directly-injected propylene glycol is eliminated or secreted in urine unaltered depending on dosage, with the remainder appearing in its glucuronide-form. The speed of renal filtration decreases as dosage increases, which may be due to propylene glycol's mild anesthetic / CNS-depressant -properties as an alcohol. In one case, intravenous administration of propylene glycol-suspended nitroglycerin to an elderly man may have induced coma and acidosis. However, no confirmed lethality from propylene glycol was reported.
Animals
Propylene glycol is an approved food additive for dog and sugar glider food under the category of animal feed and is generally recognized as safe for dogs, with an LD50 of 9 mL/kg. The LD50 is higher for most laboratory animals (20 mL/kg). However, it is prohibited for use in food for cats due to links to Heinz body formation and a reduced lifespan of red blood cells. Heinz body formation from MPG has not been observed in dogs, cattle, or humans.
PG has been used in the dairy industry since the 1950s for cows showing signs of ketosis. The negative energy balance during the early stages of lactation can cause the animal's body to have lower glucose levels, inducing the liver to make up for this by the conversion of body fat, leading to several health conditions, e.g. displaced abomasum. PG "reduces the propionate ratio of acetate to acetaminophen, while increasing conversion of ruminal PG to propionate, and aid[s] in the closure of energy deficit in cattle."
Allergic reaction
Estimates on the prevalence of propylene glycol allergy range from 0.8% (10% propylene glycol in aqueous solution) to 3.5% (30% propylene glycol in aqueous solution). The North American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) data from 1996 to 2006 showed that the most common site for propylene glycol contact dermatitis was the face (25.9%), followed by a generalized or scattered pattern (23.7%). Investigators believe that the incidence of allergic contact dermatitis to propylene glycol may be greater than 2% in patients with eczema or fungal infections, which are very common in countries with lesser sun exposure and lower-than-normal vitamin D balances. Therefore, propylene glycol allergy is more common in those countries.
Because of its potential for allergic reactions and frequent use across a variety of topical and systemic products, propylene glycol was named the American Contact Dermatitis Society's Allergen of the Year for 2018. Recent publication from The Mayo Clinic reported 0.85% incidence of positive patch tests to propylene glycol (100/11,738 patients) with an overall irritant rate of 0.35% (41/11,738 patients) during a 20-year period of 1997–2016. 87% of the reactions were classified as weak and 9% as strong. The positive reaction rates were 0%, 0.26%, and 1.86% for 5%, 10%, and 20% propylene glycol respectively, increasing with each concentration increase. The irritant reaction rates were 0.95%, 0.24%, and 0.5% for 5%, 10%, and 20% propylene glycol, respectively. Propylene glycol skin sensitization occurred in patients sensitive to a number of other concomitant positive allergens, most common of which were: Myroxylon pereirae resin, benzalkonium chloride, carba mix, potassium dichromate, neomycin sulfate; for positive propylene glycol reactions, the overall median of 5 and mean of 5.6 concomitant positive allergens was reported.
Environmental impacts
Propylene glycol occurs naturally, probably as the result of anaerobic catabolism of sugars in the human gut. It is degraded by vitamin B12-dependent enzymes, which convert it to propionaldehyde.
Propylene glycol is expected to degrade rapidly in water from biological processes, but is not expected to be significantly influenced by hydrolysis, oxidation, volatilization, bioconcentration, or adsorption to sediment. Propylene glycol is readily biodegradable under aerobic conditions in freshwater, in seawater and in soil. Therefore, propylene glycol is considered as not persistent in the environment.
Propylene glycol exhibits a low degree of toxicity toward aquatic organisms. Several guideline studies available for freshwater fish with the lowest observed lethal concentration of 96-h LC50 value of 40,613 mg/L in a study with Oncorhynchus mykiss. Similarly, the lethal concentration determined in marine fish is a 96-h LC50 of >10,000 mg/L in Scophthalmus maximus.
Although propylene glycol has low toxicity, it exerts high levels of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) during degradation in surface waters. This process can adversely affect aquatic life by consuming oxygen needed by aquatic organisms for survival. Large quantities of dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water column are consumed when microbial populations decompose propylene glycol.
External links
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
- Alton E. Martin - Frank H. Murphy, DOW CHEMICAL COMPANY
- Propylene glycol website
- WebBook page for C3H8O2
- ATSDR - Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol Toxicity U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (public domain)
- Propylene Glycol - chemical product info: properties, production, applications.
- ChemSub Online: Propylene glycol
- Propylene Glycol Toxicity in Pets