
Rolapitant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /roʊˈlæpɪtænt/ roh-LAP-i-tant |
| Trade names | Varubi (US), Varuby (EU) |
| Other names | SCH 619734 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a615041 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets), intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | nearly 100% |
| Protein binding | 99.8% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4 |
| Metabolites | C4-pyrrolidine-hydroxylated rolapitant (major) |
| Elimination half-life | 169–183 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (52–89%), urine (9–20%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.022 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
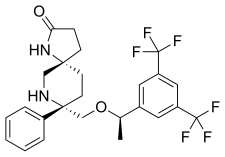
| Formula | C25H26F6N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 500.485 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rolapitant (INN, trade name Varubi /vəˈruːbi/ və-ROO-bee in the US and Varuby in the European Union) is a drug originally developed by Schering-Plough and licensed for clinical development by Tesaro, which acts as a selective NK1 receptor antagonist (antagonist for the NK1 receptor). It has been approved as a medication for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) after clinical trials showed it to have similar or improved efficacy and some improvement in safety over existing drugs for this application.
Medical uses
Rolapitant is used in combination with other antiemetic (anti-vomiting) agents in adults for the prevention of delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including, but not limited to, highly emetogenic chemotherapy. The approved antiemetic combination consists of rolapitant plus dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist.
Contraindications
Under the US approval, rolapitant is contraindicated in combination with thioridazine, whose inactivation could be inhibited by rolapitant. Under the European approval, it is contraindicated in combination with St. John's Wort, which is expected to accelerate inactivation of rolapitant.
Side effects
In studies comparing chemotherapy plus rolapitant, dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist to chemotherapy plus placebo, dexamethasone and a 5-HT3 antagonist, most side effects had comparable frequencies in both groups, and differed more between chemotherapy regimens than between rolapitant and placebo groups. Common side effects included decreased appetite (9% under rolapitant vs. 7% under placebo), neutropenia (9% vs. 8% or 7% vs. 6%, depending on the kind of chemotherapy), dizziness (6% vs. 4%), indigestion and stomatitis (both 4% vs. 2%).
Overdose
Up to eightfold therapeutic doses have been given in studies without problems.
Interactions
Rolapitant moderately inhibits the liver enzyme CYP2D6. Blood plasma concentrations of the CYP2D6 substrate dextromethorphan have increased threefold when combined with rolapitant; and increased concentrations of other substrates are expected. The drug also inhibits the transporter proteins ABCG2 (breast cancer resistance protein, BCRP) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which has been shown to increase plasma concentrations of the ABCG2 substrate sulfasalazine twofold and the P-gp substrate digoxin by 70%.
Strong inducers of the liver enzyme CYP3A4 decrease the area under the curve of rolapitant and its active metabolite (called M19); for rifampicin, this effect was almost 90% in a study. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 have no relevant effect on rolapitant concentrations.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Both rolapitant and its active metabolite M19 block the NK1 receptor with high affinity and selectivity: to block the closely related receptor NK2 or any other of 115 tested receptors and enzymes, more than 1000-fold therapeutic concentrations are necessary.
Pharmacokinetics

Rolapitant is practically completely absorbed from the gut, independently of food intake. It undergoes no measurable first-pass effect in the liver. Highest blood plasma concentrations are reached after about four hours. When in the bloodstream, 99.8% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins.
It is metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP3A4, resulting in the major active metabolite M19 (C4-pyrrolidine-hydroxylated rolapitant) and a number of inactive metabolites. Rolapitant is mainly excreted via the feces (52–89%) in unchanged form, and to a lesser extent via the urine (9–20%) in form of its inactive metabolites. Elimination half-life is about seven days (169 to 183 hours) over a wide dosing range.
Chemistry
The drug is used in form of rolapitant hydrochloride monohydrate, a white to off-white, slightly hygroscopic crystalline powder. Its maximum solubility in aqueous solutions is at pH 2–4.
See also
External links
- "Rolapitant". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Rolapitant Injection: MedlinePlus Drug Information". MedlinePlus. 20 August 2020.